Frozen Embryo Transfer: Why And How Is It Done?
In This Article
You want to have kids, but want to wait a few more years to be ready.
Your biological clock is ticking, adding to the stress and making you wonder if you can become a mom at an age you want to. Enter ‘frozen embryo transfer’ or FET, an IVF treatment option that lets you conceive from a preserved embryo of yours. This means yes, you have a chance of conceiving at any age you want.
Sounds interesting? Read this MomJunction post to find out more about the FET procedure, reasons why people opt for it, the procedure, and precautions.
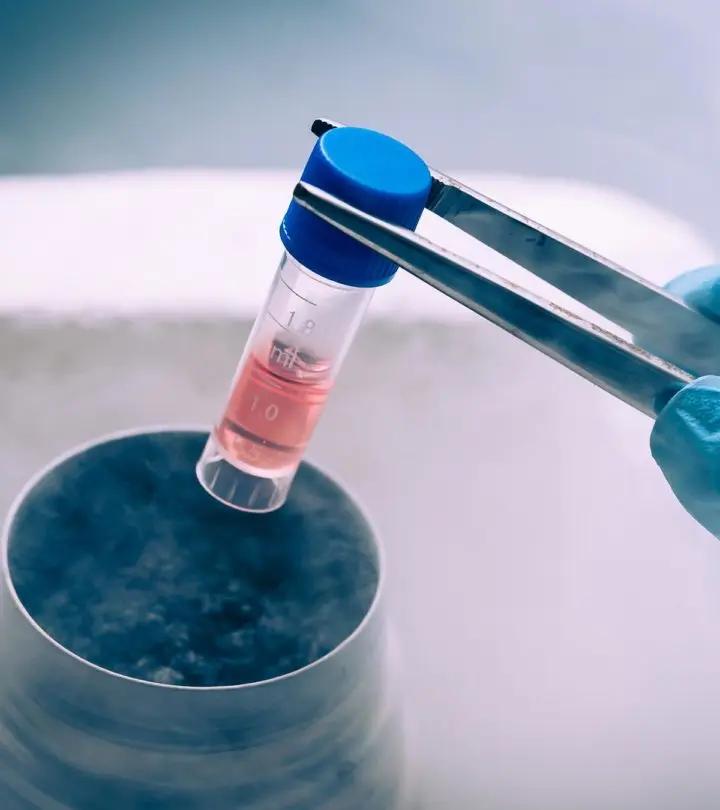
What Is A Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)?
A frozen embryo transfer process involves freezing and storing of the excess embryos procured during the in vitro fertilization (IVF)/ intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) cycles for future use. This method increases the chances of pregnancy without wastage of the embryos (1).
The frozen embryos can be thawed and transferred into the woman’s uterus for a future pregnancy. Usually, a single embryo transfer is recommended over multiple embryos to enhance the implantation rate and to decrease the complications related to multiple pregnancies (2).
Note: Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is a part of the IVF treatment wherein the fertilization is attempted by injecting a single sperm into each egg. It is mainly done in the case of male fertility or couples with previously failed IVF procedures (3).
FET can be an effective IVF method, but is it suitable for you? Read on to know if you should consider this fertility option.
When Can You Opt For The FET Cycle?
Sometimes, a fresh embryo transfer fails due to reasons such as illness or medicinal treatments. In such a case, you can decide to go for a frozen embryo transfer. Read on to know why this fertility option is considered.
What Are The Reasons For Frozen Embryo Transfer?
The frozen embryo transfer is usually done in the following circumstances (7):
- Couples who undergo IVF or ICSI treatment will be left with a few good quality embryos. Instead of wasting them, the couple can freeze the embryos for future use (pregnancy). If a fresh IVF attempt fails, then the couple can use a frozen embryo to have a baby.
With the advanced assisted reproductive techniques like preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) and preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), it is possible to select the embryo that is best for the transfer. PGD helps in determining the genetic disorder of the embryo and PGS detects any chromosomal abnormalities (8).
A biopsy of the embryo is done by performing some genetic tests on a few embryonic cells. Based on the test result, the doctor determines the best embryo for the transfer. Alternatively, the couple can try a fresh embryo transfer if the FET method doesn’t work for them.
- Women with the ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), which results from the fertility drugs, can go for FET-IVF cycle. OHSS is a serious complication of IVF treatments (9). If you are diagnosed with it before the FET cycle, then it may be canceled and rescheduled for until after the treatment. The embryos that were thawed for the FET cycle will be cryopreserved.
- If a couple decides to use an embryo donor, then the FET cycle will be considered. Here, the patient will start with the medications to develop the required environment for embryo implantation in the uterus and the FET is done on a scheduled day.
If the fertility specialists determine that FET is suitable for you, they will prep you for the procedure.
What Happens Before An FET?
The embryo is generally transferred after the release of the egg. The two cycles generally considered for an FET are the natural cycle FET and HRT cycle FET.
Natural cycle FET: This cycle is ideal for women with regular menstrual cycles. It involves monitoring the follicle development through transvaginal sonography, monitoring the LH surge and confirming the ovulation with ultrasonography (4). Once the ovulation is evaluated, you will be put on hormonal supplementation for the rest of the cycle. The embryo will be transferred three days after ovulation is observed (5). Usually, one or two embryos will be transferred.
HRT cycle FET: In the hormone replacement therapy (HRT) cycle, the endometrium is artificially prepared by progesterone and estrogen hormones. Initially, birth control pills or a hormone injection called leuprolide will be given for ten days, to halt the ovarian activity (6).
