Hernia In Children: Symptoms, Causes, Dignosis And Treatment
The condition causes several prominent symptoms in children, and timely treatment improves outcomes.
Image: Shutterstock
In This Article
Hernia in children can be treated with timely medical intervention. A hernia is a projection of an integral part of an organ, such as an intestine, through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles (1). While inside the womb, the fetuses have an opening called the inguinal canal that closes a few days after birth. However, it might stay open in some cases, leaving a space for the neighboring organs to penetrate. Such congenital anomaly leads to abnormal penetrations and stands to be the leading cause of hernias in children. Although umbilical hernia subsides when the child is one year old, an inguinal hernia might require immediate attention (2).
Read the post to know about the causes, risk factors, types, symptoms, and treatments for hernia in children.
Causes Of Hernia In Children
The following are the common causes of hernia among children (3) (4).
- Weak belly muscles: A lower muscular tone could make a child’s belly muscles more susceptible to hernias.
- Abnormal openings: The inguinal canal helps in the passage of the scrotum during fetal development. Similarly, the umbilical ring holds the umbilical cord, transporting nutrients and blood. Although these canals close by birth, sometimes they may remain open. These abnormal openings could lead to a hernia.
- Abdominal surgery: A recent abdominal surgery could weaken the neighboring muscles if not healed properly. This weakening could cause the neighboring organs to dislocate from their place, leading to a hernia.
- Increased pressure: Although rare, coughing and vomiting may sometimes cause a hernia. Chronic coughing and vomiting could tear up a chest muscle, causing a hernia.
- Sudden twists: A sudden, explosive movement or a jerk in the body, especially those occurring while playing sports, could weaken and tear the muscles of the lower abdomen.
Risk Factors For Hernia
The following factors could increase a child’s risk of developing a hernia (5).
- Premature birth
- A family history of hernia, especially among parents and siblings
- Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
- Improper descent of the testicles into the scrotum (boys), also called undescended testicles
- Urethral problems or cystic fibrosis
Types Of Hernia In Children
The type of hernia determines its severity. Hernia in children can be classified into the following types.
1. Inguinal hernia
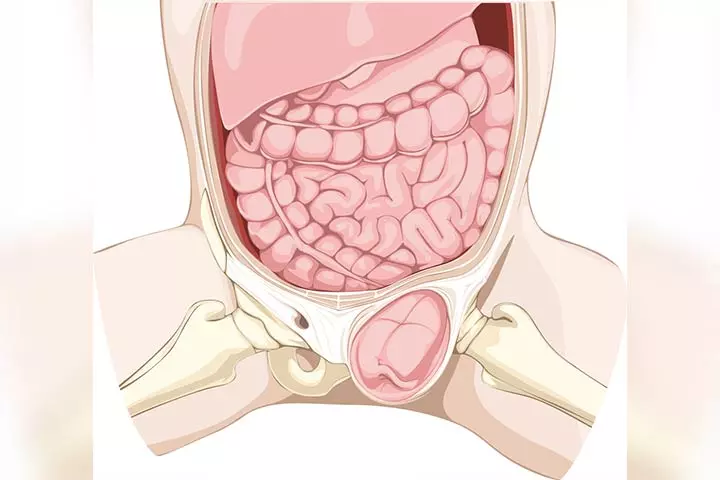
This type of hernia is observed in the groin area. It is characterized by a bulge near the pubic bone and often causes pain and discomfort. In an inguinal hernia, the loop of intestines that protrudes through a weaker part of the abdominal wall, may become stuck and require urgent surgery (6).
Although inguinal hernia can appear at any age, it is more common in the first six months, and it commonly affects boys more than girls (7).
