Weight Gain During Pregnancy: What Is Normal & How To Achieve
Start eating healthy and keep track of your pregnancy weight right from the first month.

In This Article

Weight gain in pregnancy is normal. However, it should be closely monitored because excess weight gain can induce pregnancy-related complications, such as gestational diabetes and hypertension, fetal macrosomia, and increased risk of cesarean delivery (1) (2).
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for a smooth pregnancy and successful postpartum weight loss. Following a well-balanced diet and appropriate physical exercises in each trimester can help you reach your target weight.
Read on to know more about the importance of weight gain during pregnancy and how to reach your weight gain targets while adhering to the healthy weight gain recommendations for each trimester.
How Much Weight Should You Gain During Pregnancy?
The weight gain of an expectant mother depends on several factors, such as her body mass index (BMI) or pre-pregnancy weight and overall health. It means that women with less than normal pre-pregnancy weight need to gain more weight than overweight or obese women, making trimester-wise weight gain different from one expectant mother to another. Hence, it’s advisable to consult a gynecologist or healthcare provider to know how much weight gain you require for a healthy pregnancy.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shares some general guidelines for pregnancy weight gain when expecting a single baby and twins (1).
Maternal Weight Gain Recommendations For Pregnant Women
| Pre-pregnancy BMI | Weight Gain Recommendations For Women Pregnant With One Baby | Weight Gain Recommendations For Women Pregnant With Twins |
|---|---|---|
| Underweight (less than 18.5) | 28 to 40lb (about 13 to 18kg) | 50 to 60lb (about 22 to 27kg) |
| Normal (18.5 to 24.9) | 25 to 35lb (about 11 to 16kg) | 37 to 54lb (about 16 to 24kg) |
| Overweight (25 to 29.9) | 15 to 25lb (about 7 to 11kg) | 31 to 50lb (about 14 to 22kg) |
| Obese (Greater than or equal to 30) | 11 to 20lb (about 5 to 9kg) | 25 to 42lb (about 11 to 19kg) |
BMI = Body mass index – the estimate of body fat based on the height and weight of an individual
Source: US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
How Much Weight Should You Gain In Each Trimester?
Weight gain per trimester varies from one woman to another, just like weight gain in pregnancy. Here’s a brief overview of how much weight gain a pregnant woman with normal weight before pregnancy is expected to have every trimester (3):
First trimester
Most women don’t gain much weight during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. The average weight gain that an expecting woman can have during their first trimester is roughly one to 4.5 pounds (0.5 to two kilograms). It’s because of two prominent reasons. First, the fetus during this period is quite small and hardly contributes to your total weight gain. Second, several women experience appetite loss and gastrointestinal issues, such as morning sickness and vomiting, which might initially cause weight loss (4).
However, most women rapidly gain weight in the coming months, thanks to pregnancy cravings. But as you eat different foods and satiate your cravings, keep a close watch on your total weight gain and aim to keep it within the recommended limits. In contrast, if you aren’t gaining or losing weight, consult your healthcare provider to determine the likely cause.
Second trimester
Now you are into your second trimester, and hence the weight gain would be relatively higher than the first trimester as your morning sickness resolves. Again, however, it should be steady and gradual. Ideally, a pregnant woman with normal non-pregnancy weight and BMI should gain one to two pounds (0.5 to one kilogram)per week.
Third trimester
Generally, pregnant women gain relatively more weight in the final months than in the first few months (2). It happens due to the rapid growth of the fetus and the build-up and reservation of extra fluid (water) in the body over months. It’s why an expecting mother is expected to gain one to two pounds (0.5 to one kilogram) per week in the last trimester.
Do note that some expectant mothers may lose weight during the last trimester due to reduced appetite caused by the constriction of abdominal muscles, making eating difficult. This weight loss is mostly normal and doesn’t pose a risk to you or your unborn baby. Nevertheless, if you have doubts, consult your doctor.
