How Much Protein Do Children Need: 5 Daily Intake Guidelines
The amount of protein needed daily by the child will vary as per their age.

Image: iStock
Protein is a vital macronutrient the body needs to grow and develop healthy bones, muscles, and immunity. Most healthy children can get sufficient protein from a well-balanced diet. However, if your child is a picky eater, participates in intense athletic activities, or has a medical condition that hampers protein digestion/absorption, you may consider supplementing protein under medical guidance.
Keep reading as we tell you how much protein children need and what healthy foods can help meet the needs of protein for kids.
Why Do Children Need Protein?
Proteins are made of amino acids, which are of two types, essential and non-essential. Essential amino acids are those your body can’t produce, and you need to attain them from food. Non-essential amino acids are those your body can produce, irrespective of whether you eat them or not (1).
There are a total of about 21 amino acids (9 essential and 12 non-essential) that link together in different combinations to form proteins that a child’s body utilizes to perform several physiological functions (2) (3) (4).
- Fight wear and tear of cells and tissues by repairing old cells and generating new cells to maintain growth, development, and sustenance.
- Support the regulation and expression of DNA and RNA that are responsible for all body functions.
- Build muscles and provide muscle contractility that gives strength to the body to perform day-to-day activities.
- Produce enzymes that act as catalysts to several biochemical reactions, such as digestion, in the body.
- Attach to molecules and facilitate their transportation, like globin protein joins with heme (iron) molecules and helps oxygen transportation from lungs to the entire body.
- Make hormones that the body requires to regulate different functions, such as physical growth (growth hormone) and sexual maturity.
- Manufacture antibodies that the body needs to fight microbes, such as viruses and bacteria, protecting against different infections and strengthening the immune system.
Besides these, eating protein as a part of a well-balanced diet helps keep your child’s tummy full for longer as it is digested much slower than carbohydrates. Thus, it may even help regulate hunger and keep sugar spikes under control.
How Much Protein Do Children Need Per Day?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2025-2025, advises the following when it comes to protein and daily calories.
- Ages 2 to 3 years:5-20% of total daily calories from protein
- Ages 4 to 13 years:10-30% of total daily calories from protein
Children should consume the following amounts of protein daily to receive the aforementioned total daily calories from protein (5) (6).
| Age (years) | Protein (g/day) | Food equivalent (oz) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 to 3 | 13 | 2 |
| 4 to 8 | 19 | 4 |
| 9 to 13 | 34 | 5 |
| Adolescent females (14 to 18) | 46 | 5 |
| Adolescent males (14 to 18) | 52 | 6.5 |
Source: Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2025-2025Note:
One-ounce equivalents of protein foods could be one ounce of cooked meat, poultry, or fish, one-fourth cup of cooked beans, one egg, one tablespoon of peanut butter, or one-half ounce of nuts or seeds.
What Are The Good Sources Of High-Quality Protein?
High-quality protein, also termed complete protein, has all the essential amino acids. Here are some foods that can provide high-quality protein to children (7).
- Fish: Fish, such as tuna and salmon, are high-quality protein sources rich in several other nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12, vitamin D, selenium, iodine, and zinc. These nutrients contribute to a child’s growth and development. Therefore, experts recommend children consume two servings of low-mercury fish a week (8).
- Lean meat and poultry: Lean meat, such as skinless chicken, mutton, turkey, and beef, are great high-quality protein sources low in saturated fat.
- Low-fat dairy: Low-fat milk and its products, such as cheese and yogurt, are low in saturated fat and contain vital nutrients, such as vitamin D, calcium, phosphorus, vitamin A, vitamin B12, and zinc. Experts recommend children above two years of age consume two to three servings of low-fat (1%) or non-fat (skim) milk daily.
- Beans, peas, and lentils: Beans, peas, and lentils are great sources of plant-based high-quality protein that can offer various micronutrients and dietary fiber to vegetarian and vegan children. Experts advise children consume two to three servings of these foods each day to reap their benefits to the fullest.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, cashew, pecans, walnuts, chia seeds, sesame seeds, and flax seeds are some of the common nuts and seeds children can consume daily as a part of a well-balanced diet. Nuts and seeds are an excellent source of healthy fats, vitamin E, and fiber that children can enjoy munching as quick snacks.
- Eggs are an important source of proteins and can be served boiled or fried to children.
- Soy and its products: Soy and its derivatives are a great alternative to animal-based protein sources. They also provide essential nutrients, such as vitamin B, iron, and zinc. Vegan and vegetarian children can consume soybean and its products, such as tofu, tempeh, enriched soy milk, and miso, regularly.
List Of Protein-Rich Foods For Children
Here’s a list of protein-rich plant- and animal-based foods you can offer your child (9).