2. Umbilical hernia
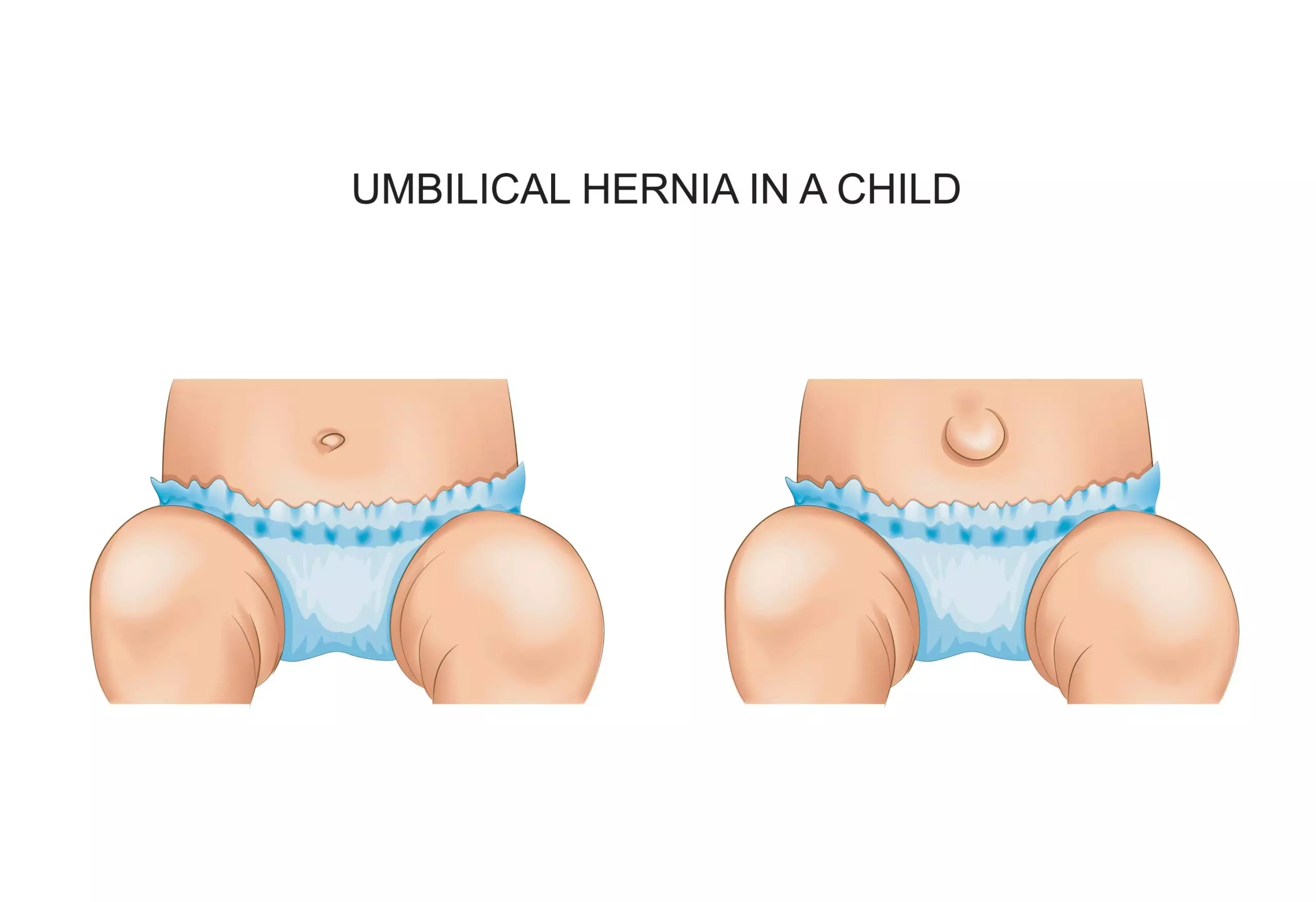
An umbilical hernia is formed when a loop of intestines protrudes near the abdominal wall of the navel. Such protrusion gives the belly button a swollen appearance. Usually, this type of hernia is seen amongst preterm babies and newborns. It is often painless and recedes on its own (4).
In most cases, umbilical hernias subside within the first year after birth. However, if the hernia doesn’t close by the time your child reaches five years or if it has increased in size, your medical professional may suggest a non-invasive intervention or a minor surgery (8).
