Appendicitis In Children: What Causes It And How To Treat It
Uncover the hidden origins and effective solutions for young ones' sudden belly pain today.
Image: Shutterstock
“My tummy hurts mom! I can’t go to school” is a line that parents often hear; so often that they sometimes don’t pay heed to it.
Although ‘tummy ache’ is an excuse that kids come up with to skip school, it could be something serious too. It could even be appendicitis, which is common in children and can be life-threatening if immediate medical attention is not provided. The good news is that you can identify the signs and symptoms of appendicitis in children and ensure that they get the necessary medical treatment in time. MomJunction tells you more about appendicitis, its causes and treatment options.
What Is Appendicitis?
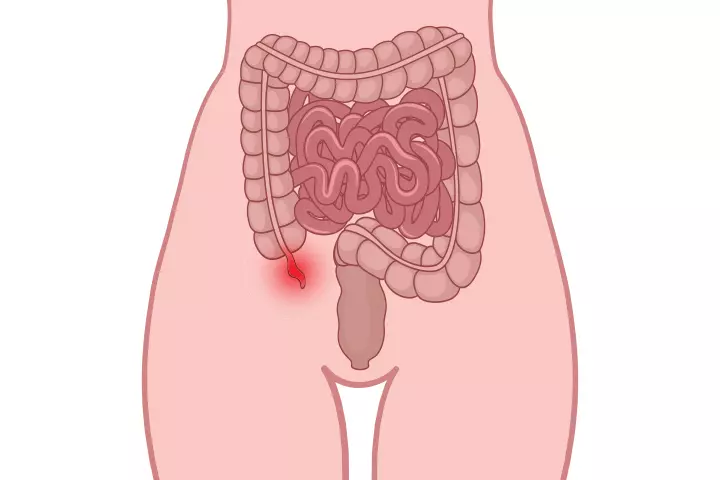
The appendix is a small finger-like organ that is attached to the large intestine. It is like a pouch that opens into the large intestine.
When the pouch is blocked, bacteria grow in the region and can spread infection. Appendicitis is a condition where the appendix gets infected by such bacteria and needs to be removed to avoid riskier medical conditions.
Besides bacteria, viruses and air pollution can also cause appendicitis.
What Causes Appendicitis In Children?
Common causes of appendicitis are:
- Infection caused by bacteria and viruses such as E. coli, bacteroides bacteria, adenovirus, salmonella bacteria, measles, shigella bacteria and fungal infections such as mucormycosis and histoplasmosis.
- Appendix stones — the appendix is blocked by hard, rock-like stool called fecolith
- Parasitic infections caused by pinworms or other intestinal worms
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Abdominal injury or trauma
- Ulcers or irritation in the GI tract, due to long-standing disorders such as Crohn’s disease
- Malignant or benign tumors
- Foreign objects such as pins, air gun pellets, and stones
Regardless of the causes, treatment for appendicitis should be immediate to avoid any complications.
Complications Of Appendicitis
The appendix is home to a variety of bacteria. But when the bacteria spread infection causing the appendix to swell with pus, and is left untreated, the infected appendix can get ruptured and burst (1), causing the mucus, stool or pus causing the infection to spread all over the abdomen. When the bacterial infection spreads inside the abdomen, it can lead to a condition called peritonitis.
Appendicitis is one of the most common reasons for emergency surgeries in people aged between 10 and 30. However, if diagnosed early on, the doctors will be able to remove the irritated appendix before it ruptures.
But how do you differentiate between a normal tummy ache and an appendicitis pain? Keep reading to know about the signs and symptoms of appendicitis.
Signs And Symptoms Of Appendicitis In Children
Because the appendix is located in the abdominal region, a pain in the lower abdomen, especially around the naval region and spreading to the lower right part of the stomach, is the most common and dominant symptom of a ruptured appendix.
Other signs and symptoms of appendicitis are:
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Mild fever
- Abdominal swelling
- Constipation or diarrhea, one of the later symptoms
- Inability to pass gas
When Should You Call The Doctor?
If any of these symptoms accompany the child’s stomach ache, you must take the child right away to the emergency room (2).
- Blood in vomit or stool
- Green liquid vomit could indicate torsion or twisting of the intestines. This needs emergency medical treatment
- Pain in the abdominal region, especially when pressed suddenly and released
- Distended abdomen
If the child lies on the side with the legs curled up to the abdomen or walks a little bent in the middle, it could also be a sign of ruptured appendix. If you suspect the child has appendicitis, take him to the doctor, who will diagnose the condition behind the problem.
Diagnosing Appendicitis In Children
While the exact location of the abdominal pain is usually a strong indicator of appendicitis in children, a proper diagnosis by the doctor is necessary.
Diagnosing appendicitis can be challenging for the doctors as well as the symptoms are similar to those of other medical conditions such as kidney stones, urinary tract infection (UTI), irritable bowel syndrome (3) and pneumonia (4).
To diagnose appendicitis, the doctor will perform the following procedures.
- Examine the abdomen for tenderness and look for signs of abdominal pain that indicates a ruptured appendix
- Order blood and urine tests
- X-ray of the abdomen and chest
- Ultrasound
- A computerized tomography (CT) scan
In cases of emergency, the appendix has to be removed immediately to prevent peritonitis. Otherwise, treatment is provided based on the test results.
Treatment For Appendicitis In Children
Mild cases of appendicitis may be treated with antibiotics alone, but in most cases, a surgery to remove the appendix is necessary (5). Patients may be treated with antibiotics even before the surgery.
Appendectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the infected appendix. As there is no known use of the appendix in the body, removing it is safer than taking the risk of its bursting.
An appendectomy can be a laparoscopic appendectomy, which is a key-hole procedure or an open surgery with one big incision.
Keyhole appendectomy
Most doctors prefer the keyhole surgery for removing the appendix. This involves making multiple, small incisions and use of specialized equipment to remove the infected organ. The procedure usually involves the use of:
- a tube to pump gas and inflate the stomach and get a better view of the appendix.
- a laparoscope, a tube that contains light and a tiny camera that transmits images from inside the abdomen to a television monitor
- small surgical equipment that helps in removing the appendix
Doctors perform the surgery by looking at the images on the television screen. The incisions are usually closed using dissolvable stitches. Keyhole appendectomy is a simpler procedure and allows the patient to recover and heal faster.
Open appendectomy
When a keyhole appendectomy is not possible, an open surgery may be recommended. An open surgery becomes necessary when:
- the appendix has burst, and a lump has formed inside
- the surgeon is not experienced in handling keyhole surgeries
- the patient has had an abdominal surgery previously
A procedure called laparotomy becomes necessary when the appendix bursts and results in peritonitis. Post-surgery care is vital after an appendectomy, regardless of the type of procedure performed.
Post-Appendectomy Care
Your child may be prescribed antibiotics post surgery. In addition to that, you should ensure that:
- the child does not play any rough, contact sports or exert himself too much.
- they do not go into the tub or the shower if the drain pipe has not been removed.
- any other medication prescribed is taken as needed.
- follow dietary restrictions or recommendations, if any.
The doctor may also recommend pain medication in some cases.
The appendix may be a small organ without any specific function in our body. While some research suggests that it could be serving as a reservoir of good gut bacteria, most consider it to be a ticking time bomb waiting to go off (6). Neglecting stomach pain, therefore, is not always a good idea, as not treating appendicitis in time can result in peritonitis or abscesses, which could have fatal results.
So, the next time your child complains of a stomach ache, don’t just guess that it’s alright. Be sure.
Have any tips on dealing with appendicitis in children? Share them in our comments section.