5 Effective Home Remedies To Treat Migraines In Pregnancy
Myriad factors can lead to migraines during pregnancy. Thankfully, it can be prevented.
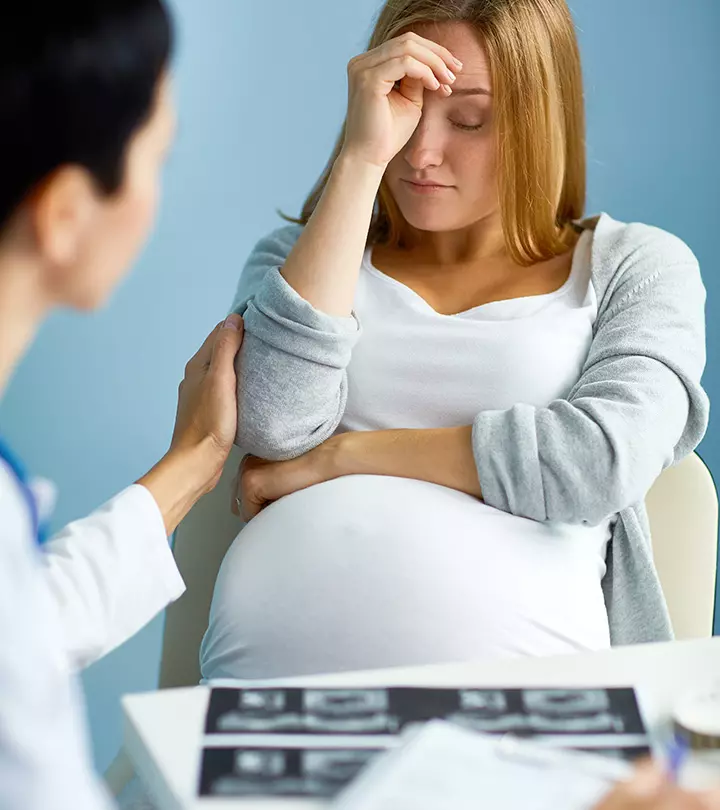

Image: iStock
In This Article
Migraine is the type of headache characterized by pounding pain on either side of the head and can sometimes worsen. Migraines in pregnancy are as common as in non-pregnant individuals. However, pregnant women may find it more difficult to deal with it because of several medication restrictions during pregnancy.
Therefore, understanding the warning signs of a growing migraine pain and knowing the right time to seek medical attention is important. In addition, migraine may also improve for some women during their pregnancy (1).
Read to know more about migraines during pregnancy, including their causes, symptoms, treatments and preventive measures.
How Frequent Are Migraines During Pregnancy?
The incidence and recurrence of migraine attacks in women vary widely. Some of them experience for the first time in pregnancy, while some women experience increasing migraine symptoms during the first trimester.
According to the American Migraine Foundation, around 50 to 80% of pregnant women experience reduced attacks (2). This reduction in symptoms is attributed to the increasing levels of estrogen during pregnancy.
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors Of Pregnancy Migraines?
Scientific findings state that naturally occurring inflammatory substances in the brain could cause severe migraines.The inflammation often hampers the blood vessels and nerves in the brain, causing exacerbating pain (3).
Some of the common triggers and risk factors of chronic migraines are as follows
- Irritation in the eye
- Change in the blood sugar levels
- Starvation
- Intake of coffee, chocolate, processed or fast food
- Consumption of food containing chemicals and food enhancers, such as tyramine and monosodium glutamate present in aged cheese and soy products or fast foods
- Sleep disturbances causing distorted sleep patterns or excessive sleepiness
- Stress and anxiety
- Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance
- Having a family medical history of migraines
- Skipping meals
- Menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause
- Exposure to bright light, loud noise, or strong smell
- Consumption of wine and alcohol
- Season and weather changes
What Are The Symptoms Of Pregnancy Migraines?
Based on the associated symptoms, migraines are classified into two types (4).
- Migraine with aura: People can experience sensory disturbances for up to an hour before the onset of a migraine, commonly known as aura experience. Such disturbances include tingling sensation, seeing sparks, bright spots, and difficulty speaking.
- Migraine without aura: People do not see an aura; however, they experience other migraine symptoms.
Some of the signs and symptoms of migraine headaches during pregnancy are (5):
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe throbbing pain in one side of the head
- Sensitivity to light, loud noise, or strong smell
It becomes essential to monitor the signs and symptoms of migraines during pregnancy. This information will be vital for a medical practitioner to understand the cause and give an effective management plan. One can note down the following details or mention them in their headache diaries.
- Time of onset of symptoms
- Were you at the home, workplace, or traveling when you experienced a migraine
- In which activity you were involved when the symptoms began
- What all eatables and drinks you have consumed throughout the day
- Time of recurrence of symptoms
When To Seek Medical Attention?
Migraines can have various signs of onset, and the diagnosis is based on some specific symptoms (2). It is imperative to identify these initial symptoms and seek immediate medical attention, if:
- Aura experienced for over an hour.
