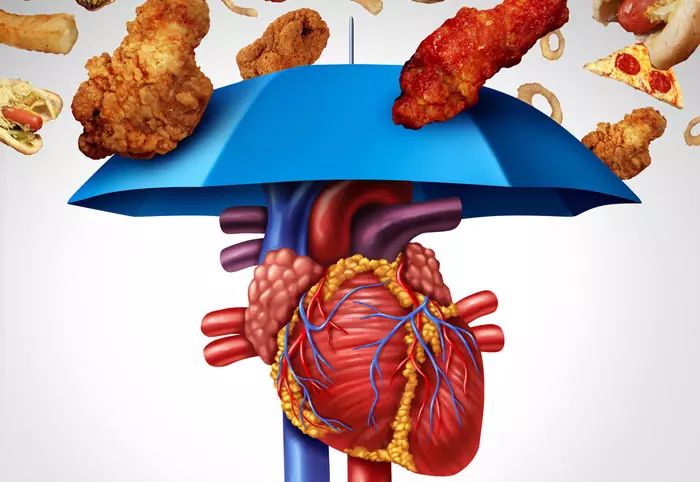
Heart Healthy Foods: 27 Ways To Cut Cholesterol & Inflammation
Boost vitality with these nutrient-packed options that support cardiovascular wellness daily.

Image: Shutterstock
Heart disease and stroke are the leading causes of death worldwide (1), (2). And the annual healthcare cost is estimated to be about 190 billion dollars (3)!
According to the American Heart Association, poor diet and physical inactivity cause cholesterol deposition on the arterial walls, which leads to heart attack (4), (5), (6). This means that modifying your diet and lifestyle can reduce your risk of heart attack.
Yes, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from heart disease (and neck-deep loans) by consuming heart-friendly foods. Read on to know about the top 27 heart-healthy foods that will help lower cholesterol and inflammation in the body and a few surprising “healthy” foods that are not so heart-healthy. Swipe up!
27 Best Heart-Healthy Foods
1. Fish
Fish are rich in lean protein and omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fatty acids that help to reduce inflammation and prevent cardiovascular diseases. Both omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are essential. However, our dietary intake does not fulfill the body’s requirement of omega-3s. So, consume salmon, sardine, and other fatty fish to improve your heart’s condition (7).
You can have grilled or baked fish for lunch or dinner. Make sure to use light dressing if you have fish in your salad. You may consume 3-5 oz of fish per day.
2. Olive Oil
Olive oil is widely used in various cuisines these days. It is rich in antioxidants and healthy fats and has anti-inflammatory properties. Olive oil consumption has been found to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular disease (8).
Use olive oil to stir-fry veggies or lean protein sources. Make a light dressing for salads with olive oil, lime juice, herbs, salt, and pepper. You can safely consume 7-8 tablespoons of olive oil per day.
3. Oranges
Oranges are rich in vitamin C, minerals, flavonoids, and have anti-inflammatory, lipid-lowering, antiallergic, and anti-tumor properties. Scientists have found that consuming orange juice can help lower bad cholesterol (LDL cholesterol) levels (9). The lower the LDL cholesterol, the lower the chances of arterial blockage.
Have an orange or a glass of freshly pressed orange juice to keep your heart healthy. You can also add orange juice to desserts, salads or chicken to give them a delicious flavor and aroma.
4. Broccoli
Broccoli is a cruciferous vegetable that is loaded with vitamins A, C, K, and folate, dietary fiber, calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, selenium, and glucosinolates. Researchers found that broccoli-fed rats had improved heart function, reduced myocardial infarction, and increased antioxidant response that helped protect the heart (10).
Have blanched, grilled, baked or stir-fried broccoli with other veggies or mushroom/chicken/fish/lentils. You can also have it in a soup to satiate your hunger and keep your heart healthy. Have one cup of broccoli per day.
5. Carrot
Carrots are rich in vitamins A, K, E, and folate and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus. Interestingly, they are also a good source of antioxidants that prevent DNA damage, reduce inflammation, and lower the cholesterol and triglyceride levels (11).
You can snack on a raw carrot. Grill/bake/stir-fry it and have it with other veggies with a source of lean protein (fish/chicken/mushroom) or add it to chicken stew or vegetable soup. Make sure not to overeat carrots to avoid health issues. You can have half a cup of carrot per day.