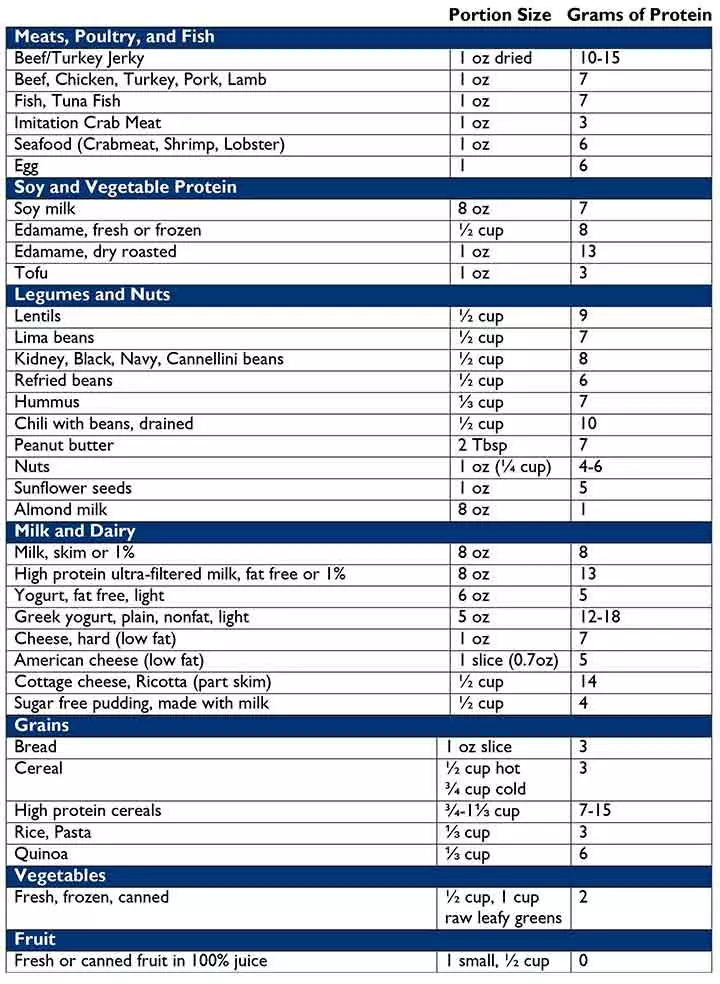
Note: The serving size of a food is the standard amount of food that is served. It doesn’t indicate the amount of food a child needs to eat. You must feed various protein-rich foods to your child as part of a balanced diet.
Do Children Need Protein Supplements?
Most healthy children can get sufficient protein from a well-balanced diet. If you feel your child is getting insufficient protein, consult a pediatrician. Your healthcare professional may assess if your child can benefit from extra protein and prescribe a protein supplement appropriate for your child’s age and overall health. Avoid giving your child protein supplements, such as protein shakes, unless prescribed by the doctor since natural foods are better sources of proteins.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What happens if my child does not get enough protein?
Inadequate protein intake can result in various health problems in children, including fatigue, hunger, muscle loss, growth stunting, and so on. However, severe protein deficiency can result in serious conditions known as Kwashiorkor and Marasmus syndromes (10) (11).
2. How much protein intake is too much protein for my child?
According to the current recommended dietary allowance (RDA), intake of more than 1.5 g protein/kg body weight/day for children and more than 1.0 g protein/kg body weight/day for adolescents is considered high protein diets (12).
3. What happens if my child consumes too much protein?
Protein overconsumption can cause intestinal discomfort, hyperaminoacidemia, hyperinsulinemia, dehydration, annoyance, nausea, diarrhea, tiredness, headache, and an increased risk of heart disease in children (10).
4. At what age can my child consume protein shakes?
Protein shakes or supplements are recommended for children aged 18 and over, especially if they participate in extreme sports, workouts, or physical activity (13).
A well-balanced diet that includes items from all food groups is enough to get the recommended dosage of protein. Additional protein supplements may be recommended for children with health issues that may interfere with protein absorption or for those who need additional protein to supplement their extra needs, such as athletes. Vegetarians and vegan children may need to focus more on their protein intake since vegetarian food is not as rich in protein as fish and meat. So, consult a nutritionist or a pediatrician to design a balanced meal chart for your child.
Key Pointers
- Children aged two to four years should consume 5-20% proteins in their diet and about 10-30% for those aged four to 13 years.
- Low-fat dairy, lean meat and poultry, nuts, seeds, and fish are some high-quality protein sources.
- Most kids get a recommended amount of protein from a healthy diet, and protein supplements should be given on the pediatrician’s recommendation.
References
- Amino acids.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002222.htm - How much protein does my child need?
https://health.choc.org/how-much-protein-does-my-child-need/ - What Are Proteins and What Is Their Function in the Body?
https://www.eufic.org/en/whats-in-food/article/what-are-proteins-and-what-is-their-function-in-the-body - Protein.
https://und.edu/student-life/dining/_files/docs/fact-sheets/protein.pdf - Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2025-2025.
https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2025-12/Dietary_Guidelines_for_Americans_2020-2025.pdf - Beyond Chicken Nuggets: Protein-Rich Alternatives for Picky Eaters.
https://www.healthychildren.org/English/healthy-living/nutrition/Pages/Beyond-Chicken-Nuggets.aspx - Jay R. Hoffman and Michael J. Falvo; (2004); Protein – Which is Best?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3905294/ - Advice About Eating Fish.
https://www.fda.gov/media/102331/download - Protein Content Of Common Foods.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/bariatrics/_documents/nutrition_protein_content_common_foods.pdf - Guoyao Wu; (2016); Dietary protein intake and human health.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2016/fo/c5fo01530h - 6.6: Diseases Involving Proteins.
https://med.libretexts.org/Under_Construction/Purgatory/Book%3A_Human_Nutrition_(University_of_Hawaii)_1st_Ed/06%3A_Protein/6.06%3A_Diseases_Involving_Proteins - Ioannis Delimaris; (2013); Adverse Effects Associated with Protein Intake above the Recommended Dietary Allowance for Adults.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4045293/ - Sports Supplements.
https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/sports-supplements.html
Kids’ Protein Needs & Top Food Sources
Watch now to learn how much protein kids need daily, discover top high-quality sources, and understand when supplements matter. Get practical tips to boost your child’s growth today!