Newborn Screening: What Is It And Why Is It Important?

- What is a newborn screening test?
- What diseases does a newborn screening test detect?
- Why is newborn screening important?
- When and where will my baby be tested?
- Newborn blood test: why is the timing important?
- How is newborn screening done?
- What do the newborn screen results mean?
- FAQs:

The birth of your baby is the happiest moment in your life. But that happiness gets disturbed when your healthcare provider talks to you about newborn screening tests.
You do not like to hear anything about possible health conditions for your just-born baby. But the reality is, there is such possibility and hence the tests.
MomJunction tells you about the screening tests your newborn has to undergo, why they are done, and what the results could mean.
What Is A Newborn Screening Test?
A newborn screening test, also known as a neonatal screening test, is a medical procedure that involves a blood test, heart screening and hearing test to check for developmental, genetic, and metabolic disorders in the newborn baby.
Developmental disorders: The most common developmental disorders are mental retardation, learning disorder, cerebral palsy and autism spectrum disorders (1).
Genetic disorders: These include chromosomal abnormalities and other disorders such as congenital hypothyroidism, hemophilia, and Huntington’s disease (2). Newborn genetic screening identifies treatable genetic disorders in newborns.
Metabolic disorders: Metabolism is the process in which the body breaks down and stores the food in the form of energy. When the metabolism process doesn’t work well, it can lead to disorders due to the abnormal levels of chemicals. Certain metabolic disorders such as galactosemia, lysosomal storage disease, and homocystinuriacan can be detected through the screening tests (3).
When these disorders are diagnosed early, treatment can be done before the condition gets too serious to address.
[ Read: How Often To Breastfeed Newborn ]
What Diseases Does A Newborn Screening Test Detect?
The newborn screening test detects the following disorders:
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
- Biotinidase deficiency
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
- Cystic fibrosis (CF)
- Galactosemia
- Hearing screening
- Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
- MCAD deficiency
- Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
- Sickle cell disease
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tyrosinemia
As certain conditions and abnormalities in the baby are detected during the pregnancy tests itself, you might be wondering if the newborn screening is required at all.
Why Is Newborn Screening Important?
Certain medical conditions are not detectable during pregnancy or at the time of birth. The symptoms begin appearing a few weeks or months after the birth.
The newborn screening tests help identify those disorders even before any symptoms appear.
They help in diagnosing and treating these conditions before they become serious or even fatal.
When And Where Will My Baby Be Tested?
The screening tests will be performed immediately after birth while the baby is still in the hospital.
- If you and your baby get discharged within a day after your delivery, then you might have to come back the next to take the tests.
- If you had your delivery at home, take your newborn to the hospital within two days for evaluation and also for screening tests.
- The blood test is usually done between 24 and 48 hours of the baby’s birth.
Do not delay the screening beyond three days because the signs of certain medical conditions show up within a couple of days after birth.
The blood test needs to be done after 24 hours but before 48 hours. Let’s see why.
[ Read: ‘Outie’ Belly Button In Newborns ]
Newborn Blood Test: Why Is The Timing Important?
The timing is crucial because certain medical conditions may not be diagnosed when the blood test is done before 24 hours of life.
And if the blood is drawn after 48 hours, treatment might get delayed if the baby has a health condition (4).
Some hospitals conduct a second screening test when the babies are 15 days old to confirm the previous results.
How Is Newborn Screening Done?
The newborn screening tests are not complicated. They involve simple procedures. The tests are done using three methods: heel stick, pulse oximetry and hearing test.
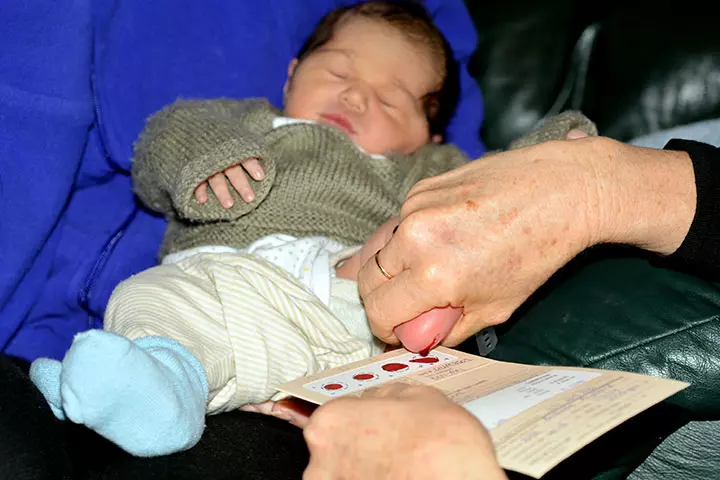
- Heel stick/ blood test: This is done 24-48 hours after the baby is born. The baby’s heel is pricked and the blood sample collected.
The lab technician places the blood sample on the filter paper card and dries it to create ‘dried blood spots’. The filter paper card is then sent to a lab for a complete analysis (5).
- Pulse oximetry: This test, too, is done when the baby is 24-48 hours of age. A small sensor called pulse oximeter is placed on the baby’s skin to measure the oxygen levels in the blood. If the oxygen is not up to the required level in the blood, it could indicate a heart condition called critical congenital heart defect (6).
