Apgar Score: What Do Normal And Abnormal Scores Mean?
Apgar comprises a set of parameters used to assess a baby’s health status after birth
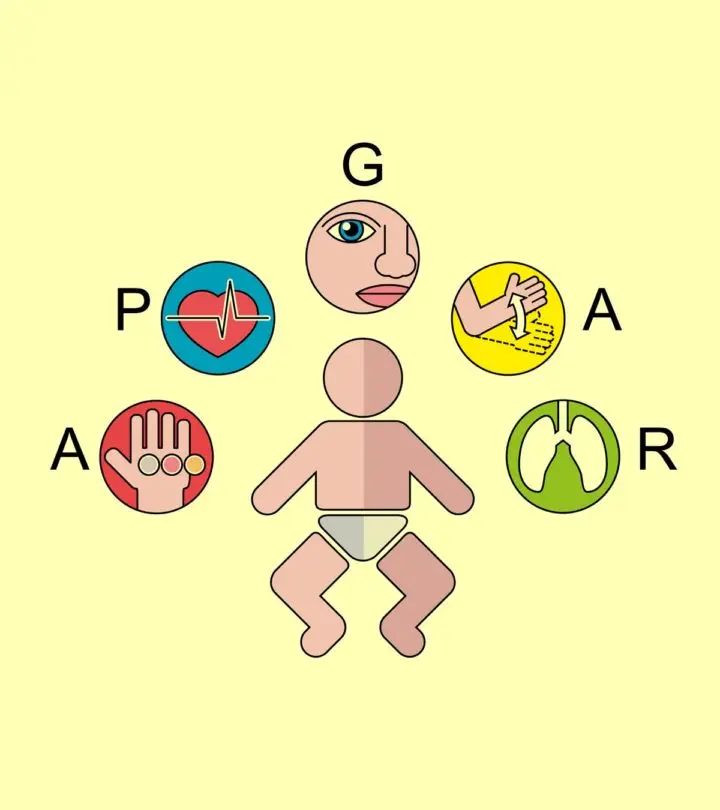
Image: Shutterstock
In This Article
The Apgar score, also called newborn scoring, is a method that helps to summarize a baby’s health status immediately after birth. It is usually done twice on a baby, one minute after birth and five minutes after birth. Re-evaluation is recommended if there are any concerns.
A baby’s vital parameters, including the heart rate and respiratory rate, are measured in the Apgar scoring system. Although Apgar score shows the newborn’s wellbeing, it alone does not predict the probability of mortality or health issues of a baby.
Read on to know when, how, and why the Apgar score is measured and the normal and abnormal Apgar score.
What Does “Apgar” Mean?
The Apgar score was developed in 1952 by Virginia Apgar, an anesthesiologist at New York-Presbyterian Hospital, to evaluate obstetric anesthesia’s effects on newborns. Each letter in ’Apgar’ stands for a parameter measured in a baby’s health status after birth.
The following five parameters are assessed in the Apgar scoring system (1).
- Appearance (skin color)
- Pulse (heart rate)
- Grimace (reflex)
- Activity (muscle tone)
- Respiration (breathing rate)
How Is The Test Performed?
A doctor, nurse, or midwife assesses the Apgar score of a baby based on physical examination at one minute and five minutes after birth (2).
Skin color and muscle tone are evaluated by observing the newborn. Heart rate is estimated using a stethoscope or feeling for pulse at the base of umbilical cord. Listening to an infant’s cry and respiration may help determine the newborns’ breathing rate and effort. Doctors may stimulate the baby with a mild pinch to observe a grimace response. Pinching causes a reflex in response to stimulation.
Based on the results of physical examination, each parameter’s score is given according to the Apgar scoring chart. Each of the five parameters is assessed on a scale of zero to two. Thus, the total score can be between zero and ten.
You may refer to the following table for parameters of Apgar scoring (3).
| Apgar score | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance
| Normal skin color all over the body | Hands and feet are blue; other parts of the body have a normal color | Blue or pale body-color |
| Pulse
| Normal, Above 100 beats per minute | Below 100 beats per minute | No pulse |
| Grimace | Pulls away, coughs, sneezes, or cries with stimulation | Stimulation causes only facial movement | No response on stimulation |
| Activity | Active and spontaneous movements | Less movement; arms and legs are flexed | Floppy tone or no movements |
| Respiration | A loud cry, normal breathing efforts | Weak cry, irregular or slow breathing | No breathing |
Some babies may be able to score the maximum in the initial evaluation. However, many babies may have low scores until they warm up. So, the score can be low in the first assessment and improve the next time.
