Bleeding During Pregnancy: Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment

In This Article
Spotting when pregnant or uterine bleeding during pregnancy is common, especially during the first and late third trimesters (1). This event could occur due to different factors and usually does not imply a serious issue, especially in the first trimester. However, bleeding later in pregnancy may have a more severe underlying cause (2).
This post discusses the difference between uterine bleeding and spotting, the various causes of uterine bleeding during different trimesters, and how it can be diagnosed and treated in pregnant women.
What Is The Difference Between Uterine Bleeding And Spotting During Pregnancy?
During the early stages of pregnancy, you may experience some light bleeding, known as spotting, where a few drops of blood may appear on your underwear occasionally. It is not enough to cover a panty liner.
Bleeding is a heavier flow of blood, necessitating the use of a sanitary pad or pantyliner to prevent your clothes from becoming soaked in blood (1) (3).
Moreover, heavy bleeding episodes (as heavy as or heavier than normal period flow) are more likely to cause pain, be of a longer duration, have bright red blood, and occur multiple times. Meanwhile, spotting episodes are more likely to occur in isolation, be of shorter duration, and be painless (4).
 Quick tip
Quick tipWhat Are The Causes For Bleeding In Pregnancy?
The underlying cause of uterine bleeding during pregnancy may or may not be serious and can differ in various trimesters.
Bleeding in the first trimester
During early pregnancy or the first trimester, bleeding or spotting is common with an incidence rate of one in four pregnant women (up to 25%) and may occur due to the following factors (1) (2) (3) (5).
- Implantation (when the fetus plants itself in the uterine wall)
- Coitus
- Pregnancy-related hormonal fluctuations
- Normal changes in the cervix
- Pap test
- Pelvic exam by your obstetrician
- Genetic testing procedures, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
- Smoking
However, bleeding and spotting during early pregnancy may also be a sign of the following serious conditions (1) (3) (4) (6).
- Pelvic cavity or urinary tract infections
- Ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterus) can be fatal if left untreated
 Quick fact
Quick fact- Threatened loss of pregnancy
- Molar pregnancy (where tissue grows inside the womb instead of a fetus)
- Subchorionic hemorrhage or hematoma (bleeding between the uterus wall and placental membrane)
Jodi Wood, a mother, recounts her encounter with bleeding during the first trimester of her pregnancy. She says, “On the day of my 12-week scan, I was experiencing some twinges in my back and abdomen – I put this down to the infamous ’round ligament pain.’ But then the bleeding began. I remember standing outside the health centre and a gush of red fluid escaped from my body. Naturally, I was in hysterics at this point; absolutely convinced I was miscarrying… I was immediately seen by a GP, she thought I was hemorrhaging and advised me to go to the ED. Fortunately, when we got to ED I was seen pretty quickly. They did an internal examination and booked me in for an ultrasound two days later.
“When they told us our baby was still there, with a beating heart, we all burst into tears. The sonographer went on to explain I had a subchorionic hemorrhage, which had caused the large episode of bleeding. She explained the clot was sitting right above my cervix so I should expect more bleeding but hopefully, it’ll reabsorb back into my uterine wall (i).”
Bleeding in the later stages of pregnancy
In the later stages of pregnancy, you may experience light bleeding because of the following reasons (1).
- Coitus
- Labor (in the third trimester)

- An internal examination by your obstetrician
- Growths on the cervix or cervical infections or inflammation
 Quick fact
Quick factHeavy bleeding in the later stages of pregnancy may be due to severe conditions, which may even cause anemia. These conditions include (1) (2) (5):
- Preterm labor (labor starts before 37 weeks of pregnancy)
- Placenta previa (the placenta lies too low in the uterus and covers the cervix)
- Placenta accreta (the placenta grows too deeply into the uterus wall and does not detach)
- Placental abruption (the placenta detaches from the uterus wall before/during birth)
- Uterine rupture during labor
- Vasa Previa (the umbilical cord blood vessels pass through the cervical membranes)
- Gestational trophoblastic disease (A uterine tumor that develops from tissue that forms after pregnancy)
- Preeclampsia (high blood pressure and protein in the urine)
When To Call A Doctor?