What Happens When You Gain Too Much Weight?
Carrying excess maternal weight during pregnancy exposes you to several mild or moderate to severe health risks, such as (5):
- Persistent backaches
- Heartburn
- Breathlessness on mild exertion
- Increased blood pressure (hypertension)
- Gestational diabetes
- Prolonged labor
- Increased risk of cesarean section
- Heavy bleeding after birth
- Postpartum weight retention
Excess maternal weight raises concerns for unborn babies, too. It exposes them to the risk of being born larger than average (fetal macrosomia) and birth complications, such as preterm birth or shoulder dystocia (6). Shoulder dystocia is a shoulder injury that a baby incurs when they get stuck in the mother’s pelvic area during labor (7). Many mothers may require a C-section due to the risk of complications caused by excess maternal weight gain during pregnancy.
Where Does The Extra Weight Go?
A pregnant woman should gain approximately 25 and 35 pounds (11.5 to 16 kilograms) during pregnancy (8). In this, the baby’s weight contributes about seven to eight kilograms. Wondering where the extra weight goes? Here’s a sample breakdown.
| Body area | Weight gain during pregnancy |
|---|---|
| Breast enlargement to support feeding after childbirth | 2 to 3 pounds (1 to 1.5 kilograms) |
| Uterus expansion to accommodate the growing fetus | 2 to 5 pounds (1 to 2.5 kilograms) |
| Placenta | 2 to 3 pounds (1 to 1.5 kilograms) |
| Amniotic fluid | 2 to 3 pounds (1 to 1.5 kilograms) |
| Increase in blood volume | 4 pounds (2 kilograms) |
| Fat reserves or fat stores to facilitate childbirth | 5 to 9 pounds (2.5 to 4 kilograms) |
Source: American Pregnancy Association
A healthy weight gain comprises balanced weight gain across these body areas. It helps the pregnancy progress to culminate smoothly, maintaining your and your baby’s overall health.
How To Achieve Healthy Weight Gain During Pregnancy?
Gaining and maintaining optimum weight in pregnancy isn’t difficult, provided you know the basics and follow the expert’s guidance. For instance, since your weight requirements rely on your pre-pregnancy weight and BMI, the first step is to know your weight gain requirement and adjust it according to factors, such as your and your baby’s overall health (1) (8).
1. Know your weight target
It’s crucial as your additional calorie requirement depends on the weight gain recommended for you. For instance, if you are underweight, you need to eat more calories to gain weight, as not gaining sufficient weight during pregnancy could cause the baby to be born smaller than expected or be born preterm.
Speak to your doctor. They will monitor your overall health, calculate your BMI, and give you a trimester-wise target weight to attain and maintain. After that, the next step is to consult a qualified nutritionist and chart out a calorie-specific, well-balanced pregnancy diet plan.
2. Plan your calorie intake
According to the American Academy of Dietetics, women with healthy pre-pregnancy weight require around 2,200 to 2,900 calories a day (9). Based on your trimester-wise target weight, you will know how many extra calories you need to consume every day, depending on the trimester. Here’s how you need to raise your calorie intake trimester-wise.
- During the first trimester, you need not increase your calorie intake.
- From the second trimester, however, you need to consume an additional 340 calories per day.
- Then, from the third trimester, you need to consume an additional 450 calories or more per day than when you were non-pregnant.
If you were overweight or obese before pregnancy or gained weight too quickly during pregnancy, trying for weight loss isn’t advisable. Instead, you should eat a well-balanced diet and try keeping your weight in the recommended range.