6. Green Tea
Green tea contains active polyphenolic compounds called catechins. They have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antihypertensive, lipid-lowering, and anti-thrombogenic properties. The catechins help scavenge the harmful oxygen radicals, prevent vascular inflammation, reduce the risk of atherogenesis, and inhibit lipid synthesis and absorption (12).
Have 2-3 cups of green tea per day. You may have it in the morning or 20 minutes before lunch or dinner. Add cinnamon, lemon, honey, tulsi, or other herbs to make your own flavored green tea.
7. Strawberries
Strawberries are rich in antioxidants that help to lower high blood pressure and blood lipid levels, prevent hyperglycemia, and decrease the LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels (13). These attributes make strawberries one of the most potent foods to prevent cardiovascular disease.
Include strawberries in your breakfast cereal or smoothies or have them with other fruits a couple of hours after lunch. You can also have strawberries with yogurt or sour cream as dessert.
8. Chicken Breast
Chicken breast without the skin is a great source of lean protein. Proteins are the building blocks of muscles. Since heart works 24*7, it is quite natural that there is muscle wear and tear. Consuming chicken breast will supply the body with protein that can be used to repair the heart muscles.
Have 3-4 oz of chicken breast per day. You can grill, poach, bake, boil or stir-fry chicken and have it with lots of green leafy and other colorful veggies to balance your meal.
9. Nuts
Consuming nuts can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by 40-50%. Nuts contain vitamin E and monounsaturated fats that act as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents. Researchers have found that consuming almonds, in-shell pistachios, walnuts, pecan nuts, and peanuts can help reduce LDL cholesterol (14).
You can have nuts in the morning with your breakfast so that you can use the energy generated to carry out your daily activities. You can also toss a few nuts into your salad or eat them as a snack in the evening with a cup of green tea.
10. Apple
Researchers have found that consuming apples can help lower inflammation, increase lipid metabolism, reduce weight, and regulate blood pressure (15). So, have an apple every day to keep your heart fit.
Include apples in your breakfast cereal or smoothies. You can also have an apple as a mid-morning or evening snack. Add a few pieces of apple to your salad to give it an exotic flavor.
11. Flax Seeds
Flax seeds are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) that helps to reduce inflammation, oxygen radical formation, and blood cholesterol levels (16). They are also rich in dietary fiber that aids weight loss.
Have 2 -3 tablespoons of ground flax seed powder per day. You can also add flax seed powder to your cereal, smoothies, juices, and salads.
12. Asparagus
Asparagus contains steroidal saponin that helps to reduce the cholesterol levels. It also has antioxidant properties that act against atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases (17). Make sure not to discard the section near the roots because all the heart-protective nutrients are concentrated in that part.
You can blanch, grill or stir-fry asparagus and have it along with veggies and a source of lean protein. You can also make asparagus juices. You can safely have a cup of asparagus or 7-8 asparagus tips per day.
13. Garlic
Garlic contains allicin, a phytonutrient that helps lower cholesterol and high blood pressure (18).
Have a clove of garlic every morning before breakfast. Or you can add garlic to your whole wheat toast, salads, lettuce wraps, brown rice, stir-fries, etc. You can have 6-7 cloves of garlic per day.
14. Spinach
Spinach is loaded with dietary nitrate that helps to lower blood pressure, improve exercise performance in people with peripheral arterial disease, inhibit platelet aggregation, and reduce inflammation and arterial stiffness (19).
Have blanched, baked, stir-fried or boiled spinach in salads, soups, and smoothies to keep your heart healthy. You can have 1-1 ½ cups of spinach per day.
15. Red Wine
Red wine helps to increase good cholesterol (HDL cholesterol), has antioxidant properties, and suppresses platelet aggregation (20). Scientists have concluded that these attributes of red wine make it one of the best drinks to keep your heart healthy.
Have a peg of red wine with your dinner. Make sure not to consume it in excess as doing so and not working out can lead to obesity and heart disease.
16. Papaya
Papayas are rich in antioxidants, dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals that help lower high blood pressure and strengthen the blood vessels (21).
Have a medium bowl of ripe papaya for your breakfast or evening snack. You can also make papaya smoothie for breakfast.