If you experience bleeding or spotting while pregnant, it is recommended to visit your doctor. However, contact your doctor soon if you experience (1) (6):
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding with cramps or pain
- Bleeding and dizziness (lightheadedness)
- Abdominal pain or pelvic pain with bleeding
- Bleeding in the second or third trimester of pregnancy
How Are The Causes Of Uterine Bleeding Diagnosed?
Even if your uterine bleeding has stopped, contact your healthcare provider for a diagnosis. Your doctor may inquire about any other symptoms you may be experiencing with bleeding. Additionally, they may suggest the following tests (5).
- Uterus or pelvic examinations
- Ultrasonography
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) blood testing to measure the hormonal level
How Is Uterine Bleeding During Pregnancy Treated?
Uterine bleeding is treated depending on its underlying cause and severity.
If your symptoms and bleeding are not severe, or your due date is far, you may be asked to closely monitor yourself at home. In severe circumstances, your doctor may suggest hospitalized observation. You may be required to stay overnight or until your baby is born so that you both can receive immediate medical attention (5).
Usually, adequate rest is sufficient to treat the condition. Other treatment options may include (1) (7):
- Taking some time off from work

- Staying off your feet for a little while
- Avoiding coitus
- Not douching (using cleansing products for the intimate area ) or using tampons
- Taking a folic acid-fortified prenatal vitamin
- Abstaining from smoking, consuming alcohol, and using illegal substances
- Surgery, in case of heavy bleeding due to serious complications
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is uterine bleeding a symptom of pregnancy?
Yes, uterine bleeding is a common symptom of early pregnancy. You may experience light bleeding (spotting) 1–2 weeks after fertilization when the egg implants in the uterus, also known as implantation bleeding.
2. Can climax cause uterine bleeding when pregnant?
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), spotting and cramps are normal after having coitus or experiencing a climax during pregnancy. Further, a study also suggests that experiencing climax during late pregnancy may reduce the risk of preterm delivery (8). However, if you have heavy vaginal bleeding or persistent cramps after coitus, you should contact your doctor (9).
3. Should I worry if my leukorrhea contains more than blood?
During pregnancy, you may experience uterine bleeding, usually without blood clots or tissues. However, if you notice something other than blood, contact your doctor. While visiting the emergency room, it is advised to take a sample of your leukorrhea discharge in a small jar or plastic bag for examination. Your health care provider may conduct blood tests to ensure there is no fetal distress or pregnancy loss. And in case you have a miscarriage or stillbirth, your doctor will provide additional care and perform surgical procedures such as dilation and curettage (D & C) (3) (7).
4. Can stress cause bleeding in pregnancy?
Too much stress can lead to hormonal fluctuations, which, in turn, may affect the menstrual cycle (10). However, there is no such study on whether or not stress can cause bleeding during pregnancy.
Uterine bleeding and spotting during pregnancy are common, especially during early pregnancy. However, they could be a sign of pregnancy complications. Hence, consult your doctor if you notice any bleeding or spotting, even if the bleeding has stopped. Taking adequate rest and relaxing your body can also be useful.
Infographic: Why Does A Woman May Experience Vaginal Bleeding When Pregnant?
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can make expectant mothers concerned and alarmed. While sometimes it may be harmless, it can also indicate a more serious underlying issue. Check out the infographic below to learn about several possible causes of vaginal bleeding in different stages of pregnancy.
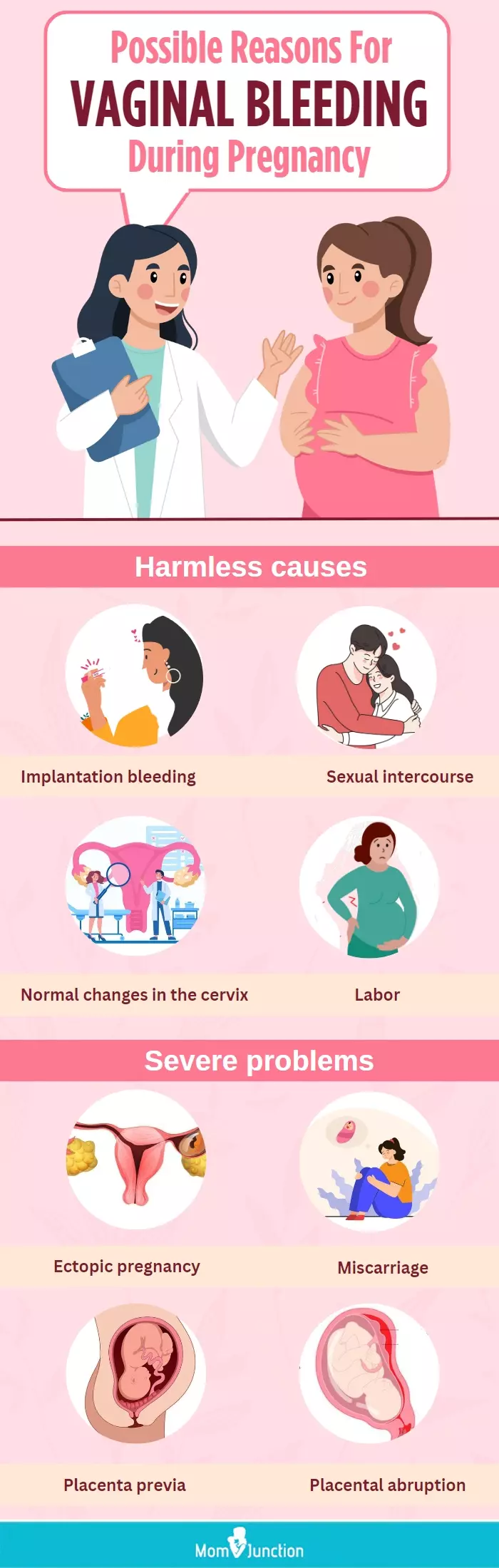
Illustration: The Bridal Box Design Team
Key Pointers
- Pregnancy commonly involves uterine bleeding or spotting, especially during early and late stages.
- Implantation, hormonal changes, or medical procedures are potential causes of bleeding during the first trimester.
- Bleeding later in pregnancy may be caused by sexual activity, labor, or cervical infections.
- Severe bleeding during late pregnancy could be a sign of critical conditions like preterm labor or placenta problems.
- Pregnant women who experience cramping, pain, heavy bleeding, or lightheadedness should promptly seek medical advice.
Illustration: Bleeding During Pregnancy: Causes Diagnosis And Treatment