- Symptoms do not subside for a long time
- One-sided weakness
- Levels of anxiety and consciousness changes
- High blood pressure.
- First-time symptoms of migraine during pregnancy.
How To Treat Migraines During Pregnancy?
Despite the doctor’s advice on avoiding medications, over 50% of women consume pain medications in their first trimester, and two-thirds take them throughout the pregnancy (2). It is, therefore, crucial to understand the available safe treatments for migraines during pregnancy.
Home Remedies For Migraines
Here are some at-home quick remedies that can soothe the grueling pain (6) (7).
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Try to stick to a routine, eat well-balanced meals, get consistent sleep, and include gentle exercise.
- Hot and cold treatment: A soothing cold and hot treatment can ease the headache. Wrap a towel around a cold pack and place it on the head around the pain area. You can also apply a warm towel to the neck area to relax the muscles and ease the tension.
- Seatback and relax: Choose a quiet and dark place to sit back and relax to stay away from activities triggering a migraine.
- Get a massage: A good massage can help relieve anxiety, stress and soothe tension headaches.
- Consider biofeedback: A biohacker approach can help you understand the trigger for a headache. Fitness bands can be used to monitor changes in heartbeat and sleep patterns during the day. By recognizing your body signals, you can work on them to find relief.
Pain Medications For Migraines
Some of the safe migraine medications your doctor might suggest are as follows (8):
In the first trimester and beyond
- Paracetamol/Acetaminophen helps reduce pain
- Metoclopramide treats nausea and vomiting symptoms during pregnancy
- Triptans, such as Imitrex and Amergecan, can ease migraine headaches
After the second trimester:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help. However, these can cause severe complications such as preterm birth and birth defects if consumed in the first trimester.
Some of the medications you should avoid
- Aspirin: It can cause miscarriage and bleeding.
- Opioids: These can cause severe complications, such as stillbirth, premature deliveries, and congenital disabilities.
How To Prevent Migraines During Pregnancy?
The following measures could help you stay away from migraine headaches in pregnancy (9).
- Identify and avoid triggers that can lead to migraines and headaches.
- Follow a healthy routine of daily activities, including a gentle walk or breathing exercise, and stick to them. That way, the body and the mind get accustomed to the timings.
- Stay away from stress and anxiety by avoiding stressful activities and anxiety triggers.
- Have a nutritious and healthy diet, do not skip meals, and follow a routine.
- Get a good night’s sleep to help avoid stress and headache.
There is no scientiic evidence stating that a baby boy in the womb can trigger a migraine. However, there are many fun ways to know the gender of the child.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do migraines during pregnancy affect my baby?
Pregnant women are more prone to migraine headaches. It is due to changes in the estrogen hormone levels in the body (10) (11).
2. Do migraines get worse when pregnant?
Usually, migraines get worse during the first trimester. However, a reduction in the intensity and frequency of migraines is seen at a later stage of pregnancy (5).
3. Can migraines cause miscarriage?
Migraine has been associated with pregnancy-associated hypertension, which, if untreated, may increase the risk of miscarriages and other pregnancy complications such as low birth weight, preterm delivery, and requirement for C-section delivery (12).
Migraines during pregnancy can cause excruciating pain. Some women find it difficult to cope with it as certain medications are not good to take in pregnancy. However, there are few treatment options and medications available that can help a pregnant woman. It is essential to make a migraine management plan with the doctor by discussing individual migraine triggers.
Key Pointers
- Migraines are headaches that cause throbbing pain on the sides of the brain.
- The triggers of chronic migraines are changes in blood sugar level, stress, eye irritation, etc.
- Nausea, throbbing pain in one side of the head, and sensitivity to light are some migraine symptoms.
- You can manage migraine at home by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, relaxing, getting a massage, etc.
References
- Migraine in pregnancy.
https://migrainetrust.org/live-with-migraine/self-management/migraine-in-pregnancy/ - Migraine.
https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/migraine - Migraine And Pregnancy: What Moms-to-Be Need To Know.
https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/resource-library/migraine-pregnancy/ - Differences in treatment response between migraine with aura and migraine without aura: lessons from clinical practice and RCTs.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6734209/ - Headaches during pregnancy.
https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/headaches-during-pregnancy - Headache and migraine remedies that are safe during pregnancy.
https://utswmed.org/medblog/headache-migraine-pregnancy/ - Migraine in pregnancy: what are the safest treatment options?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9825951/ - Headache and pregnancy: a systematic review.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5648730/ - Headaches in pregnancy.
https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/pregnancy-symptom-checker/headaches-pregnancy - Migraine Headaches During Pregnancy.
https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/migraine-headaches-during-pregnancy - Migraine Headaches During Pregnancy.
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=90&contentid=p02476 - Adverse Pregnancy Risks Linked to Migraine in Women.
https://americanheadachesociety.org/news/adverse-pregnancy-risks-linked-to-migraine-in-women/

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Mona Hardas