How Parental Involvement Can Lead To Students’ Success
Positive parental involvement can be the key to a student’s academic achievements.
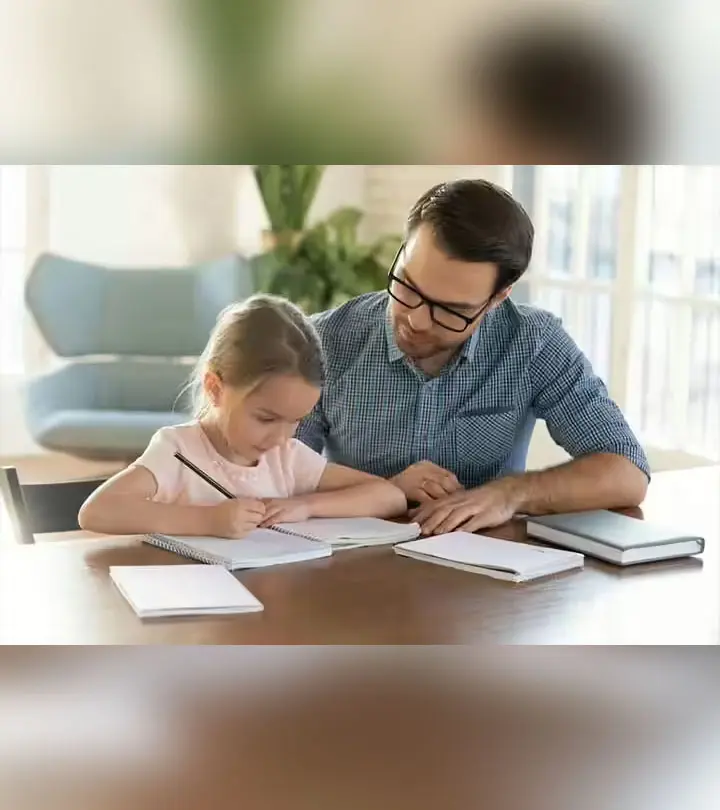

Image: Shutterstock
In This Article
The role of a parent in the growth and development of a child is vital. According to studies, parental engagement at home and school has an impact on child’s academic performance and their personality development (1), (2). Experts believe that parental involvement at home and school fuels the success of a student (3). Nevertheless, parents may often get confused about how to involve in their child’s affairs without breaching their freedom. They would want to know the boundaries and what they have to do, and what not to. In this post, we talk about parental involvement and engagement and how it can benefit the child in the long run. Scroll down.
What Is Parental Engagement?
Parental engament encompasses an extensive and complex range of parental involvement, including monitoring the child, discussing with children at home, communicating with the school or teachers, participating at the child’s school, and assisting with homework. It has three different aspects (4).
- Home-based involvement: It may entail parents’ involvement in different activities at home, such as checking their child’s homework, supervising their homework, or discussing life at school.
- School-based involvement: It may entail parents’ active involvement or participation in activities organized by the school, including attending parent–teacher meetings or events, participating in school activities (volunteering), or communicating with teachers regularly. Understanding how the child interacts with peers during school hours.
- Academic socialization: It may entail parents’ expectations and confidence in their child’s education.
Why Is Parental Involvement Important?
Parental involvement matters more than ever because of the increasing use of remote digital tools of communication.
Here we discuss why such involvement is important.
- Online portals keep parents up-to-date on grades, assignments, or progress without much hassle. No doubt, these platforms keep the parents informed, but children often miss when parents are not able to extend their support and time with their presence.
- Parental involvement leads to engagement and a collaborative partnership to support positive and healthy behaviors among children and adolescents. When parents and teachers work together, it has an overall positive impact on children.
- In addition, research has shown that students whose parents are more engaged tend to perform better at schools, attend school regularly, and have better social skills and self-esteem.
How Parental Involvement Affects Student Achievements
A meta-analysis across 50 studies showed that parental involvement was positively associated with students’ achievement (5).
- Researchers have found that parent engagement is strongly associated with an increase in daily attendance, a decrease in chronic absenteeism from school, or both (6).
- This engagement has also been shown to have a close link with higher grades at school and classroom test scores.
- Children with engaged parents are more likely to graduate from high school and opt for or pursue post-secondary education (7).
Apart from student achievement, parental engagement has shown other benefits too.
- Children whose parents are engaged are more likely to develop self-confidence, better self-esteem, and increased motivation. They are also less likely to have behavioral issues at school (7).
- Parental engagement at school has been identified as a potential factor in protecting adolescents from risky sexual and reproductive health behaviors, which include early sexual debut, frequency of sex, and pregnancy or birth (8), (9). The parent can find out if their child is getting bullied.
- Moreover, various studies have shown that when parents are engaged in their children’s school lives, and schools offered a supportive and caring environment, the students are less likely to be involved in violence, drug or substance abuse, and other problematic behaviors that are associated with risk of HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases (10).
How To Increase Parental Engagement?
When parents and teachers work collaboratively, it is a win-win situation for everyone, including children. Both parents and teachers should take initiatives to increase parental engagement.
As a parent, you can get involved in the following ways.
- Communicate regularly: Establish a line of communication with teachers to know about your child’s progress at school. If there are any special needs of your child, make sure to communicate with the educators.
- Attend orientation events / parent–teacher meetings / school events: Know your child’s educators or teachers at the beginning of the school year. Such orientation events are also useful in getting to know other families. Attending parent-teacher conferences also helps in tracking your child’s progress and resolving issues. Visit the school exhibitions, concerts, games, plays, or community events.
- Create a conducive environment at home: Involvement is not only school-based, but also home-based. Communicate your attitude and values towards education to your child, and set realistic goals for them to keep them motivated.
