Covid-19 And Breastfeeding: Safety, Precautions & Implications
You may breastfeed by taking certain preventive measures.
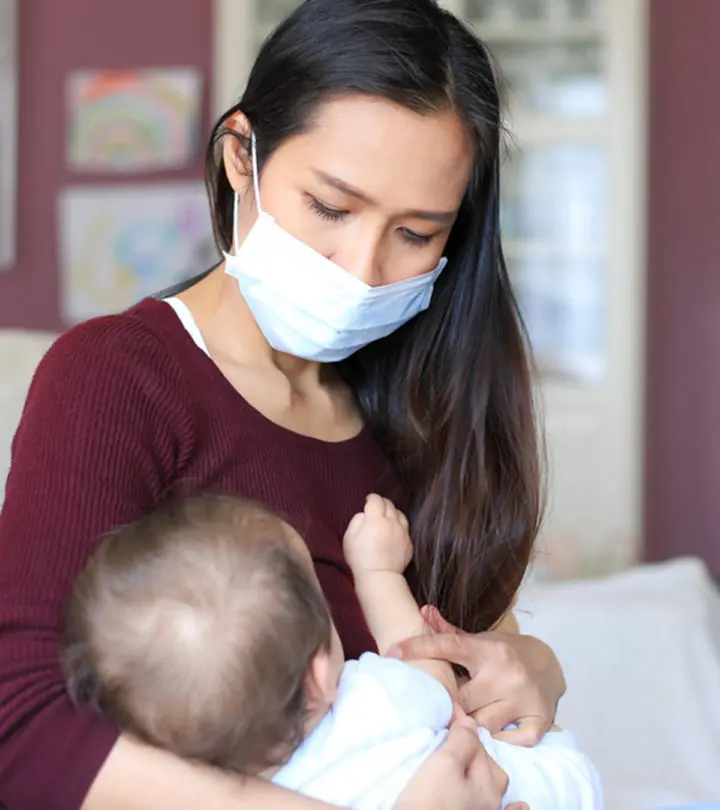

Image: Shutterstock
In This Article
There are several apprehensions amongst mothers regarding COVID-19 and breastfeeding. However, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommend initiating and continuing breastfeeding for mothers who test positive for COVID-19.
Breast milk provides immunity against various diseases, and breastfeeding is pivotal in the baby’s normal growth and development. COVID-19-positive mothers can safely nurse their babies by observing necessary precautions such as frequent and thorough handwashing and wearing masks while nursing and caring for their babies.
In some cases, the doctor may suggest separation of mother and continuing breastfeeding by expressing breast milk and bottle-feeding. Read this post to learn about the implications of COVID-19 on breastfeeding.
Is COVID-19 Transmitted Through Breast Milk?
Current evidence demonstrates that breast milk is not likely to spread COVID-19 to babies. You may discuss with your healthcare provider to decide how to begin and continue breastfeeding. The decision to breastfeed during COVID-19 should be based on the benefits of breastfeeding that outweigh the risks of breastfeeding with coronavirus disease.
A study of COVID-19 positive women found antibodies against COVID-19 in breast milk. The RNA (ribonucleic acid) of SARS-CoV-2, which causes the disease, was not found in any breast milk samples. However, several swabs of the nipple contained SARS-CoV-2 RNA. The study noted that there seems to be no risk of viral transmission through breast milk, but the virus may transmit through the breast’s skin. However, more extensive research is needed to arrive at a conclusion (1).
Is It Safe To Breastfeed During COVID-19 Infection?
You may breastfeed your child after discussing with your doctor if you have symptoms of COVID-19 infection or a positive test result. Breast milk is the best source of nutrients for your baby, and it protects against many illnesses.
The decision to breastfeed and mother-infant contact should not be based only on risks of contracting COVID-19 infection but also risks of mortality and morbidity due to not breastfeeding. Infant formula may not provide all the immunity factors provided by breast milk.
The World Health Organization recommends initiating or continuing breastfeeding by mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infection and counseling mothers about the benefits of breastfeeding (2).
Precautions For Breastfeeding With COVID-19
The following tips are recommended for COVID-19 positive mothers during breastfeeding (3).
- Wear a mask that covers your mouth and nose when you are near (within six feet) your baby.
- Wash your hands with soap and water or rub an alcohol-based sanitizer containing more than 60% of alcohol before breastfeeding, that is, before touching your baby.
The following tips are given to COVID-19 positive mothers who choose to express breast milk for feeding (3).