3. Epigastric hernia
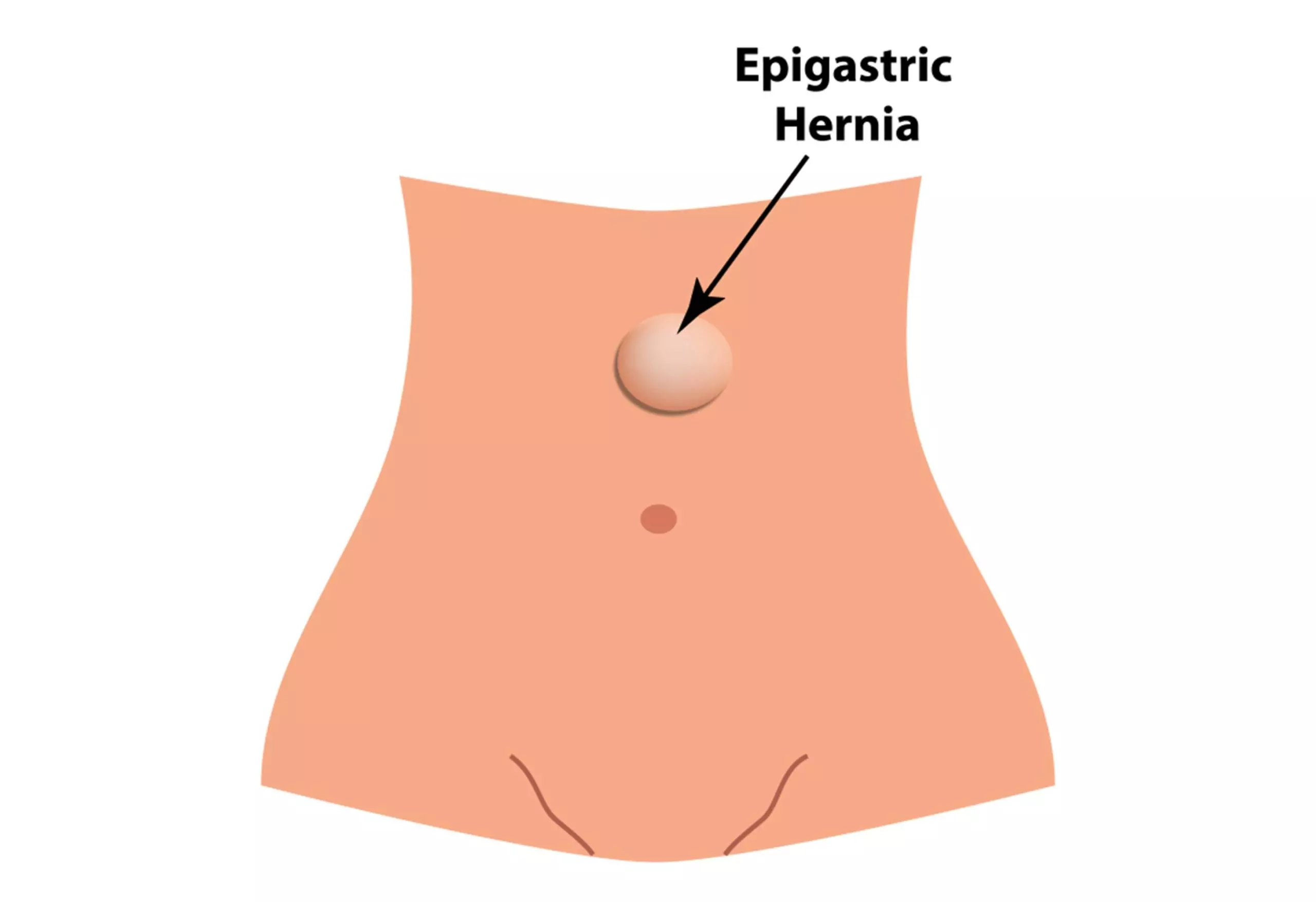
The area above the belly button and below the sternum of the rib cage is called the epigastric region. When fat pushes through a weaker abdominal wall in this region, it causes an epigastric hernia. These types of hernias are usually painless, but you may observe a bump in the child’s epigastric region. Based on the size of the lump, your child’s doctor may suggest a minor surgery (9).
