PCOS And Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide To Conception
Unlocking fertility insights and support for a smoother journey to motherhood success.
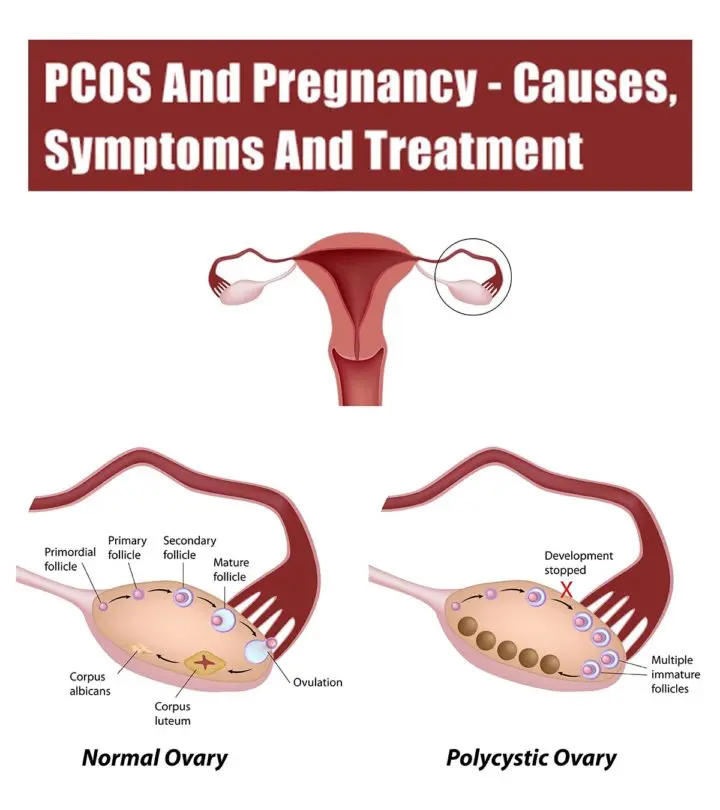
Image: Shutterstock
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a common problem among women in their childbearing years. It can also happen to girls as young as 11 years old. Almost 5 million women in United States are affected with polycystic ovaries. Research is still on to find the exact cause behind polycystic ovaries. PCOs can throw a spanner to your attempts to become pregnant. However, it is possible to become pregnant even if you have polycystic ovaries. Since, polycystic ovaries can be prevented by making lifestyle changes and can be treated with medicines. So there is a solution and hope for those who suffer from PCOS.
You must have a lot of questions buzzing around in your mind and may not find the answer you are looking for. The first question that comes to your mind is why polycystic ovaries actually happen.
Click here to view an enlarged version of this infographic.
Causes of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Some genetic factors are behind polycystic ovaries. If your mother had polycystic ovaries there are high chances that you will have polycystic ovaries also. The underlying factor behind polycystic ovaries is hormonal imbalance. Women with polycystic ovaries produce excessive amounts of androgens or human male hormones that interfere with the release of egg during the ovulation process.
Some researchers state that insulin is linked to polycystic ovarian syndrome. The Insulin hormone helps to convert the sugar and starches and other food into energy for the body to store. If the body can’t utilize the amount of insulin secreted or if there is over secretion of insulin then the female body starts to produce androgens. The high levels of androgens can trigger:
- Acne
- Facial hair growth
- Weight gain
- Ovulation disorders
However the exact reason behind polycystic ovaries are unknown and more study needs to throw some light in this area to make treatment possible.
What is PCOS?
Dr. Jesse Hade, medical director at Neway Fertility in New York City tells Fox News: “PCOS is an endocrine disorder where women don’t ovulate on a regular basis. It’s usually characterized by having multiple little follicles in the ovaries that appear on ultrasound, or having irregular periods, coupled with elevated male hormone levels, or elevated androgen levels.”
If you are overweight or obese, it could be harder for you to conceive. This is because being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing PCOS, or polycystic ovary syndrome. This is a condition that is associated with your reproductive system and makes it difficult for you to get pregnant.
While doctors are still unsure about the exact causes of PCOS, they do know that the condition develops due to high levels of insulin, which, in turn, causes your ovaries to produce more than normal amounts of androgens, which are male hormones.
How PCOS Affect Menstrual Cycle and Fertility
The ovary is comprised of tiny fluid filled sacs called follicles or cysts. As the eggs develop there is fluid buildup inside the follicles. Once the egg matures the follicle breaks open and the egg is released. The egg travels to the fallopian tube and then it reaches the uterus to get fertilized. This is the normal ovulation process.
In women with PCOS, the reproductive system does not produce hormones required for the egg to mature. The follicles start to grow and the fluid builds up but the ovulation does not happen. As a result some follicles remain in the ovaries as cysts. Since ovulation doesn’t occur the hormone progesterone is not produced and without progesterone the menstrual cycle becomes irregular or totally absent. Ovaries also make male hormones or androgens which disrupts the normal ovulation period.
