What Causes Tooth Decay In Children, Treatment & Prevention
Many factors can cause tooth decay, and treatment depends on the severity of the issue.
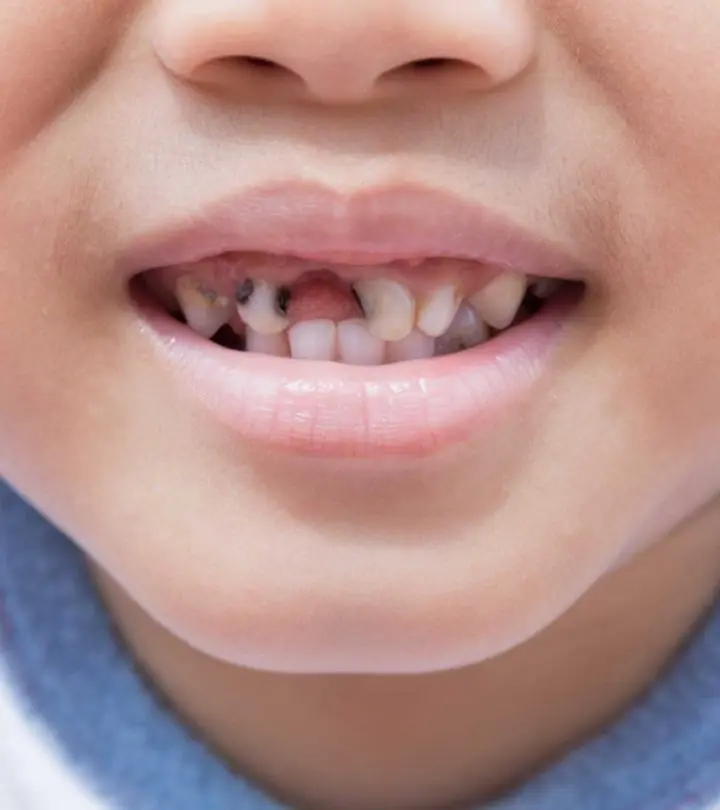
Image: Shutterstock
In This Article
Tooth decay in children is a frequent problem that affects those up to 19 years old. Tooth decay, often known as cavities or caries, results from the acid created by decay-causing oral bacteria damaging the tooth. If left untreated, it can also result in discomfort, foul breath, and tooth loss.
Teeth are necessary because they enhance our smiles and serve a crucial function in the digestive process. Additionally, teeth impact our speech and can influence how it develops in children.
Continue reading to learn about the causes of tooth decay, its symptoms, and ways to clean or encourage your child to clean their teeth properly to keep them healthy.
How Does Tooth Decay Happen?
The development of tooth decay is a gradual process, and below are its salient features (1).
- Unclean teeth and sticky food provide an environment suitable for the bacteria to multiply.
- These bacteria form colonies and release acid on the tooth surface.
- The acids attack the tooth surface leading to loss of minerals from the tooth enamel (outermost layer).
- This is followed by the appearance of white spots just below the enamel surface.
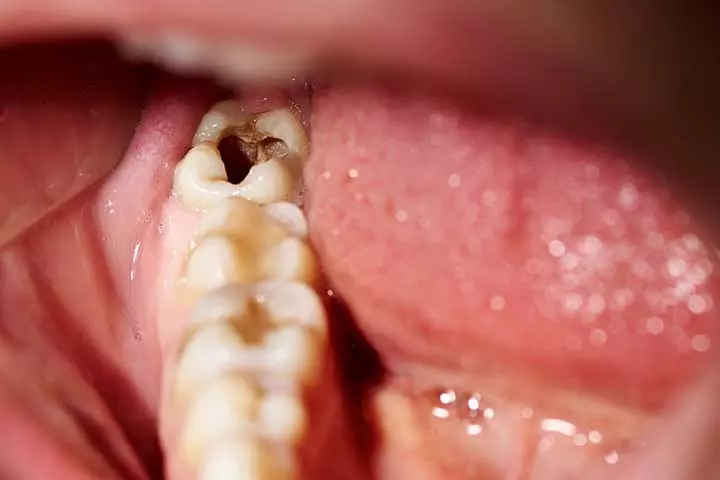
- As the enamel is further damaged, small holes or lines are developed called cavities or dental caries
- Eventually, the cracks begin to show brown to black discoloration, which indicates decay.
- When the cracks are in the enamel (outermost layer), there is no pain. However, when the bacteria reach the dentin (inner layer next to enamel), they cause teeth sensitivity. If bacteria reach the pulp (innermost part of the tooth with blood and nerve supply), it can lead to severe pain, swelling, and even bleeding.