Then, estradiol (2mg) will be given as an injection or orally to prepare the endometrium for the embryo transfer. Once the endometrium attains a thickness of 7mm, 40-60mg of progesterone oil will be injected intramuscularly. The thawed embryo will be transferred three days later.
The HRT-FET takes considerably less time than the natural cycle FET.
What are the benefits of FET?
According to studies, pregnancies from frozen embryos result in increased birth weight and enable embryo screening without any adverse perinatal outcomes (10). Other benefits include:
- Less stress, as there is no stimulation phase for egg retrieval.
- Fewer medications are used, including the progesterone and estrogen hormones for endometrial thickening.
Keep reading to know how the frozen embryo transfer is done.
Frozen Embryo Transfer Process
During the programmed and the natural FET cycles, the doctor will closely monitor the patient with the help of ultrasounds to check the ovaries and uterus and to detect any uterine abnormalities such as cysts or polyps that could interfere with the transfer cycle. Blood tests are also done to check the hormonal levels.
Once the peak receptivity of the endometrium lining is evaluated, they schedule the FET. Accordingly, the embryo that reaches a blastocyst stage that matches the uterine lining will be thawed and transferred on the same day.
Anesthesia is very rarely used during this procedure. A transfer catheter with the embryo is passed through the cervix and into the uterus using ultrasound images for guidance. This can trigger mild cramping. The doctor will wait for the cramping to subside, and then the embryo along with a small amount of fluid is gently deposited into the uterine cavity. The patient will be allowed to rest for 20 minutes after the procedure, and then be discharged (11), (12).
Post FET, you must take care of your health. The section below explains the precautions you must take.
Precautions To Take After The Procedure
The body needs time to adjust to the embryo transfer. For successful conception through this procedure, it is imperative that you take these precautions:
- Do not take any stress and try to rest as much as possible.
- Avoid sexual intercourse.
- Do not lift heavy weights.
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet.
- Avoid using hot tubs and saunas that can elevate the body temperature.
- Always ask for support from your spouse, friends, and family members in managing household chores.
FET is an effective procedure that works when it is administered properly. If you wish to try this method of conception, you must focus on certain points. Keep reading to know it.
Tips To Follow Before Going For Frozen Embryo Transfer
Here is a list of the things you must take care of before the FET cycle.
- Find an expert IVF specialist who has profound experience in carrying out the procedure.
- Do not skip the prescribed pre-tests that are essential before initiating the process. These include a few blood tests and an intravaginal scan to check the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes.
- Follow a balanced diet and take folic acid supplements to prevent neural tube defects like spina bifida in the fetus.
- Keep stress at bay as it can be bad for your health. Engage yourself in activities that give you pleasure and uplift your mood.
- Yoga (13), meditation, and tai chi (a form of meditation) are a few activities you can engage in for stress reduction after the embryo transfer (14).
Frozen Embryo Transfer vs. Fresh Embryo Transfer
One study indicates that there isn’t much difference in the outcomes of frozen embryo transfer and fresh embryo transfer (15). Another suggests that the outcome can be improved with FET, although it depends upon the development of the endometrium lining, which is the key factor for a successful pregnancy (16).
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. For how long can the embryos be stored?
Since the deterioration time for the frozen embryos has not been established yet, it is not clear for how long the embryos can be stored for implantation. Usually, a short to medium term storage time is considered ideal.
2. Are there any risks associated with FET?
Preeclampsia is a risk associated with FET. It occurs if the patient undergoes a programmed cycle FET, wherein the development of the corpus luteum is suppressed by hormonal supplementation. However, if a natural cycle is adopted, then the corpus luteum is allowed to develop and the risk of preeclampsia can be tamed (17).
If the couple decides to have a sibling for their baby, they can go for FET instead of fresh cycle IVF. This kind of elective method helps them to know about the quality of the embryo and also they can get the process done faster than a fresh cycle.
Did you opt for FET? How was your experience? Share it with us in the comment section below.
References
2. M.R. Freeman et al.; Elective single embryo transfer criteria should be applied to frozen embryo transfer cycles; American Society For Reproductive Medicine (2016)
3. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI); American Society for Reproductive Medicine
4. Frozen Embryo Transfer: Natural Cycle; UT Health San Antonio
5. A Study: the Different Outcomes Between Natural Cycle and Hormone Replacement Cycle in FET; NIH
6. Frozen Embryo Transfer Cycle; University of Washington Medical Center
7. Embryo Freezing; Australia’s National Infertility Network
8. Preimplantation Genetic Testing; American Society for Reproductive Medicine
9. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (2016)
10. N. Herlihy et al.; An obstetrical perspective: the benefits of a frozen embryo transfer cycle; American Society for Reproductive Medicine (2017)
11. Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET); Weill Cornell Medicine
12. Frozen Embryo Transfer: Natural Cycle; UT Health San Antonio
13. P. Nayar et al.; Can Yoga Affect IVF Outcomes?; American Society for Reproductive Medicine
14. The health benefits of tai chi; Harvard University (2009)
15. E Shahrokh-Tehraninejad, Z Vosoog, F Farajzadeh-Vajari; Comparison of Outcomes of IVF Cycles Between Transferred Frozen Thawed Embryos and Fresh Embryos by a 2 Year Survey; JRI (2017)
16. Matheus Roque, M.D et al.; Fresh embryo transfer versus frozen embryo transfer in in vitro fertilization cycles: a systematic review and meta-analysis; American Society for Reproductive Medicine (2019)
17. Why do IVF pregnancies with frozen embryos increase preeclampsia risk?; American Heart Association (2019)

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.












