When Do Women Ovulate And What Are The Ovulation Symptoms
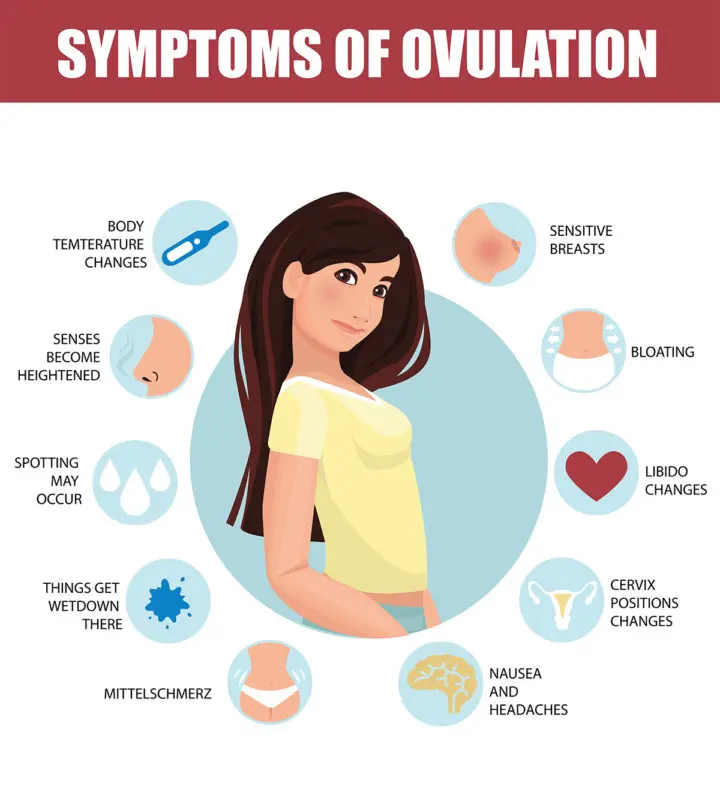
Image: Shutterstock
In This Article
Ovulation is an integral part of a woman’s menstrual cycle. Whether you want to have a baby or avoid getting pregnant – making note of your ovulation dates will help you in both scenarios.
While we can guess the days of ovulation every month, it may not be possible to be sure about them. However, if you continuously keep a note of the ovulation symptoms for some months, then it will be easy to know when you are ovulating.
In this post, MomJunction tells you about such symptoms that could signal ovulation, and also the signs that show you are not ovulating, treatment for ovulation problems and more.
What Is Ovulation?
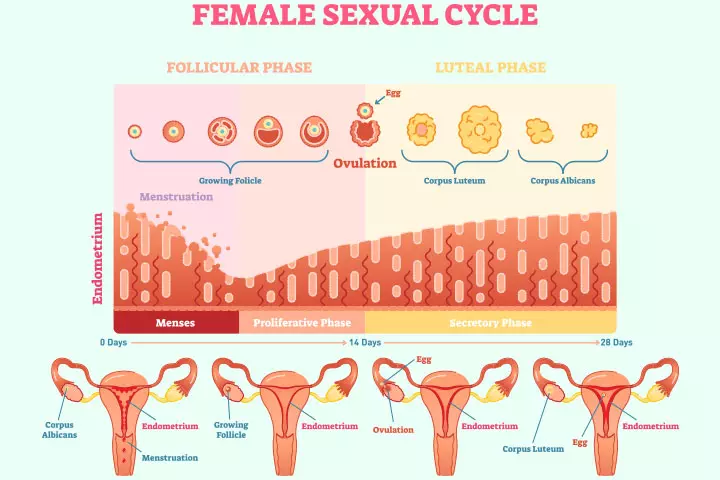
Ovulation refers to the release of a mature egg from one of the ovaries. The egg then travels down the fallopian tube where it can get fertilized on meeting the sperm. This is the most fertile stage of a menstrual cycle.
The hormone that is responsible for ovulation is estrogen. The estrogen levels, which are low at the beginning of the period cycle, eventually rise until they reach a threshold and trigger the luteinizing hormone. This LH hormone stimulates the ovaries to release an egg (1).
When Do Women Usually Ovulate?
Women are likely to ovulate on the 14th day if they have a 28-day menstrual cycle. The timing may vary from woman to woman, and from cycle to cycle. Therefore, you should get familiar with your menstrual cycle by keeping track of the dates for at least three months. It could help you estimate your ovulation phase (2).
