Benefits Of Carbohydrates: 4 Ways They Boost Your Health
Fuel your body efficiently with essential energy sources that support health and vitality.

Image: Shutterstock
When you say you are on a low-carb diet, do you really know what you mean?
Carbs are not fattening. Yes, you read it right. Carbs don’t spike your blood sugar levels either. And cutting down on potatoes or bread is not the entire solution. Banishing carbs from your life doesn’t do you any good. When you say you are on a low-carb diet, do you actually know what you are saying?
Think about it. You think carbs are unhealthy? Fruits contain carbs. The bowl of veggies you had for lunch contains carbs. Whole grains contain carbs.
Your body’s preferred fuel for daily activities is carbohydrates. Your brain and neurons rely on carbohydrates. This means eliminating all forms of carbs from your diet may be unwise.
In this post, we will tell you what you need to know about carbohydrates, and how you can use them for a healthier and energetic lifestyle. Scroll down!
What Are Carbohydrates Anyway?
Carbs are one of the main types of nutrients, and they are the most important energy source for your body. When you ingest carbs, your digestive system converts them into glucose – and this glucose is what your body uses for energy for daily functions. Extra glucose is stored in your liver and muscles for later use.
There are three major types of carbohydrates – monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Each differs from the other on the basis of its molecular structure.
Monosaccharides are the smallest sugar units. When two monosaccharide molecules are bonded together, you get a disaccharide. When an entire chain of three to ten monosaccharide molecules are bonded together, you get an oligosaccharide. More than ten monosaccharide molecules give us polysaccharides. A polysaccharide molecule can contain hundreds of thousands of monosaccharides.
We also have sugar alcohols, which are known as sweet carbohydrates. They are popular alternatives to sugars that are produced industrially. Though some sources suggest they could be healthy in a few ways, more research is being done.
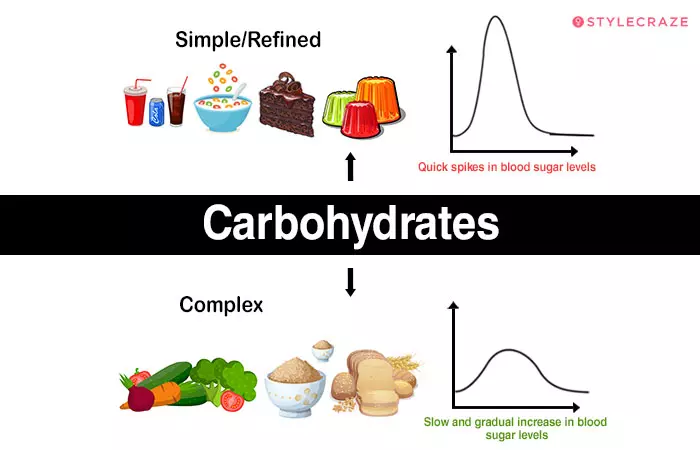
In simple terms, carbs are classified into two – simple and complex. While monosaccharides and disaccharides are simple carbs, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides are complex.
Simple carbs are the sugars. They have simple molecular structures (just two molecules). They offer a quick short burst of energy, but you feel hungry soon. Examples are sugars, candies, and white bread.
Complex carbs have long chains of sugar molecules. They take time to digest and fill you up. They offer a steady boost of energy. They also contain more nutrients and keep you feeling full for a long time. Examples include vegetables and whole grains.
Understanding the difference between simple and complex carbs is key. That is where the secret lies. Studies show that to cut the risk of disease and improve longevity, adults must get 45-65% (225 to 325 grams) of their daily calories from carbohydrates. And when these calories come from complex carbs, you have just hit the sweet spot.
Complex carbs are those loaded with fiber – these include fruits and vegetables and whole grains.
Talking about all this, a low-carb diet doesn’t make sense, does it? Because carbohydrates have an important role to play.
Why Are Carbohydrates Important? What Do They Do?
1. Carbohydrates Offer Energy
This is the primary function of carbohydrates. Your body breaks down carbs into glucose before they enter the bloodstream. Your body’s cells take this glucose and produce a fuel molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This ATP helps the cells power the body’s functions.
Without carbs, this won’t be as effective.
2. Carbohydrates Store Extra Energy
Something like a backup. If your body has the required glucose to meet its needs, the extra glucose is stored in the liver and muscles for later use. This stored glucose is called glycogen.
This glycogen is used in times of need. While the liver glycogen can be used for energy across the body, muscle glycogen can be used only by the muscle cells – more so during intense physical exertion.
When the body has all the glucose it needs, and its glycogen stores are full, excess glucose is stored in the form of triglycerides and fat. In a way, taking too many carbohydrates can invariably lead to fat gain.
