Arthritis In The Hands – Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment

Image: Shutterstock
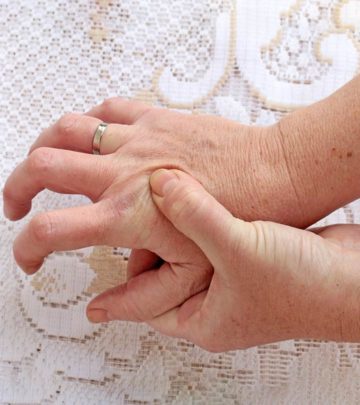
Osteoarthritis is one of the most common types of arthritis affecting the hands. This condition is also the most commonly diagnosed joint disorder in the United States (1).
Several factors can contribute to the development of arthritis in the hands. If you are unable to straighten some of your fingers completely or even hold a cup of tea, there are high chances that you could be dealing with arthritis. To know more about this condition, its treatment options, and prevention tips, read on.
In This Article
What Types Of Arthritis Affect The Hands And Fingers?
Most of the bones in your body are made up of a flexible connective tissue called cartilage, which wears down with time. The wearing down of cartilage can cause a condition called osteoarthritis (OA), which is also commonly referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can also affect your hands and fingers. While osteoarthritis is caused due to degenerative changes in the cartilage, RA is an autoimmune condition that causes your body’s immune system to attack the healthy tissues protecting the joints.
Some individuals may also experience post-traumatic arthritis in the hands, which occurs due to a serious physical injury. Such injuries can accelerate the breakdown of cartilage and also cause inflammation.
The following factors may play a major role in the onset of arthritis in the hands.
What Causes Arthritis In The Hands?
Arthritis in the hands is caused by the deterioration of cartilage, an autoimmune condition, or a traumatic injury.
Some factors that may contribute to this development are:
- Joint injuries
- Repetitive stress on a joint
- Congenital bone deformities
- Genes – A family history of the condition.
Certain factors can also put you at an increased risk of developing certain types of arthritis, like OA and RA, that affect the hands. They are as follows.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for arthritis in the hands include:
- Advancing age
- Obesity
- Medical conditions like diabetes and hemochromatosis, which cause your body to produce too much iron.
- Occupations that put repeated stress on certain joints in your hands and fingers.
The signs and symptoms associated with arthritis affecting the hands may differ depending on the type of condition.
Symptoms Of Arthritis In Hands
Osteoarthritis may cause symptoms like:
- Bony lumps in the joints of your middle finger
- Bony lumps or nodes in the joint that is closest to your fingernail
- A deep pain under the base of the thumb
- Difficulties in holding or gripping items
Rheumatoid arthritis can cause symptoms like:
- Sharp pain at the wrist and the knuckles of your fingers
- Deformities in the wrist and finger joints that do not allow you to straighten them
- Fatigue
- Body aches
Post-traumatic arthritis is associated with the following symptoms:
- Pain at the site of injury
- Worsening deformity in the affected joint
Most symptoms of post-traumatic arthritis are similar to that of OA and RA, but its cause can be attributed to a previous injury.
In case you notice any of these symptoms, it is best to seek medical intervention immediately.
How To Diagnose Arthritis In The Hands
The type of arthritis affecting the hands can be diagnosed by analyzing your symptoms and medical history.
Imaging tests like an X-ray or MRI scan may also be conducted to look for bone deformities.
A blood test may also be suggested to look for the presence of inflammation and confirm rheumatoid arthritis. A sample of fluid from the affected joint may also be taken to diagnose osteoarthritis based on the test results.
If the diagnosis hints at arthritis, your doctor will discuss the available treatment options with you.
Medical Treatment For Arthritis In The Hands
Medical treatment for arthritis in the hands mainly aims at managing the symptoms. This may include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen to relieve pain
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow down the progression of the condition if you are diagnosed with RA
- Steroids to manage inflammation
- Cortisone injection to alleviate pain and inflammation
In addition to availing medical treatment for arthritis in the hands, you can also try out home remedies to manage the symptoms.
Home Remedies To Manage The Symptoms Of Arthritis In The Hands
1. Hot And Cold Therapy
The application of a hot or cold compress can help relieve pain and inflammation in the affected area (2).
You Will Need
A hot or cold compress
What You Have To Do
- Apply a hot or cold compress to the affected hand.
- Leave it on for 3-5 minutes and remove.
- Repeat two to three times.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this multiple times daily.
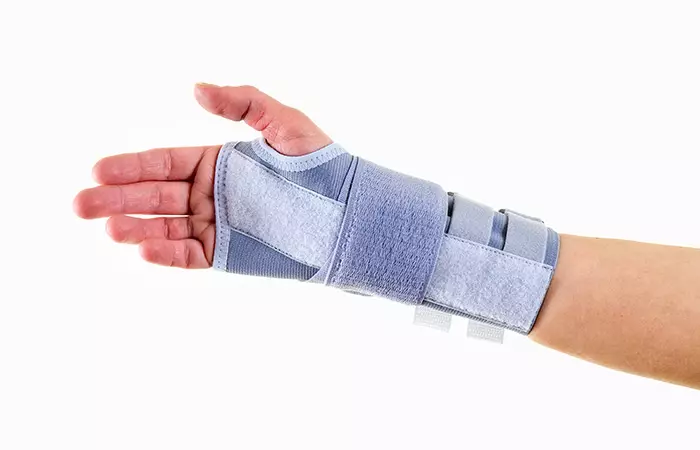
2. Braces
Splints and braces are available that may be used to offer support and rest to the wrists and hands affected by arthritis. With time, such braces can also help improve the functioning of the affected hand by alleviating symptoms of pain, inflammation, and swelling (3).