When Are You Fertile?
In an average 28-day menstrual cycle, there are about six days, called the fertile window, when you can get pregnant. These are the five days before ovulation, and the ovulation day itself (3).
The fertile window is counted from five days before ovulation because the sperm can live inside the woman’s body for three to five days. If you have intercourse on these six days, there is the highest probability of fertilization since the sperm waits in your fallopian tubes for the egg to release.
You are most fertile two to three days before ovulation than on the ovulation day itself (4).
Knowing your ovulation days is not easy but you can keep track of your mid-cycle symptoms to identify your fertile days.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Ovulation?
If you can track the symptoms for at least three months, you are likely to identify the pattern. Below we list some of the symptoms that most women have during their ovulation.
Common signs that occur in most women
Following are the primary signs that could be studied and tracked to predict the accurate ovulation days.
- Increase in cervical mucus: The volume of cervical mucus is observed to be increasing from nine days before ovulation, and peaks from four days before ovulation (5). It resembles egg white and turns slippery during this time.
- Rise in basal body temperature (BBT): The BBT comes down just before ovulation and sharply rises after the ovulation is over, due to an increase in progesterone level. The rise in BBT confirms that the ovulation has occurred. By the time you know about it, it would be too late to conceive in that cycle. But it will help you track the ovulation days, and prepare for the coming months (5).
- Changes in the cervix: The cervix that is relatively low with a small opening will move higher, gets softer and widens (6). For feeling the cervix, you can insert your clean finger into the vagina until you feel a little nub. You may have to do this every day to know when it opens.
Secondary ovulation symptoms
Secondary symptoms do not occur all the time. However, when you observe any of the three primary symptoms, you may check for the secondary symptoms too. In fact, the secondary symptoms are easier to spot than the primary ones.
- Light spotting: Some women experience mid-month pinkish or brownish spotting when the production of the progesterone hormone is not enough to keep the lining intact. Progesterone usually thickens the uterine lining that is released during the period. Inadequate secretion of this hormone could result in spotting (7).
- Pelvic pain: You may have cramping and pain in the lower abdomen on one side of the pelvis. This pain is referred to as mittelschmerz (a combination of German words that mean middle pain). However, it might not occur right during ovulation and cannot be regarded as a definitive ovulation symptom (8).
- Sore breasts: Hormones stimulate the breasts to retain fluid that causes them to slightly stretch out. This could lead to tender, sore and heavy breasts (9). However, you may not be sure about ovulation based on this symptom as the breasts may turn sore even during PMS and pregnancy.
- Bloating: Just as the breasts retain fluid, the abdomen can also retain water and make you feel bloated. However, fluid retention could also peak on the first day of menstrual flow (10).
- Increased libido: You may experience an increase in sex drive due to high estrogen levels leading up to ovulation. However, this may occur even during the luteal phase that is after ovulation (11).
- Pleasant body odor: In a study, men were asked to smell the t-shirt worn by women during the follicular (ovulatory) phase and the luteal (non-ovulatory) phase. Men found the odor of ovulatory phase t-shirts more pleasant and sexy than those worn by women during their non-ovulatory phase (12).
- Increase in pulse rate: Resting pulse rate (RPR) increases in the days leading to ovulation. It is the lowest during periods and increases around two to five days before ovulation by around two beats per minute (BPM) (13).
These symptoms are not obvious. You need to keenly observe them to know if you are ovulating. Moreover, your ovulation can get irregular if you are (14):
- Going through the perimenopause phase
- Taking hormonal medications e.g. birth control pills
- Having certain conditions such as premature ovarian failure or polycystic ovary syndrome
- On certain medications such as anti-nausea pills, antidepressants or chemotherapy
- Stressed, overweight or underweight
- In these cases, tracking ovulation can become difficult.
Signs That You Are Not Ovulating (Or Having Ovulation Problems)
If you are not ovulating, it is medically termed as Anovulation, and if you are irregularly ovulating, that is Oligoovulation. In both cases, you may find difficulty in conceiving naturally.
Following are the possible signs and symptoms of ovulation problems (15):
- Irregular cycles: If your cycles are irregular, you may have ovulation issues. It is natural for your period to vary by a couple of days, but it may not be reasonable if the variation is for several days or even weeks.
- Short or long menstrual cycles: A normal period could vary from 21 days to 35 days. But if they are either shorter or longer than this, you might have issues with ovulation.
- No periods for months: If you go without cycles for several months, especially during the childbearing age, it is a sign you are not ovulating regularly.