4. Hiatal hernia
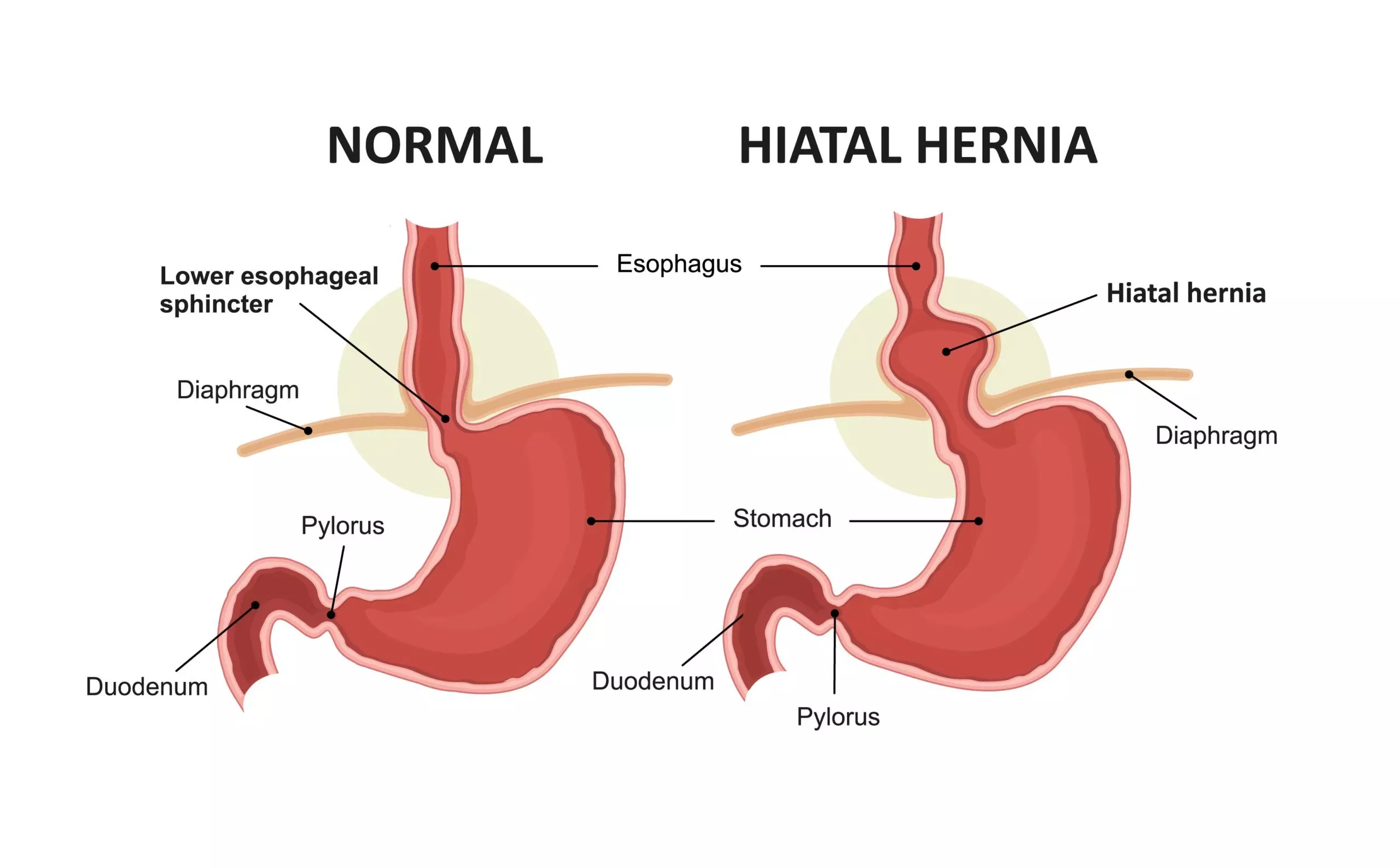
It is the least common type of hernia among children and is observed near the diaphragm. The diaphragm separates the abdomen from the chest and has a small opening termed the hiatus (10). When a part of the stomach bulges into the hiatus, it is called a hiatal hernia (3). It is mostly asymptomatic but may sometimes cause heartburn, indigestion, and chest pain.