- Wash hands before touching bottle parts, breast pump, and while expressing the breast milk
- Wear a mask during breast milk expression
- Use your own pump and avoid sharing it with others
- Clean the pump and bottles as recommended
- Consider having a caregiver who does not have COVID-19 to bottle-feed and take care of the baby when you are in isolation
How To Keep Your Baby Safe During The Pandemic?
The following tips may help reduce COVID-19 exposure and other risks associated with the pandemic in babies (4).
- Do not put masks or face shields on children under age two since this may increase the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), strangulation, and suffocation.
- Caregivers, parents, and anyone with suspected or confirmed infection must wear face masks, sanitize their hands, and maintain social distance with the babies. CDC does not recommend face shields as an alternative to masks.
- Limit in-person visits to your newborn since asymptomatic persons can also spread illness if they are infected. You may encourage friends and family to see the newborn virtually until the pandemic subsides.
Caregivers, parents, and other family members should also follow appropriate behavior outside the home to avoid contracting the virus. Seek prompt medical advice if your newborn has any signs and symptoms of COVID- 19 or other infections.
mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Safety During Breastfeeding
The Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines are mRNA vaccines without inactivated viruses. You may see the recent recommendations in your country to choose the lactation-safe vaccine.
Clinical trials for the COVID-19 vaccine in the U.S. did not include breastfeeding mothers. Thus, there is no data available on vaccine safety and its effects on breastfed babies and breast milk production. However, based on the studies on how vaccines work in the body, vaccines are considered not to be a risk to nursing moms and breastfed babies. Therefore, lactating mothers can receive the COVID-19 vaccine (5).
Recent studies show that the breast milk of vaccinated mothers could contain COVID-19 antibodies, which could protect their babies. However, more data is required to know the effectiveness of these antibodies in babies.
Separation And Expressed Milk During COVID-19
The decision to separate the mother and newborn due to COVID-19 and the breastfeeding method should be made by the healthcare team based on the risks and benefits. If the mother and baby can stay together, breastfeeding is encouraged with precautions.
Breast milk expression and separation are recommended for some cases with severe infection, or the infant has risk factors. The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding and skin-to-skin contact in all possible cases considering it has several benefits for the mother and the baby.
Is It Possible For A Newborn To Have COVID-19?
Newborns may contract COVID-19 during childbirth or from exposure to sick caregivers after delivery. Although vertical transmission has not been reported, close contact with an infected person, including the mother, can make the baby get COVID-19. The spread of the virus can be through direct contact or by inhalation of respiratory droplets.
If you are waiting for the results of the tests, it is recommended to wear masks and sanitize hands before caring for newborns.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I breastfeed my baby if I am not fully vaccinated?
You may feed your baby if you are not fully vaccinated. SARS-CoV-2 spreads through close contact with infected people. So, if you have not been in contact with someone who has COVID or if you do not experience any symptoms of the infection, you do need to take any specific care. The virus has not been found in breast milk, so far (6).
2. How should I maintain my milk supply if I have COVID-19?
If you have a COVID-19 infection, you may maintain your milk supply by hand expressing or pumping at regular intervals (6). Expressing milk 8 to 10 times a day may fulfill your newborn’s demands. Check with your doctor for safe medications during breastfeeding. Also, try to relax, sleep adequately, and eat well to maintain a good milk supply during infection. If you have any concerns with latching or feeding your baby, do not hesitate to discuss them with your doctor.
Since breast milk protects babies from diseases and is critical for their growth and development, mothers should continue breastfeeding even when they suspect a COVID-19 infection or are COVID-positive. The current studies do not indicate that the virus can be transmitted through breast milk. However, you may consult your doctor regarding the connection between COVID and breastfeeding. Most doctors recommend wearing a mask and washing your hands thoroughly before feeding your baby. In severe cases, they may also suggest feeding expressed breast milk to babies. Nursing mothers should also get vaccinated because the antibodies against COVID-19 seep into the breast milk and provide extra protection to babies.
Key Pointers
- Recent studies suggest antibodies against Covid-19 may transmit to a baby while breastfeeding.
- If you have tested positive for Covid-19, you must take the necessary precautions while with your baby.
- Wear the mask around your baby and maintain a six feet distance when not feeding them.
- In severe cases of infection, separation from the mother and the use of expressed milk is advisable.
References
2. Breastfeeding and COVID-19;World Health Organization
3. Breastfeeding and Caring for Newborns;Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
4. Bringing home a newborn — how to keep them safe during COVID-19;Loma Linda University Health
5. COVID-19 Vaccines While Pregnant or Breastfeeding;Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
6. Breastfeeding During the COVID-19 Pandemic; HeathyChildren

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Dur Afshar Agha