Is Tooth Decay A Common Problem?
According to the CDC, dental caries is a common chronic disease among children between the ages of six and 19 years (2). Tooth decay is the second most common disorder among children after the common cold (3).
Signs And Symptoms Of Tooth Decay In Children
Here are some signs and symptoms of tooth decay in children (4).
- Black spots and lines over the teeth
- Bad breath or a foul smell from the mouth
- Food lodgment between two teeth
- Visible holes in the teeth
- Toothache
- Swelling near the teeth
- Tooth sensitivity, especially when eating cold and hot food
- Pain while chewing food
Causes Of Tooth Decay
There are many causes that can lead to bacterial growth and tooth decay (5).
General causes
- Poor brushing leads to unhygienic oral conditions.
- Eating sticky foods, such as chocolates, could increase the risk of dental caries. Such foods cling to the teeth and provide favorable conditions for bacterial growth.
- Eating acid-rich foods, such as processed foods and soda.
- Harsh brushing could cause abrasion lines on the teeth, which are conducive to food adhesion.
- Unhealthy gums and plaque on the teeth can cause bacteria to grow, causing acid to attack the tooth structure.
- Misaligned teeth could lodge more food particles, increasing the risk of bacterial propagation.
- Dry mouth also helps bacteria to accumulate, leading to tooth decay. Dry mouth could occur due to poor fluid intake, medications, and some medical conditions.
- Bruxism is a condition where teeth are eroded by excessive grinding action. Erosion promotes the formation of holes, which provide spaces for bacteria.
Early childhood caries
- Incorrect bottle-feeding and breastfeeding can cause the teeth to have prolonged exposure to milk, increasing the risk of dental caries.
- Babies who sleep with bottles can have milk pool in their mouths for a long time, thus increasing the risk of bacterial growth.
- Falling asleep with a pacifier with a sweetened nipple (6).
- Not paying attention to oral hygiene and brushing early in childhood (7).
Complications Of Tooth Decay
The following are the complications of untreated tooth decay (8).
- Severe pain that interferes with chewing
- Pus formation, abscess, and swelling
- Tooth loss
- Incorrect teeth alignment due to premature loss of decayed teeth
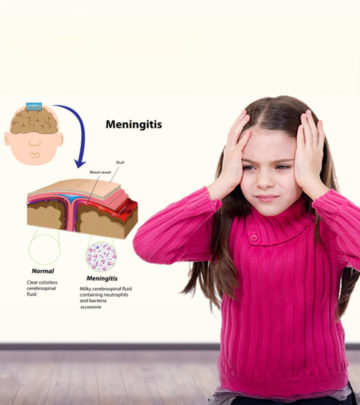
- Infection and pus may flow into different parts of the mandible leading to masticatory space infection
- Masticator space infections may spread to the brain and cause meningitis (9)
- Cellulitis where the skin and other tissues inside the mouth become infected
- Infected dental cysts (10)
Diagnosis Of Tooth Decay
A dentist diagnoses tooth decay through the following methods (11).
- An X-ray of the teeth can determine the extent of dental caries.
- Percussion of the tooth. The dentist taps the teeth to identify the infected tooth and the degree of tooth damage.
- Using blue light for identifying caries. Blue light helps diagnose the developing cracks in teeth.
- Probing the tooth to determine the extent of caries and the firmness of its roots.
- Intraoral cameras help determine the extent of tooth decay.
- The white light fluorescence technique helps identify decay by illuminating the tooth. Decayed parts often appear darker than the rest of the tooth.
- CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) is used to capture 3D images of teeth and surrounding tissues
- A laser-based endoscope could be inserted into the mouth to detect the presence of tooth decay.
Treatments For Tooth Decay
The treatment depends on the extent of tooth decay and complications. The following are the various treatment options that could be considered for tooth decay in children.
- Caries removal and tooth fillings. The decayed part of the tooth is removed and replaced by materials such as silver amalgam and composite resins.
- Root canal treatment. It is commonly performed in cases where the decay involves the pulp of the tooth or leads to an infection.
- Pain and Infection. Pain-killers and, in some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed by the dentist.
- Abscess drainage. It can be performed when there is excessive pus formation, which cannot be cured with antibiotics alone.
- Teeth scaling (cleaning) and polishing. Scaling is usually done with an ultrasonic scaler, but for highly sensitive teeth, hand scaling is required. Polishing helps to smoothen the tooth surface so that food particles do not stick to it.
- Removal of cysts. Cysts require surgical removal and are usually followed by root canal treatment.
- Removal of broken root pieces of the tooth. It is important to remove these roots as they will continue to decay and result in pus formation.