- Negative ovulation test result: An ovulation kit detects the LH hormone that rises before ovulation. If you get negative results, it means you are not ovulating. Also, getting multiple positive results also indicates a problem with ovulation. It might be because your body is attempting to ovulate but is unable to achieve it.
You might also miss ovulation if you are pregnant. Therefore, do not assume that you are having ovulation problems when you do not observe some of the symptoms. But if you have been following the symptoms for some months and then find something amiss with ovulation or if your periods have become irregular, then it is good to see a doctor.
How Does A Doctor Test For Ovulation?
The doctor will ask you questions about your menstrual cycle, and its regularity. They might also suggest some tests:
- Progesterone blood test. The levels are lower if you are not ovulating properly (16).
- Tests are done to check the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteal hormone (LH), estradiol (E2) and testosterone (T).
- Prolactin level test (PRL) is done to measure the levels of the hormone. High prolactin can disrupt ovulation (17).
- Transvaginal ultrasound to check the condition of follicle development in the ovary. It can detect if the follicle has broken to release an egg after ovulation (17).
If the tests confirm that there is a problem with ovulation, the doctor would suggest a treatment to address the underlying cause.
Treatment For Ovulation Problems
The treatment might begin with oral medications such as clomiphene citrate (Clomid or Letrozole or Serophene). They improve FSH and LH levels, thus stimulating the ovaries to cause ovulation.
The drug is usually administered for five days starting from the second day after the onset of menses. (18).
How To Increase Your Chances Of Ovulation?
In addition to medication, you may take the below measures to increase your chances of ovulation:
- Maintain a healthy height as per your age and height. Overweight or underweight may cause ovulation problems.
- Too much exercise can affect ovulation. Ease back on your exercises, and get expert advice on the type of exercises you can take up.
- Crash dieting, skipping meals, fasting and other unhealthy eating habits can have an effect on ovulation. Check with a health expert and switch to healthy eating habits.
- Emotional stress has an adverse effect on your period cycle. Learn to cope with stress, and try some relaxation exercises.
Keep observing the changes in your body for each cycle and make a note of them. Within three to four months you will be able to notice a pattern in the symptoms. This will help you know your days of ovulation.
If you are sexually active, you do not have to know the exact days of ovulation to get pregnant. Even a rough estimate is good enough for you to have unprotected sex with your partner. It is even better if you have regular intercourse throughout the month. Do remember to take folic acid at least 3 months before conceiving.
Did you try tracking your ovulation? Let us know about it in the comments section below.
References
2. Allen J Wilcox et al.; The timing of the “fertile window” in the menstrual cycle: day specific estimates from a prospective study; BMJ; NCBI (2000)
3. What are some possible causes of female infertility; NIH
4. Allen J Wilcox, David Dunson, and Donna Day Baird; The timing of the “fertile window” in the menstrual cycle: day specific estimates from a prospective study; The BMJ
5. Pregnancy – identifying fertile days; NIH
6. Martin Owen; Physiological Signs of Ovulation and Fertility Readily Observable by Women; Linacre Q (2013)
7. James P.Nott, et al.; The structure and function of the cervix during pregnancy; Translational Research in Anatomy Volume 2 (2016)
8. Natalie M. Crawford, et al.; A prospective evaluation of the impact of intermenstrual bleeding on natural fertility; NCBI (2017)
9. Mid-Menstrual Cycle Pain (Mittelschmerz); Harvard University (2019)
10. Breast Conditions in Young Women; University of Rochester Medical Center
11. Colin P. White et al.; Fluid Retention over the Menstrual Cycle: 1-Year Data from the Prospective Ovulation Cohort; Obstet Gynecol Int (2011)
12. Susan B. Bullivant et al.; Women’s sexual experience during the menstrual cycle: Identification of the sexual phase by noninvasive measurement of luteinizing hormone; The Journal of Sex Research
13. Devendra Singh and P. Matthew Bronstad; Female body odour is a potential cue to ovulation; Proceedings: Biological Sciences (2001), Royal Society
14. What are some possible causes of female infertility?US Department of Health and Human Services; NIH (2017)
15. I Katsikis et al.; Anovulation and ovulation induction; Hippokrati. (2006)
16. Progesterone Test; NIH (2018)
17. Evaluating Infertility; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (2017)
18. The Practice Committee; Use of clomiphene citrate in infertile women: a committee opinion; American Society for Reproductive Medicine (2013)

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.