5. Incisional hernia
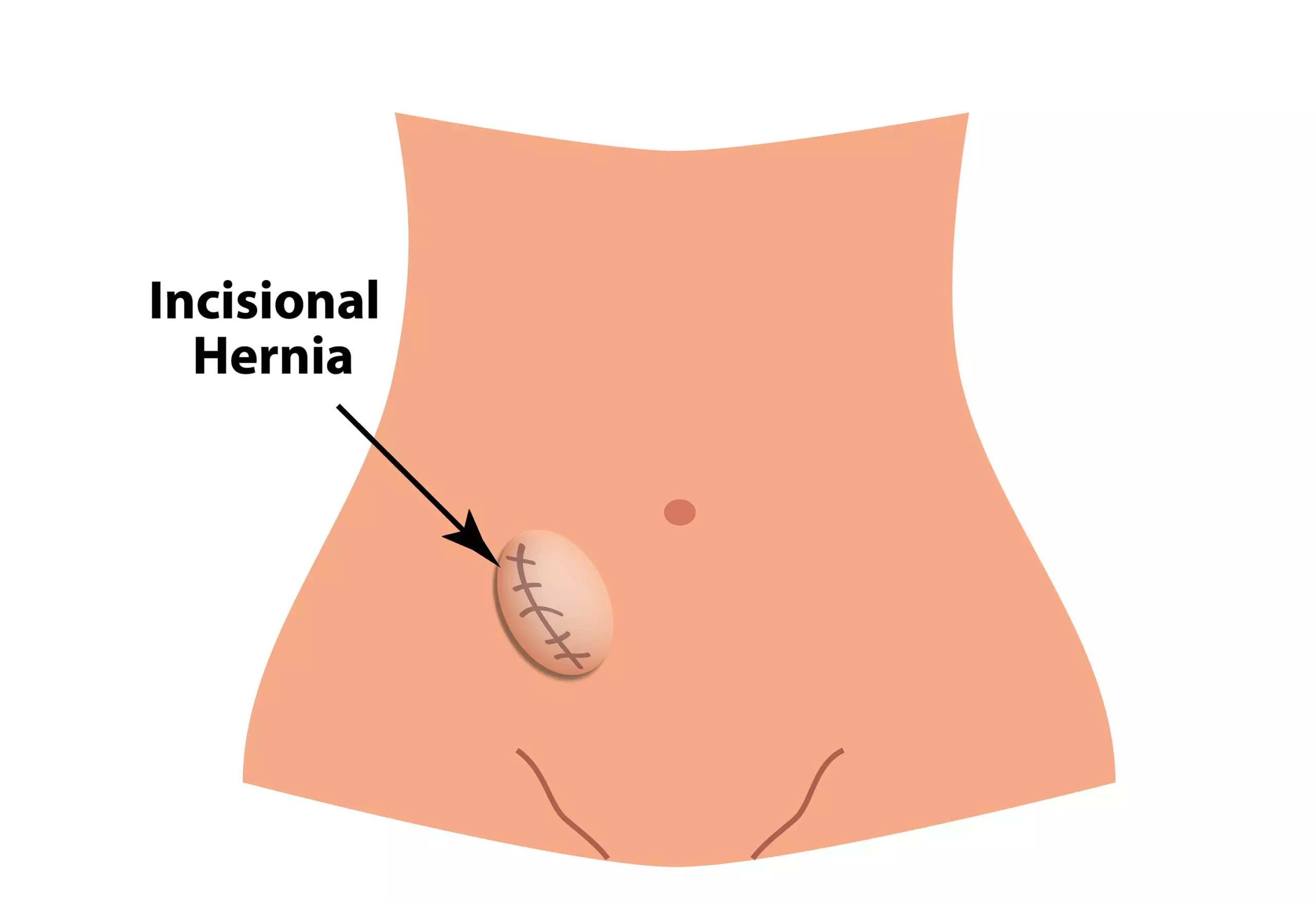
This type of hernia in children is a postoperative complication (11) (12). In this condition, an abdominal tissue protrusion forms at the site of the recovering surgical scar. Your child may also have a fever, abdominal discomfort, and pain near the site of the incision.
This type of hernia is a medical emergency and requires the attention of a doctor.
6. Sports hernia

A sports hernia is uncommon, but it could occur in children who play sports, such as soccer, tennis, or ice hockey (13). Sports hernias are not often seen with the naked eye, and the most common symptom is pain and discomfort in the groin area when sitting, turning, or twisting (14).
Is Hernia In Children Serious?
The severity of a hernia is dependent on the type. Inguinal and incisional hernias need immediate treatment as they may cut the blood supply to the affected region. Irrespective of the type and severity, consult your child’s pediatrician on the first sign of a hernia. The pediatrician will determine the severity and the follow-up procedures.
Symptoms Of Hernia In Children
A bulge or swelling near the abdomen or groin is the most noticeable symptom of a hernia. This bulge may be easier to see when your child cries, coughs, or has bowel movements.