17. Avocado
Avocados are rich in healthy fats, vitamins A, E, K, C, B6, folate, pantothenic acid, niacin, potassium, magnesium, sodium, phytosterols, riboflavin, and other phytonutrients. They reduce bad cholesterol, lower blood lipid levels, improve antioxidant activities, suppress inflammation, and normalize blood glucose levels, thereby reducing the risk of heart diseases (22).
You can have an avocado smoothie for breakfast or include it in salads or wraps for lunch.
18. Tomato
Tomatoes contain antioxidants that help protect against DNA mutation, unlimited cell proliferation, and cardiovascular diseases. Scientists have found that tomatoes improve post-ischemic heart function and reduce myocardial infarction (23).
You can have tomato juice or smoothie for breakfast or as an evening snack. Add tomatoes to your salad, curries, stir-fries, baked veggies, and grilled chicken to add a tangy flavor to your food.
19. Watermelon
Citrulline is one of the compounds found in watermelons that helps to decrease inflammation and arterial stiffness, lower LDL cholesterol and elevated blood pressure, and reduce body weight (24).
Have watermelon juice or smoothie for breakfast. You can also have a bowl of watermelon as an evening snack. Do not eat more than 1 ½ cups of watermelon in a day to avoid stomach upset.
20. Rice Bran Oil
Rice bran oil is rich in vitamin E, plant sterols, oryzanol, and healthy fats that help lower the LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels (25).
You can use rice bran oil for all cooking purposes. However, do not use it for salad dressing. You may have 4-5 tablespoons of rice bran oil per day.
21. Kale
Rich in vitamins A, C, K, folate, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, omega-3-fats, dietary fiber, and antioxidants, kale helps to reduce the risk of coronary artery disease (26).
You can have kale smoothie for breakfast. You can also add kale to your salad, but make sure to blanch it. Add black pepper, salt, lime, and flax seed powder along with veggies and a medium portion of protein source to make your kale salad exciting and tasty.
22. Beetroot
Beetroot is a great source of nitrate that helps to reduce inflammation. It also has antioxidant properties and helps to reduce cholesterol and high blood pressure and improve lipid profiles (27).
Have beetroot juice or raw beetroot as an evening snack. You can also toss beetroot into your chicken stew or vegetable soup. Have half a cup of beetroot every day for better heart health and improved overall health.
23. Watercress
Watercress is loaded with phytonutrients, vitamins, minerals, and fiber that help to improve heart health and blood circulation (28).
The best way to consume watercress is to juice it. You can have it the first thing in the morning, for breakfast, or as a post-workout drink.You can have one glass of watercress juice per day.
24. Blueberries
Blueberries are rich in a cardioprotective polyphenol called resveratrol. Resveratrol helps prevent cardiac heart failure, has anti-thrombolytic properties, and helps repair any damage caused to the heart morphology (29).
Add blueberries to your smoothie or breakfast cereal along with nuts to give it a rich flavor. You can have up to half a cup of blueberries per day.
25. Cauliflower
Cauliflowers are rich in sulforaphane, an isothiocyanate that triggers many antioxidant enzymes. These enzymes help prevent oxidation of LDL cholesterol, inhibiting vascular inflammation, which, in turn, prevents atherosclerosis (30).
Blanch, boil, stir-fry or add cauliflower florets to your soup for lunch or dinner. You can have one cup of cauliflower per day.
26. Pomegranate
Pomegranate is loaded with anthocyanins and tannins that possess antioxidant properties. This makes it a potent cardioprotective fruit. It helps to lower LDL cholesterol and blood pressure and reduce inflammation (31).
Have pomegranate juice or the fruit for breakfast or as an evening snack. You can also add it to your salad for a Mediterranean touch.
27. Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate is a rich source of catechins, theobromine, and procyanidins that prevent platelet aggregation, lower blood pressure, and improve endothelial function. Hence, having a piece of dark chocolate will help protect your heart from cardiovascular diseases (32).
Consume dark chocolate that contains 80% or more cocoa. Have a piece after dinner to satiate your sweet tooth without risking weight gain or any harm to your health.
You should also make sure to avoid the following foods to keep your heart healthy.
Foods To Avoid For A Healthy Heart
- Trans fats
- Processed foods, such as salami, hot dogs, sausages, etc.