3. Eat a well-balanced diet
A well-balanced diet contains moderate amounts of healthy foods from different food groups, such as whole grains, low-fat dairy, lean meat, fruits, and vegetables. However, the nutritional needs may vary as per one’s overall health and existing medical conditions, if any. Thus, it’s vital to consult a nutritionist and have a personalized diet plan. The diet plan will represent:
- How your meals should look
- What foods you should include with their portion sizes
- Foods to avoid
4. Split the meals throughout the day
A pregnant woman should eat five to six meals a day, comprising three main meals and two to three snacks. The main meals should have healthy foods, such as vegetable spaghetti with sauce or tuna sandwiches with fresh coconut water. Snacks should include healthy, on-the-go items, such as a handful of lotus seeds, dried fruits and unsalted nuts, seeds trail mix, unsweetened, low-fat yogurt, and smoothies/shakes.
5. Avoid eating extra calories than recommended
It’s pertinent as several pregnant women are advised to eat for two. Here, eating for two should be in terms of quality, not quantity. Thus, maintain your calorie intake within the recommended limit and focus on eating healthy foods. Some of the choices to make are fruits, veggies, unsalted nuts, seeds, low-fat dairy, lean meat, pulses, fatty fish, and high-fiber carbohydrates such as whole grains and millets. Eating nutrient-rich, quality food will give you sustained energy and help the baby’s growth and development in the womb.
6. Avoid excess salt and sugar
Consuming too much sugar from foods, such as cookies, chocolates/candies, syrups, and honey can cause unwanted weight gain. Hence, you must limit or avoid eating these foods during pregnancy. Likewise, you should limit or avoid eating high-sodium, high-fat processed items, such as donuts, cakes, pastries, and chips daily. These foods contain too much fat and salt that can cause excess weight gain and water retention, leading to complications, such as high blood pressure and preeclampsia. Therefore, opt for healthier alternatives, such as fresh or dried fruits and unsweetened low-fat yogurt.
7. Make healthy dietary choices
For instance, use fats in moderation and avoid consuming high-fat foods, such as margarine, butter, lard, mayonnaise, sour cream, red meat, whole milk, and cream cheese. Instead, consume healthy fats, such as PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acids) through nuts, seeds, and oily fish. Besides these, use less oil for cooking and prepare food using healthy cooking methods, such as sautéing, broiling, boiling, and grilling. Also, eat fresh, home-cooked meals as much as possible and have healthy snacks whenever you feel hungry between meals or have cravings.
8. Drink more water
It will help you stay hydrated and curb your craving for sweetened beverages, such as soda, coffee, energy drinks, and fruit juices. These drinks are best avoided during pregnancy because they contain high amounts of sugar. Besides, some of them, such as coffee and energy drinks, contain caffeine that may adversely affect you and your baby upon excess consumption.
9. Do exercise regularly
According to the CDC, a pregnant woman should do “at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking per week”(1). You can divide this target of 150 minutes into smaller targets like 20 minutes, every day or 30 minutes, five days a week. Your doctor or the expert will tell you what plan and type of exercises will be appropriate for you, post evaluating your overall health.
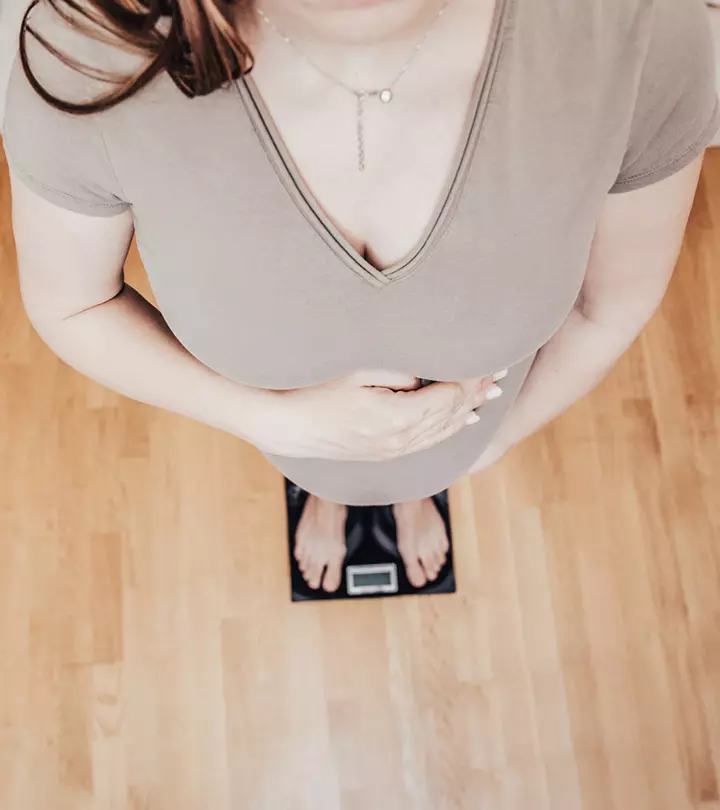
10. Keep an eye on your weight