The other symptoms of hernia include (3) (6) (8)
- Pain at the site of swelling
- Discomfort
- Round belly
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Redness and tenderness near the site of bulging
Complications Of Hernia In Children
Any hernia must be reported to a medical professional as soon as possible. This is because the swollen part of the intestine could get stuck in the protruded muscles (incarcerated hernia) and lead to decreased blood flow to the affected region (strangulated hernia). Such complications are most common in unattended inguinal hernias (5) (8). If left untreated, it could result in permanent damage to the intestines.
How Is Hernia Diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider may perform a physical examination to determine a hernia in your child. They may gently push the swelling to check if it can be pushed back into the abdomen (reducible) (5). Your doctor may also conduct an ultrasound or X-ray to detect hernias.
Treatment For Hernias In Children
The following are the possible treatment plans based on the type of hernia.
- Inguinal and incisional hernias: A low-risk hernia repair surgery is performed immediately after the identification of an inguinal hernia or incisional hernia. The protruding parts are gently pushed back into the abdomen manually or laparoscopically (5) (15).
- Umbilical hernias: Umbilical hernias usually close on their own. But if your child’s hernia is present even after two years or if the size of the hernia increases, your doctor may recommend a low-risk surgery. First, the loop of intestines is pushed back into the abdomen. Then, a mesh may be placed near the navel to prevent the relapsing of the hernia (16).
- Hiatal hernia: To treat a hiatal hernia, your doctor may suggest a diet change or minor surgery (10).
- Epigastric hernias: These are treated surgically (9)
- Sports hernia: Your doctor may primarily suggest physical therapy or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. However, a hernia repair surgery may also be recommended (14).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it common for children to have a hernia?
Yes. It is common for children to develop a hernia. Some hernias may usually be more common in children, while others may be uncommon. For instance, 80% of hernias in children are inguinal hernias (17) (18).
2. Which hernia has the highest risk of strangulation?
Research notes that femoral and inguinal hernias often carry a higher risk of strangulation (19).
As scary as hernias may sound, they are treatable. Children usually make it back home on the same day after the surgery, and the recovery rates are high. The primary goal is to prevent the strangulation of the affected region. If you observe any signs of hernia in children, seek medical intervention.
Key Pointers
- Hernia is a condition where an organ projects through a weak spot in the muscles.
- Weak abdominal muscles, abdominal surgery, and sudden body twists are some causes of abdominal hernia in children.
- A family history of hernia and premature birth may increase the risk of this condition.
- The common symptoms of hernia include swelling near the abdomen or groin, discomfort, and a round belly.
- Some hernias close on their own, while some may require surgical treatment.
References
- Hernia.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15757-hernia - Inguinal and Umbilical Hernias in Children.
https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/health-library/inguinal-and-umbilical-hernias-in-children - Hiatal Hernia.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8098-hiatal-hernia - Inguinal Hernia.
https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/i/inguinal-hernia - Inguinal Hernia in Children.
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=90&ContentID=P03092 - Inguinal Hernia.
https://www.childrenshospital.org/conditions-and-treatments/conditions/i/inguinal-hernia - Umbilical Hernia.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/hernias/umbilical-hernia - Umbilical Hernia in Children.
https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tp17785 - Epigastric Hernia.
https://www.childrensmn.org/educationmaterials/childrensmn/article/18005/epigastric-hernia/ - Rajesh U. and Prasad A.N. ; (2008); Hiatus Hernia in a Ten Year Old Boy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4921585/ - Incisional Hernia.
https://www.mountsinai.org/care/surgery/services/general-surgery/conditions/hernia/incisional-hernia - Tanaka K. et al.; (2018); Risk Factors for Incisional Hernia in Children.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29288306/ - Sports Hernia.
https://www.mottchildren.org/health-library/uf5025 - Sports Hernia.
https://orthokids.org/en-US/Sports-Injury-Prevention/Sports-Hernia#:~:text=Sports%20hernias%20usually%20occur%20during - Hernias: Incisional Hernia Repair.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK395550/#:~:text=The%20treatment%20options%20for%20incisional - Umbilical Hernia Repair.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/umbilical-hernia-repair/ - Hernias in Children: What Parents Should Know.
https://health.choc.org/hernias-children/ - Recognizing and Caring for Hernias.
https://www.chop.edu/news/recognizing-and-caring-hernias - Alexander Smith et al.; (2021); Laparoscopic mesh repair of strangulated groin hernias requiring bowel resection.
https://misjournal.net/article/view/4189

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.
Read full bio of Dr. Neema Shrestha