- Flour and white bread
- Yogurt, milk, and cheese (if you are lactose intolerant)
- GMO whole grains and flour
- Refined sugar, cane sugar, and high fructose corn syrup
- Junk foods, such as potato chips, deep fried foods, burgers, etc.
- Aerated and sweetened beverages
- Legumes )as they are loaded with lectins that trigger inflammation in the body)
Start taking care of your heart health by including these heart-friendly foods in your diet. Also, make sure to workout regularly to strengthen your heart muscles. If you have any questions, please leave a comment in the box below.
References
1. “The top 10 causes of death” World Health Organization.
2. “Mortality from ischaemic heart disease by country, region, and age: Statistics from World Health Organisation and United Nations” International journal of cardiology, US National Library of Medicine.
3. “Health and Economic Costs of Chronic Diseases” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
4. “Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics 2018 At-a-Glance” American Heart Association.
5. “Heart Disease Facts” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
6. “Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
7. “Omega-3 Supplements and Cardiovascular Diseases” Tanaffos, US National Library of Medicine.
8. “Olive oil intake and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in the PREDIMED Study” BMC Medicine, US National Library of Medicine.
9. “Long-term orange juice consumption is associated with low LDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein B in normal and moderately hypercholesterolemic subjects” Lipids in health and disease, US National Library of Medicine.
10. “Broccoli: a unique vegetable that protects mammalian hearts through the redox cycling of the thioredoxin superfamily.” Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. US National Library of Medicine.
11. “Drinking carrot juice increases total antioxidant status and decreases lipid peroxidation in adults” Nutrition journal, US National Library of Medicine.
12. “Green Tea Catechins and Cardiovascular Health: An Update” Current medicinal chemistry. US National Library of Medicine.
13. “ Strawberries decrease atherosclerotic markers in subjects with metabolic syndrome”Nutrition research, US National Library of Medicine.
14. “Dietary Intake of Nuts and Cardiovascular Prognosis” The Ochsner journal, US National Library of Medicine.
15. “Apples and Cardiovascular Health—Is the Gut Microbiota a Core Consideration?”Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine.
16. “Flaxseed and cardiovascular health.” Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology, US National Library of Medicine.
17. “Asparagus Root Regulates Cholesterol Metabolism and Improves Antioxidant Status in Hypercholesteremic Rats” Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, US National Library of Medicine.
18. “Effect of garlic on cardiovascular disorders: a review” Nutrition journal, US National Library of Medicine.
19. “Vascular effects of dietary nitrate (as found in green leafy vegetables and beetroot) via the nitrate‐nitrite‐nitric oxide pathway” British journal of clinical pharmacology, US National Library of Medicine.
20. “Red wine: A drink to your heart” Journal of cardiovascular disease research, US National Library of Medicine.
21. “Eat Papayas Naked: The PH-Balanced Diet for Super Health and Glowing Beauty” Susan M. Lark.
22. “Hass Avocado Composition and Potential Health Effects” Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, US National Library of Medicine.
23. “Lycopene, tomatoes, and coronary heart disease.” Free radical research, US National Library of Medicine.
24. “Citrullus lanatus `Sentinel’ (Watermelon) Extract Reduces Atherosclerosis in LDL Receptor Deficient Mice” The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, US National Library of Medicine.
25. “Effect of low calorie diet with rice bran oil on cardiovascular risk factors in hyperlipidemic patients” Journal of research in medical sciences : the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, US National Library of Medicine.
26. “Kale juice improves coronary artery disease risk factors in hypercholesterolemic men.”Biomedical and environmental sciences : BES, US National Library of Medicine.
27. “The Potential Benefits of Red Beetroot Supplementation in Health and Disease” Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine.
28. “Body into Balance: An Herbal Guide to Holistic Self-Care” Maria Noel Groves
29. “Polyphenols: Benefits to the Cardiovascular System in Health and in Aging” Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine.
30. “The influence of sulforaphane on vascular health and its relevance to nutritional approaches to prevent cardiovascular disease”The EPMA journal, US National Library of Medicine.
31. “Pomegranate for Your Cardiovascular Health” Rambam Maimonides medical journal, US National Library of Medicine.
32. “The cardiovascular benefits of dark chocolate”Vascular pharmacology, US National Library of Medicine.
Read full bio of Dr. Karyn Shanks
Read full bio of Charushila Biswas