- Extraction of severely damaged teeth. It is done to remove the source of infection and prevent further spread of the infection.
- Crown placement over the tooth. A root canal treated tooth needs protection while performing its functions. It is achieved by placing a crown or tooth cap on top of the affected tooth.
- Tooth replacement to compensate for tooth loss due to decay If a tooth is removed due to decay, it is replaced with a prosthesis like a bridge, implant or a denture to maintain optimal chewing function.
- Orthodontic treatments. It can align the teeth to reduce the chances of dental caries.
- Fluoride treatments. The most common clinical application is fluoride gel and fluoride toothpaste (1). Adding fluoride to drinking water is a way to consume fluoride.
Prevention Of Tooth Decay
There are many ways to maintain healthy teeth and gums (2).
- Brush your teeth regularly twice a day.
- Gargle with water after every meal.
- Clean between the teeth using dental floss.
- Avoid eating sticky, sugar-rich, and acid-rich foods (such as chocolates, biscuits, chips, and cold drinks).
- Replace toothbrush every three months.
- Use a soft bristle brush if your tooth enamel is prone to erosion.
- Do not apply excessive pressure on the teeth when brushing.
- Use fluoridated toothpaste. If a person lives in an area rich in fluoride in drinking water, the percentage of fluoride consumed by other methods should be monitored (1).
- Visit the dentist for regular check-ups. This can be done every six months to diagnose new caries formation.
- Choose sugar-free medications and mouthwash.
- Treat conditions such as misaligned teeth in a timely way.
- Dental pit and fissure sealants can be applied by the dentist in children who are prone to caries.
- Dental pit and fissure sealants. It can be used in children who are prone to caries.
Brushing Technique To Teach Kids
The following brushing techniques can help maintain optimal oral hygiene and prevent tooth decay in children.
- Hold the brush at a 45° angle to the teeth.
- Brush three teeth at a time.
- Use pea-sized toothpaste.
- The brushing action should be round. The poem “spin up and down” can be used to teach the correct brushing action.
- Drink water after eating and gargle after each meal.
- Help children brush their teeth until they are six years old
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can tooth decay be reversed?
When dental caries is in the enamel layer, fluoride treatment, and good oral hygiene can reverse dental caries to a certain extent. Once the enamel layer is destroyed due to caries, it cannot be reversed (1).
2. Do milk teeth (primary/deciduous/baby teeth) decay need treatment?
Yes, it is important to treat baby teeth. Milk teeth need treatment because dental caries can cause pain, irritation, discomfort, and fever in young children. If the milk teeth are left untreated, they can cause caries in the permanent teeth that form below them, leading to permanently damaged teeth (12).
3. Does milk cause tooth decay?
If fed inappropriately, such as given in a bottle while sleeping at night, milk might cause tooth decay and cavities (13). Hence, parents must be aware of good feeding practices to maintain their child’s dental health.
Tooth decay in children is the breakdown or destruction of tooth enamel caused by bacteria. It is common among children between six and 19 years of age. Poor hygiene and accumulation of bacteria on tooth surfaces lead to discoloration and tooth decay. It might lead to tooth loss, incorrect teeth alignment, and infected dental cysts. Tooth decay can be treated with dental polishing, root canal, crown placement, or tooth replacement, but it cannot be reversed once the enamel layer is destroyed due to caries. However, all these teeth issues can be prevented by following proper brushing techniques and hygiene.
Key Pointers
- Poor hygiene and accumulation of bacteria on tooth surfaces lead to discoloration and tooth decay in children.
- Bad breath, black spots or lines on teeth, food lodgment between teeth, and toothache are common signs of tooth decay in children.
- Tooth decay can be treated with dental polishing, root canal, crown placement, or tooth replacement.
References
2. Hygiene-related Diseases; CDC
3. Tooth Decay (Caries or Cavities) in Children; Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
4. Tooth Decay; NIH
5. Tooth Decay; U.S. National Library of Medicine
6. Preventing early childhood dental decay; Government of Western Australia
7. Tooth Decay in Children; University of Rochester
8. Hidden dental dangers that may threaten your whole body; Harvard Medical School
9. Paolo Cariati et al., Meningitis and subdural empyema as complication of pterygomandibular space abscess upon tooth extraction; NCBI
10. Everything you need to know about dental cysts; City Dental Clinic
11. Adepu Srilatha et al., Advanced diagnostic aids in dental caries; Journal of Global Oral Health
12. Does Tooth Decay in Baby Teeth Affect Permanent Teeth?; DentalCube
13. Can milk cause cavities?; Nationwide Children’s

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Tazeen Raees