- Hearing test: It is done anytime after the baby is 12 hours old. The process involves placing a small earpiece or microphone in the infant’s ear to test their hearing abilities and detect any hearing loss. If detected early, it can help prevent speech and language problems, and improve hearing skills (7).
The hearing loss in babies can be screened using two tests. These tests are easy and safe and are quickly done while the baby is sleeping. The hospital may use one or both the tests.
i. Otoacoustic emissions (OAE) test checks the hearing ability of the baby and how the baby responds to sound.
A small earphone and microphone are placed inside the baby’s ear and a sound is played.
If your baby’s hearing is normal, then an echo is reflected in the ear canal. But if an echo is not produced, it indicates hearing loss.
ii. Auditory brain stem response test (ABR) is used to check the response of the brain to sounds. This test also involves placing small earphones in the ear and playing the sounds.
Electrodes are fixed on the baby’s head to check the brain’s response to sounds. If the brain responds inconsistently, then it indicates a problem in the hearing ability of the baby.
If your baby is detected with a hearing loss, you must consult an audiologist and otolaryngologist to assess the degree of hearing loss.
[ Read: Swollen Breasts In Newborns ]
What Do The Newborn Screen Results Mean?
The screening tests give only the preliminary information. Based on it, the doctors will decide whether or not to go for precise diagnostic testing. Here’s what the results mean:
Negative/normal: A negative result means that the results of all tests are normal and there is no risk of any condition. There is no need to go for follow-up tests in this case.
False-negative: This result is rare. False negative means that the condition was missed by the screening test. It comes as negative, but the child actually has the condition. Such results can occur due to laboratory errors, combining of samples or conducting the test too early.
As there are chances of false-negative results, the follow-up tests should be done if there are symptoms or familial history of a certain condition.
Positive/abnormal: A positive or an abnormal result means that the test results are out of the normal range (8).
A positive result indicates that follow-up tests are required to know the exact condition. Your healthcare provider will intimate you if there is a positive result.
False-positive: If the follow-up test after a positive result shows that your baby doesn’t have any medical condition then the first test results are termed as false-positive. It means that the test has identified a risk where the baby has none.
A false-positive result can occur if the blood sample was collected immediately after birth, or if the baby was not fed well before the sample collection.
Most parents have concerns regarding the screening tests. Here are some FAQs that might address your concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What if they find something wrong with my baby?
Only a few babies are diagnosed with any conditions. But if your baby gets a positive result, then it is good to detect the problem early and start the treatment as soon as possible.
2. What is the testing procedure for premature, low birth weight (LBW) or NICU babies?
The screening test could be unreliable in the case of premature, LBW or sick babies due to their health condition or treatment. Therefore, a newborn screening testing protocol-2014 recommends screening of such babies immediately after 24 hours of birth and again after 28 days. The second screening is to rule out any false-negative result in the first one (9).
3. Is the newborn screening blood test painful for babies?
The heel stick or the blood test causes slight uneasiness or bruising in the area where it is pricked, but it heals quickly. To make the process comfortable, you can feed or comfort your baby before and after the screening test. Hold your baby close to you to make them cozy during the screening.
According to studies (10), babies are not likely to cry when their primary caregiver or mother comforts them during the heel stick test.
[ Read: Things Know About Newborns ]
4. Do parents have to ask for the screening test?
As a standard procedure, all the US states recommend newborn screening. In most hospitals, newborn screening is an integral part of the procedures and is performed whether or not the parents ask for it.
But if you do not want the test to be done for religious or other reasons, you need to discuss with the healthcare provider, and sign a form.
A newborn screening test is crucial for the baby to receive timely treatment. While it is natural for you to get anxious when your newborn is called for tests, it is important to understand that it is done only to ensure the overall wellness of your child. Early detection of disorders can save the child. And if your baby comes out with a negative result, then you can just relax.
Share your thoughts with us in the comments section below.

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.