Image: Dalle E/MomJunction Design Team
Bleeding during pregnancy can be a scary experience, alarming the expectant mothers. Learn what could be the underlying causes, when to be concerned, and how to manage it.
Personal Experience: Source
thebridalbox's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. The first trimester is never nice.https://medium.com/@jodiwood_54417/pregnancy-so-far-has-not-been-what-i-would-have-hoped-or-what-i-expected-acdc0de17e87
References
- Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy.
https://www.marchofdimes.org/find-support/topics/pregnancy/bleeding-and-spotting-vagina-during-pregnancy - Bleeding during pregnancy.
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/bleeding-during-pregnancy - Vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000614.htm - Reem Hasan et al.; (2011); Patterns and predictors of vaginal bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2884141/ - Bleeding during pregnancy.
https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/bleeding-during-pregnancy - Bleeding during pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-complications/bleeding-during-pregnancy/ - Bleeding During Pregnancy – What’s Normal?
https://familydoctor.org/bleeding-pregnancy-whats-normal/ - Sex During Pregnancy: What Works, What Doesn’t.
https://www.healthywomen.org/your-health/pregnancy–postpartum/sex-during-pregnancy-what-works-what-doesnt - Is it safe to have sex during pregnancy?
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/experts-and-stories/ask-acog/is-it-safe-to-have-sex-during-pregnancy - Hormonal Imbalance.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22673-hormonal-imbalance - Cervical stitch (cerclage) for preventing preterm birth in singleton pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6481522/

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Mona Hardas