Does PCOS Change During Menopause?
PCOS affect other systems in the body. Though there are hormonal changes and ovarian function changes as women near menopause but the symptoms persists. There are excessive hair growth in face, chest, back and abdomen. Thinning of hair and male pattern of baldness continues during menopause and sometimes become worse.
PCOS can also cause other health complications like diabetes, heart attacks and strokes.
What Increases The Risk of PCOS?
It is difficult to prevent PCOs if it is in your genes. You can’t help it if your family history is responsible for PCOs. In addition to this if you have diabetes, you are obese and have irregular menstrual cycle there is increased risk of PCOS.
Also having a seizure medicine called valproate such as Depakote can cause PCOS.
Complications Associated With PCOS
If polycystic ovaries are not treated in the right time then it can cause complications like:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure
- Cholesterol and Lipid Abnormalities. Increase in triglycerides and low high density lipoprotein or HDL cholesterol. This cause cardiovascular problem.
- Elevate d levels of C – reactive protein which is a cardiovascular disease marker.
- Metabolic Syndrome that also cause cardiovascular problems
- Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: This is an acute inflammation in the liver due to excess fat accumulation.
- Sleep Apnea
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
- Cancer of the lining of the uterus, it is called endometrial cancer. This is caused by the overexposure of high levels of estrogen.
- Gestational Diabetes or pregnancy induced high blood pressure
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Women with PCOs have a risk of developing ectopic pregnancy and other birth complications. Ectopic pregnancy happens when the embryo implants itself in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus. This can cause the fallopian tubes to burst and also cause miscarriage. Ectopic pregnancy is both dangerous for mother and child.
PCOS and Obesity
Those women who are affected with PCOs generally have diabetes too. This is because when the insulin secreted in the body can’t convert the sugar and starches into energy then there is an increase in the blood sugar levels, thus causing diabetes. PCOs create a domino effect.
Since high levels of androgens triggered by insulin cause abnormal hair growth, acne and weight gain. Since the weight gain is triggered by androgens the fat tends to accumulate in the abdomen. The abdomen fat is very dangerous as it increases the risk of heart disease. Also the increase of fat in abdomen changes the equilibrium and women who suffer from PCOs have a pear shaped body structure. Pear shaped structure means the fat gets accumulated in the waist and below the hips.
Actually PCOs can change the way you look, but take heart it can be cured. You need to make lifestyle changes like you need to become active and exercise more regularly. Also stop alcohol and smoking to curb weight.
PCOS and Pregnancy
A healthy woman’s body produces some amount of male hormones, but when the levels of these hormones rise, they interfere with normal reproductive functions, including menstruation and ovulation. As a result, it becomes difficult for the woman to get pregnant.
This said, there are chances of getting pregnant with polycystic ovaries provided there is regular menstruation and ovulation.
Symptoms and Signs of PCOS
There are several signs of PCOS and the symptoms can be mild or severe. Some of the signs are as follows:
- Irregular or absent periods
- Heavy bleeding from the vagina.
- Under normal circumstances, two weeks after you ovulate, the ovaries produce progesterone. Thereafter, progesterone levels fall and the uterus lining sheds, resulting in menstrual periods. If you do not ovulate, the uterus lining gets thick, a condition known as hyperplasia, and you can get extremely heavy and prolonged bleeding as a result.
- Oily skin / Acne
- Darkening / thickening of skin in certain areas, particularly in the folds of your groin, armpits and neck
- Excessive hair growth on the thighs, abdomen, chest and face
- Type 2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Thinning of hair on the crown of your head
- High cholesterol levels
- Cardiovascular problems
- Large number of cysts on your ovaries which will be visible during ultrasound
Diagnosis of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome:
How will you understand that you have polycystic ovaries? An accurate diagnosis of PCOS is essential, and earlier the better. Based on the diagnosis the treatment of polycystic ovaries takes place. If you are confirmed with PCOS don’t lose faith since there is a solution.
The methods to detect polycystic ovarian syndrome are:
- Medical History:
The doctor will ask you about the pattern of your menstrual cycle and whether you are facing any of the symptoms like excessive bleeding from the vagina, cramps in the lower abdomen, acne and hair fall or hair thinning. Observe the changes in your body carefully and give accurate answers to all your queries.
- Physical Exam:
Your doctor will measure your blood pressure, body mass index (BMI) and waist size. He will also check the areas of abnormal hair growth.
- Pelvic Exam:
The doctor will check whether your ovaries are swollen with small number of cysts. He will check the whether there is an increase in the number of cysts.
- Blood Test:
Through the blood tests the doctor will check the levels of androgen or male hormone and blood glucose levels.
- Vaginal Ultrasounds (Sonogram):
This test is done by using sound waves to capture images of the pelvic area. This pictures help to detect whether there are any cysts in your ovaries and whether the walls of your uterus have thickened. The walls of the uterus thickens when you don’t have regular menstrual cycle, this condition is called endometriosis.