- Encourage reading habits (if possible, do it together): Inculcate the habit of reading in your child. You can do so by setting an example. You can also read books together or discuss with them after reading the book.
- Help them with their homework: Let them know that homework is a priority. Make sure to prepare a schedule for doing homework. Help them manage their assignments and stay organized. Monitor their work and appreciate their efforts.
- Volunteer at school or events: Extend your support and lend a hand at various volunteer events, including workshops, trips, or classroom activities. Put your skills to good use in various school-related activities when such opportunities arise.
- Encourage a healthy learning process: Encourage them to ask questions, follow their interests, and develop problem-solving skills. Initiate conversations at home about what new things they are learning at school. This will help them to actively participate in school activities of their interest.
- Try to learn more: Explore a new curriculum, workshops, or classes that are being offered at the school. You may not be alone as other parents might be equally interested in gaining more knowledge about school policies.
- Know your rights: Know your rights as a parent. For instance, learn more about the special services for immigrant families or minority groups, mode of instruction in any specific language, cultural awareness, or customized learning plans for individual needs.
Parental engagement at school is necessary for understanding the child’s overall development. However, over involvement can make the child feel that he/she lacks space. The child should not feel that their parents are always watching them.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the negative effects of parental involvement?
Too much or excessive parental involvement may have negative consequences on a child. A child’s ability to control their behavior and emotions may be hampered by overly parental involvement. Such children may also perform worse on tasks that assess executive functions and skills associated with impulse control and the skill to shift their attention between conflicting demands. Therefore, avoid becoming overly involved, especially when your children perform the assigned task properly (11).
2. What are the five barriers to parental involvement?
Lack of parent education, language differences, cultural or socioeconomic differences, parent attitudes toward the school, and school staff’s attitudes toward parents are some of the major barriers that may hinder parental involvement in their children’s education (12).
3. What is the difference between parental involvement and engagement?
Parental involvement is defined as participating or volunteering in school programs, communicating with teachers and your children about the school, and establishing rules at home that are regarded as education-related. Parental engagement, on the other hand, refers to active and meaningful involvement in children’s learning or the additional input that parents bring to the school or classroom, such as visiting the teacher and planning the child’s studies (13).
Parental engagement is essential for good education. Parents should encourage an environment conducive to learning at home. This further supports what is being taught at school. Be available and approachable to maintain open communication with your children and their teachers. Participation in parents’ activities in school is crucial in this respect. This involvement will ensure that your child remains confident and motivated in the future. Make sure your child feels free to discuss any untoward occurrences in school so that you can extend your help and support.
Key Pointers
- Parents’ involvement in their children’s academics, such as homework and PTA meetings, can help them feel motivated to perform better.
- Studies show such attention from parents can encourage children to become confident and better in all aspects of life.
- Try to stay updated about your child’s progress at school by communicating with their teachers. Help them learn new things at school, or take part in it yourself.
References
- Fan X. & Chen M. Parental involvement and students\’ academic achievement: A meta-analysis: Educational Psychology Review (2001).
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED430048.pdf - Trask-Tate A. J. & Cunningham M. Planning Ahead: The Relationship Among School Support Parental Involvement and Future Academic Expectations in African American Adolescents: The Journal of Negro Education (2010).
https://www.jstor.org/stable/20798332?seq=1 - Building Successful Partnerships: A Guide for Developing Parent and Family Involvement Programs: National PTA National Education Service (2000).
https://www.pta.org/docs/default-source/files/programs/national-standards-for-family-school-partnerships/the-power-of-partnerships.pdf - Duan W. Guan Y. & Bu H. The Effect of Parental Involvement and Socioeconomic Status on Junior School Students’ Academic Achievement and School Behavior in China: Frontiers in Psychology (2018).
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00952/full - Hill N. E. & Tyson D. F. Parental Involvement in Middle School: A Meta-analytic Assessment of the Strategies That Promote Achievement: Developmental Psychology (2009).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PmC2782391/ - Epstein J. L. & Sheldon S. B. Present and Accounted for: Improving Student Attendance Through Family and Community Involvement: The Journal of Educational Research (2002).
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Steven_Sheldon/publication/228712368_Present_and_Accounted_for_Improving_Student_Attendance_Through_Family_and_Community_Involvement/links/551d45480cf23e2801fe0dde/Present-and-Accounted-for-Improving-Student-Attendance-Through-Family-and-Community-Involvement.pdf - Parent Engagement: Partnering Together: Grand Rapid Public Schools
https://www.grps.org/parents/parental-engagement - Guilamo‐Ramos V. et al.; A Comparative Study of Interventions for Delaying the Initiation of Sexual Intercourse Among Latino and Black Youth: Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health (2011).
https://www.guttmacher.org/sites/default/files/article_files/4324711.pdf - Resnick M. D. et al.; Protecting Adolescents From Harm: Findings From the National Longitudinal Study on Adolescent Health: Jama (1997).
https://academiccommons.columbia.edu/doi/10.7916/d8-78f6-mt67/download - What is Parent Engagement: American Psychological Association
https://www.apa.org/pi/lgbt/programs/safe-supportive/parental-engagement/ - Stanford-led study highlights the importance of letting kids take the lead.
https://news.stanford.edu/2021/03/11/study-reveals-impact-much-parental-involvement/ - Parent Involvement in Children’s Education: Efforts by Public Elementary Schools.
https://nces.ed.gov/surveys/frss/publications/98032/index.asp?sectionid=7 - What is ‘Parental Involvement’ and ‘Parental Engagement’?
https://education.gov.scot/improvement/research/what-is-parental-involvement-and-parental-engagement/

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Shreshtha Dhar