3. Essential Oils
a. Lavender Essential Oil
Lavender oil has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties (4). It can work wonders in alleviating the pain and inflammation that accompany arthritis in the hands (5).
You Will Need
- 3-4 drops of lavender oil
- 2 teaspoons of coconut oil or any other carrier oil
What You Have To Do
- Add three to four drops of lavender oil to two teaspoons of any carrier oil.
- Mix well and apply it to the affected areas.
- Leave it on until it dries.
How Often You Should Do This
You may do this 1-2 times daily.
b. Eucalyptus Essential Oil
Eucalyptus oil exhibits impressive anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity that may help in reducing inflammation and pain in the hands (5), (6).
You Will Need
- 3-4 drops of eucalyptus oil
- 2 teaspoons of coconut oil or any other carrier oil
What You Have To Do
- Mix three to four drops of eucalyptus oil with two teaspoons of any carrier oil.
- Apply the mixture to the affected area.
- Leave it on until it dries completely.
How Often You Should Do This
Repeat 1-2 times.
4. Green Tea
Green tea is a rich source of a polyphenol called epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG). This compound exhibits both chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, which may help in slowing down the progression of arthritis in the hands (7).
You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of green tea
- 1 cup of hot water
What You Have To Do
- Add a teaspoon of green tea to a cup of hot water.
- Steep for 5-7 minutes and strain.
- Drink the warm tea.
How Often You Should Do This
You may drink green tea two times daily for best results.
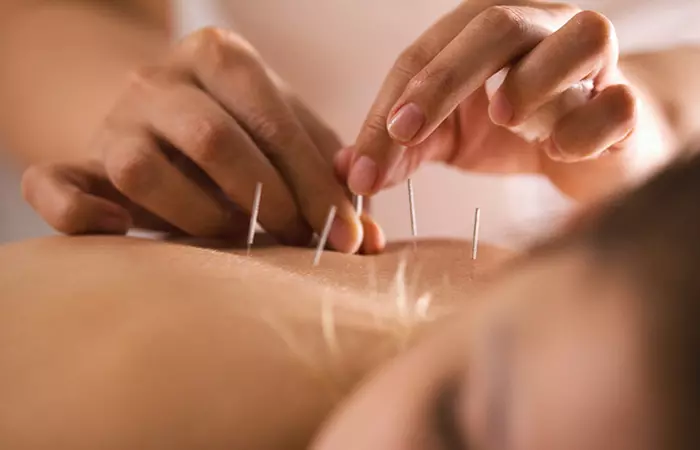
5. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is one of the popular treatments for relieving pain associated with arthritis. Acupuncturists insert thin needles into specific acupuncture points of your body. This stimulates healing and can also help in managing the symptoms of arthritis (8).
While these remedies work their magic in relieving the painful symptoms of arthritis, here are some tips that will help in preventing the progression of the disease.
How To Prevent Progression Of Arthritis In The Hands
- Keep a check on your weight.
- Follow a healthy and well-balanced diet.
- Quit smoking.
- Exercise caution while playing sports or indulging in other physical activities.
- Practice good posture if your job requires a lot of typing.
- Stay physically active.
- Do simple hand exercises like bending, flexing, finger touching, and finger sliding to increase the function of the synovial fluid.
These remedies and tips can help assist any ongoing medical treatment you are undergoing. However, do not solely rely on these remedies to treat your condition. Medical intervention is essential to manage arthritis and prevent its progression.
We hope you found this post helpful. For any further queries, get in touch with us by leaving a comment in the box below.
References
Articles on thebridalbox are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- “Epidemiology of Osteoarthritis” Clinics In Geriatric Medicine, US National Library Of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Mechanisms and efficacy of heat and cold therapies for musculoskeletal injury.” Postgraduate Medical Journal, US National Library Of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Benefits of wrist splinting in patients with rheumatoid arthritis” Reumatologia, US National Library Of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Antioxidant, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of lavender essential oil.” Annals of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences, US National Library Of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Topical dermal application of essential oils attenuates the severity of adjuvant arthritis in Lewis rats” Phytotherapy Research, US National Library Of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of essential oils of Eucalyptus.” Journal of Ethnopharmacology, US National Library Of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Green tea polyphenol treatment is chondroprotective, anti-inflammatory and palliative in a mouse posttraumatic osteoarthritis model” Arthritis Research and Therapy, US National Library Of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Acupuncture in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind controlled pilot study” BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, US National Library Of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Shaheen Naser