Ectopic Pregnancy – Causes, Symptoms And Treatments You Should Be Aware Of
Understanding unusual embryo placement: key signs, risks, and medical solutions explained.
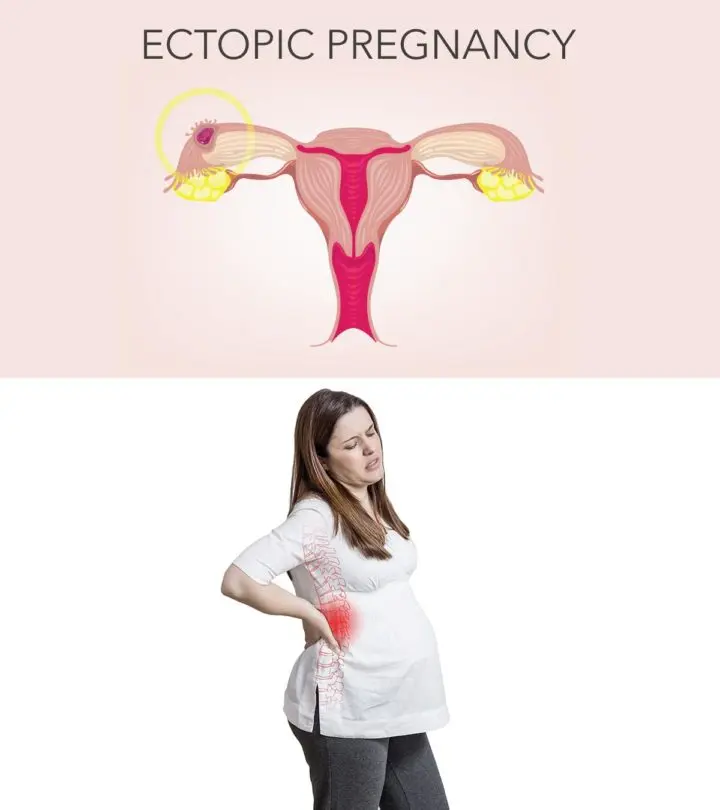
Image: Shutterstock
Diagnosing An Ectopic Pregnancy
It is tricky to diagnose an ectopic pregnancy. If the symptoms suggest that you are experiencing an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor will start an examination by performing an ultrasound and a blood test. The combination of both blood hormone pregnancy test and pelvic ultrasound test helps to establish a better diagnosis.
Blood Test:
A blood test checks the levels of the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone. If the levels are too high, but not as much as they need to be, then it can be an ectopic pregnancy. If you do not experience any pain, but still doubt the result, the test can be repeated.
Ultrasound:
Transvaginal ultrasounds help detect an ectopic pregnancy. Here, an ultrasound probe is slipped into the vagina and images are checked on a monitor. The sonographer carefully notices the uterus and tubes. If he sees an embryo in the Fallopian tube, it is an ectopic pregnancy. In most cases, the embryo will die since it cannot survive in an ectopic pregnancy. Here, he can notice a swollen tube along with some blood clots and tissue.
Then, the sonographer will examine the uterus. If the pregnancy test is positive, but he could not find the embryo, it can be a sign of ectopic pregnancy. There are also chances that you may be in the initial stages of pregnancy, or you may have miscarried. Your doctor will continue to examine you through repetitive blood tests and ultrasound exams until he establishes a proper diagnosis.
Other Diagnostic Tests:
If the above tests aren’t conclusive, your doctor may recommend a Dilation and Curettage (D&C) surgery to detect and remove the unwanted tissue from the uterus.
In rare cases, you may have to go for laparoscopy. It is a procedure where a small camera is inserted into the abdominal region to view the internal structures, to detect an ectopic pregnancy.
Treating An Ectopic Pregnancy
Treatment depends on the basis of diagnosis, like the pregnancy stage, hormonal levels and your symptoms.
Expectant Management:
If your ectopic pregnancy is detected too early within the first six weeks and you notice no symptoms, then there is an option for expectant management. The option is not to undergo any treatment, just a “wait and see” option.
Nearly 50% of ectopic pregnancies end up in miscarriage. If the blood hormone pregnancy test and the ultrasound show nil results, then expectant management is advisable. But, in rare cases, some women who opt for the method may still require medical or surgical treatment later.
Medical Treatment:
If your health care provider diagnoses low pregnancy hormonal levels, no visible heartbeat and minute symptoms in early pregnancy stages, medical treatment is suggestible. It involves injecting an anti-cancer drug, methotrexate (Trexall, Rheumatrex) into the thigh. This drug, inhibits pregnancy. Some women may not respond to medical treatment, while some may require surgical treatment.
Methotrexate treatment has a high success rate and side effects are quite rare. Factors like the embryo size and hCG hormone concentrations help the doctor to choose the medical treatment. Also, the medical treatment is 90% effective in preventing the ectopic pregnancy.
Surgical Treatment:
If the ectopic pregnancy is detected during Laparoscopy, the surgeon will directly remove the tissue during diagnosis. If not during diagnosis, there is another surgical method called Salpingectomy that your surgeon may prefer. It involves removal of Fallopian tube and pregnancy through two small incisions.
It is also possible to preserve the Fallopian tube and remove the embryo without damaging or rupturing the tube. This method is called Salpingotomy. It is suggestible if you possess only one Fallopian tube, or the other tube seems to be unhealthy.
Your doctor will explain the benefits and risks of each treatment before proceeding to any. He will ensure to offer you the required support all through the treatment.
Can You Get Pregnant After You Had An Ectopic Pregnancy?
Most women who experience an ectopic pregnancy will have normal pregnancies in the future. It does not matter if one of the Fallopian tubes is removed since one healthy working tube is enough to help the fertilization. The earlier you prevent an ectopic pregnancy, the lesser the damage to the tube and the greater are the chances of becoming pregnant again.
If an infection or sexually transmitted disease were the causes for your ectopic pregnancy, then getting them treated improves the chances of conception. But, if the ectopic pregnancy occurs due to tubal ligation or exposure to diethylstilboestrol (DES), there are lesser chances of a normal pregnancy.
Check with your doctor before you plan for a next pregnancy. You should leave a quality time to heal your body and mind. Check with your doctor about counseling groups and consider getting some counseling for yourself and your partner.
We hope our guide helped you know about ectopic pregnancy better. Feel free to share your experiences, post your queries if any.