It’s essential to know if your weight gain is as per the recommendation. Keeping gestational weight gain within recommended limits is vital for averting health complications that you and your baby may develop due to excess maternal weight gain. So, ensure you weigh yourself periodically, say every week, at:
- The same time of the day
- On the same weight scale
- Wearing the same amount of clothes
If you want, you can maintain a weight diary to record your weight changes. Then, you can share the weight record with your healthcare provider and help them know if your weight gain is on track.
Most women achieve and maintain a healthy weight during pregnancy by eating healthy and staying active. But, if you gain too much weight, suddenly, even after following the proper dietary guidelines, talk to your doctor. In some cases, excess maternal weight gain can be caused by medical conditions, such as preeclampsia.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What percentage of women have pregnancy weight gain within recommendations?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, a study has indicated that around 32% (one-third) of women gain the recommended weight during pregnancy. All others gain either more or less weight than the recommended one (1).
2. Why is it essential to gain weight during pregnancy?
Healthy weight gain when expecting is essential to protect you and your baby from health risks. Too little weight gain may lead to babies with low birthweight, whereas too much weight gain may lead to overweight babies (5).
Weight gain is common during pregnancy, but it can be managed with a well-balanced diet and regular exercise. Pregnant women who weigh normal before pregnancy may gain a few pounds in order to have a good pregnancy. Due to higher calorie demands, these extra pounds are usually lost following delivery and breastfeeding. Being overweight can be associated with many pregnancy complications and cause persistent backache, heartburn, and gestational diabetes. You may seek doctors’ advice and plan a diet to keep the weight under control.
Key Pointers
- Weight increase in pregnancy differs for every woman, based on factors like BMI or pre-pregnancy weight and overall health.
- Women gain one to 4.5 pounds (0.5 to two kg) on average during their first trimester.
- A pregnant woman with an average pre-pregnancy weight and BMI could gain one to two pounds (0.5 to one kg) every week throughout the second and third trimesters.
- To maintain a healthy weight during pregnancy, you must first determine your target weight and then plan your calorie intake and diet accordingly.
References
- Weight Gain During Pregnancy.
https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternalinfanthealth/pregnancy-weight-gain.htm#important - Pregnancy and birth: Weight gain in pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279575/ - Weight gain during pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-health-wellness/pregnancy-weight-gain/ - Healthy weight gain during pregnancy.
https://www.health.govt.nz/your-health/healthy-living/food-activity-and-sleep/healthy-weight/healthy-weight-gain-during-pregnancy - Weight gain during pregnancy.
https://www.marchofdimes.org/pregnancy/weight-gain-during-pregnancy.aspx - Managing your weight gain during pregnancy.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000603.htm - Excess Weight and Weight Gain During Pregnancy.
https://www.lifespan.org/centers-services/multidisciplinary-obstetric-medicine-service-moms/pregnancy-weight-gain - Shoulder Dystocia.
https://www.marchofdimes.org/complications/shoulder-dystocia.aspx - Healthy Weight during Pregnancy.
https://www.eatright.org/health/pregnancy/prenatal-wellness/healthy-weight-during-pregnancy

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Ng Kai Lyn