3. Carbohydrates Preserve Muscle
When there is a deficiency of carbohydrates, there is a deficiency of glucose (and glycogen too). This provokes the body to break down muscle into amino acids and use them as glucose to fuel the body. And this is not an ideal scenario.
This is why ensuring you have the right kind of carbs in the right amounts is crucial.
4. Carbohydrates Can Prevent Heart Disease And Diabetes
Of course, we are not talking about refined carbohydrates here. They are unhealthy.
But taking complex carbs in the form of dietary fiber can boost heart health and control blood sugar levels (1), (2). Fiber has shown to lower blood cholesterol levels as well. Fiber prevents the reabsorption of bile acids in the intestines. This makes the liver use cholesterol to produce the required bile acids, which might otherwise get accumulated in the blood.
Fiber also doesn’t spike blood sugar levels. In fact, the fiber in foods containing carbs delays their digestion – resulting in lower blood sugar levels post meals.
Not including carbs in your diet may not be dangerous. The cells in your body can generate ATP not just from glucose, but from fat as well. And during times of a glucose-crunch, your brain also uses ketones (molecules formed by the breakdown of fatty acids) as fuel. This means your body has alternate ways of generating energy. But good carbs are still important – your brain needs one-third of its energy to come from glucose, and also, complex carbs are replete with other essential nutrients anyway.
These are the major ways carbohydrates benefit you and keep you going. But what are the foods you must take?
Making The Right Carbohydrate Choices
It all boils down to choice. You can choose to go for the right carbs. These include:
- fruits and vegetables
- legumes
- nuts and seeds
- whole grains
Minimize bad carbs like
- sugary drinks and fruit juices
- white bread
- ice cream
- chocolates and candies
- pastries and cakes and cookies
- potato chips and French fries
Whenever you are tempted to go for the bad carbs, you can instead choose a good variant. The following table can help.
| Carbs to Limit | Smarter Carbs | Best Choices |
|---|---|---|
| Instead Of | Choose | Or better yet choose |
| Candy | Dried fruits | Whole fruit |
| Soda or Punch | Fruit juice | Seltzer with a dash of juice |
| White bread | Whole wheat bread | Seven grain bread |
| Enriched pasta | Whole-wheat pasta | Cracked wheat pilaf |
| White Crackers | Whole grain Cracker | Vegetable sticks |
| Cotton Candy | Caramel apple | Apple |
| Chocolate chip cookie | Oatmeal raisin cookie | Strawberries |
| Sugary cereal | Bran cereal | Rolled Oats |
Complex carbs are great. Simple carbs – not really. What could be the consequences of consuming simple carbs?
What Are The Ill Effects Of Simple Carbs?
Stroke And Obesity
Simple carbs are combined with fat and can cause obesity when taken in excess. Fat can lead to abdominal obesity, which has been linked to stroke.
Increased Diabetes Risk
Consuming an excess of simple carbs can cause a series of blood sugar highs and lows. This eventually increases the risk of diabetes.
Chronic Diseases
Fluctuations in blood sugar can lead to increased hunger and overeating. This leads to chronic ailments like heart disease and inflammation.
Conclusion
Keep in mind to choose complex carbs. They contain fiber and other important nutrients. You don’t have to eliminate carbs from your diet. You just have to choose the right type.
Tell us how this post has helped you. Leave a comment in the box below.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does your body take to digest carbohydrates?
Though we don’t have an exact answer, your digestive system can start extracting energy from carbs in 15 to 30 minutes from ingestion.
Which organ first receives carbs after getting absorbed from your intestine?
Your liver receives carbohydrates first.
Which enzyme breaks down carbohydrates?
Salivary amylase. This enzyme in your saliva breaks down the starch in your food (carbs) into maltose. This maltose travels down the esophagus to your stomach. In the intestine, maltose is broken down into glucose.
What are indigestible carbohydrates?
Complex carbohydrates containing fiber are also called indigestible carbohydrates. Their fibrous structure makes them indigestible, and hence, they contribute to calories and energy.
What elements are carbohydrates made of?
Carbohydrates are made up of three elements – carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Different arrangements of these elements make the different types of carbohydrates.
How are carbohydrates different from proteins and fats?
Though the three are macronutrients, they differ in terms of their basic units. Carbohydrates are made up of sugars, proteins are made of amino acids, and fats are made of fatty acids and glycerol.
Carbs are polymers and are made of monomers called monosaccharides.
References
1. “A prospective study of dietary glycemic load…”. US National Library of Medicine.
2. “Glycemic index, glycemic load…”. US National Library of Medicine.