What Does A Normal Apgar Score Mean?
Babies with good health will have scores of 7 or above. A newborn with a score of 7,8, or 9 is normal and may not require any immediate medical care. A score of 10 is infrequent since many babies may have bluish extremities soon after birth (4).
A score below seven does not mean that the baby is unhealthy. It indicates that your baby may need immediate medical care, such as oxygen or airway suctioning, to improve breathing. Healthy babies may also have low scores on the initial evaluation, and the score usually improves after a few minutes.
What Does An Abnormal Apgar Score Mean?
A slight reduction in Apgar score, especially one minute after birth, is typical. The following factors can be the reason for a lower Apgar score at the one-minute mark evaluation (5).
- High-risk pregnancies
- Cesarean delivery
- Labor and delivery complications
- Premature birth
- Fluid in the newborn’s airway
If the score is less than 7 at the five-minute mark, the Apgar score is measured every five minutes for the next 20 minutes (6). If the score continues to remain low, the baby may require medical care and close monitoring.
Babies with low scores usually improve after airway clearing and oxygen supplementation. Some babies may require artificial breaths or cardiopulmonary resuscitation to stimulate heart functioning.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does Apgar score determine a child’s intelligence?
Although the Apgar score determines the baby’s overall health, certain studies found a connection between the score and the child’s cognitive function. One study showed that a low Apgar score might increase the chances of lower IQ levels at 18 years of age. At the same time, another study showed that an Apgar score of less than seven might result in decreased cognitive functioning in the early adolescent years (7) (8).
2. Does the Apgar score predict the future health of a baby?
No, Apgar scores cannot predict your child’s future health conditions (9). However, it can help you identify the baby’s heart rate, breathing, and other reflexes.
3. Are Apgar scores reliable?
Although some experts believe that the Apgar scoring system may lack specificity and sensitivity, its reliability greatly depends upon the healthcare professionals in charge of the scoring and assessing (10).
4. Why is the Apgar test given twice?
Each of the two tests using the Apgar scoring system serves a different purpose. The first test at one minute monitors the baby’s tolerance of the birthing process, while the one at five minutes monitors the baby’s adaptability to the outside world (9).
The Apgar score assesses a baby on five parameters immediately after birth. The scores given for each parameter represent your baby’s health at birth. The test can’t predict a baby’s long-term health, behavior, or intelligence. Also, a slight dip in a baby’s Apgar score after birth is typical. However, if the score continues to remain low for up to 20 minutes after birth, the baby may need medical care. Most babies get better after targeted medical intervention and do not experience any long-term effects.
Key Pointers
- The Apgar score is used to evaluate the health status of newborns.
- The Apgar score of a baby is assessed based on physical examination at one minute and five minutes after birth.
- The normal Apgar score can be between zero and ten.
- High-risk pregnancies, cesarean deliveries and premature births are a few reasons for an abnormal Apgar score.
References
- What Is the Apgar Score?; Johns Hopkins Medicine
https://www.hopkinsallchildrens.org/Patients-Families/Health-Library/HealthDocNew/What-Is-the-Apgar-Score - Apgar Score;University of California San Francisco
https://www.ucsfhealth.org/medical-tests/003402 - The Apgar Score;American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2015/10/the-apgar-score - Apgar Scores; Healthychildren; American Academy of Pediatrics
https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/prenatal/delivery-beyond/Pages/Apgar-Scores.aspx - Apgar Score; MedlinePlus; The United States National Library of Medicine
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003402.htm - The Apgar Score;American Academy of Pediatrics
https://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/136/4/819 - D E Odd et al. (2007); A cohort study of low Apgar scores and cognitive outcomes; BMJ Journals
https://fn.bmj.com/content/93/2/F115 - Vera Ehrenstein et al. (2009); Association of Apgar score at five minutes with long-term neurologic disability and cognitive function in a prevalence study of Danish conscripts; BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
https://bmcpregnancychildbirth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2393-9-14 - Apgar score; Medline Plus
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003402.htm - Kristen S. Montgomery (2000); Apgar Scores: Examining the Long-term Significance; NCBI
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1595023/

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Anuradha Bansal













