Breastfeeding With Breast Implants: What You Need To Know
Ability to breastfeed after the procedure depends on the size and place of the implant and the type of augmentation procedure.
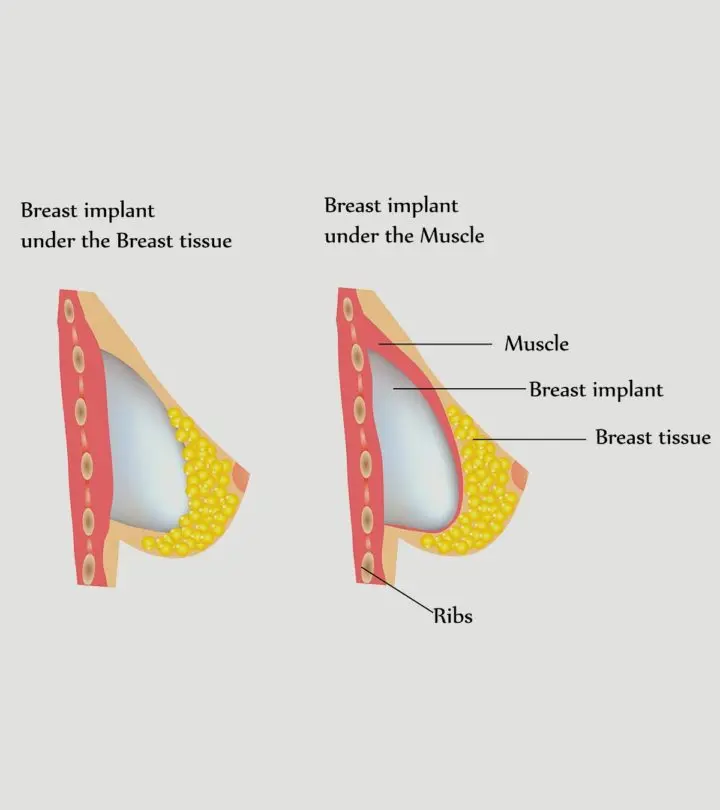
Image: Shutterstock
Women who have undergone cosmetic surgeries on breasts may often wonder if they can opt for breastfeeding after breast augmentation. It is important to know that while most women can breastfeed, certain anatomical modifications of the breast, such as breast implants, may impact the mother’s ability to nurse their child. So, read this post to know more about breastfeeding with implants, factors influencing nursing, problems that may arise, precautions to take, and more.
Can You Breastfeed With Breast Implants?
Yes. Most women with implants never face problems or complications with breastfeeding, although there is limited research on the subject (1).
In most cases, implantation affects neither the breasts’ ability to produce milk nor the baby’s ability to latch to the breast. However, the influence of breast implants on breastfeeding usually depends on the type of breast augmentation surgery. Certain other factors may also play a role in deciding the woman’s ability to breastfeed after a breast implant.
Factors Influencing Breastfeeding With Implants
Here are some factors that play a crucial role in determining whether or not a woman with breast implants can breastfeed (2):
- Time of surgery: Breasts change significantly during pregnancy, and there is an increase in the number of milk lobules within the breasts. Pregnancy-related changes in the breasts may interfere with their ability to heal, which eventually could affect the production of breast milk and the ability to breastfeed. So women who undergo breast implantation several years before motherhood stand a better chance at breastfeeding, compared to those who have had it done close to conceiving.
- Type of incision: A surgeon can use different types of incision for insertion of the breast implant. The periareolar incision goes around the outer edge of the areola region and may damage to the nerve endings around the nipple. There are chances of damage to the milk lobules as well. Therefore, women with intentions to get breast implants should opt for inframammary incision. This is done around the lower edge of the breast or transaxillary incision, which is in the armpit, and poses a lesser risk of damage.
- Placement of the implant: There are two ways to place the breast implant within the breast: beneath the chest muscle or above it. An implant placed above the chest muscle is more likely to interfere with the secretion of milk. Therefore, women who intend to breastfeed should place the breast implant within the chest muscle.
- Healing process: The extent of the incision and how fast it heals plays a significant role in whether a woman can breastfeed her baby. Precautionary care after the surgery and medications are thus vital to help your breasts get right back on track for breastfeeding.
While you may be able to breastfeed in spite of these factors, breastfeeding with breast transplant may not always be free from problems.
Breastfeeding Problems That Arise Due To Breast Implants
The following challenges may arise when breastfeeding with a breast implant:
- Breast engorgement: Implants enhance the size of the breasts. Experiencing engorgement during lactation may cause the breast to swell way beyond their normal size due to the implant.
- Altered nipple sensitivity: Women with breast implants often report a heightened or lowered nipple sensitivity. It may cause some problems during latching. Women with greater sensitivity may find the baby’s latch painful while the ones with lower sensitivity levels may not feel the baby’s latch at all.
- Decreased or inconsistent milk production: A breast implant placed over the chest muscle may press on the milk lobules and interfere with their ability to produce milk.
- Less inclination towards exclusive breastfeeding: A study found that women with implants are less likely to breastfeed their babies exclusively, and in some cases, they may be less likely to breastfeed at all (3).
No direct link has been established between the presence of a breast implant and reluctance of the women to breastfeed. The diminished interest in breastfeeding is often attributed to breast hypoplasia, which is underdeveloped breasts that are often observed in women with implants. Another reason could be the constant maintenance of breasts with implants, which could fade the mother’s interest in breastfeeding.
- Risk of rupture: Breast implants do not last forever. They eventually tend to deflate or rupture (4). This can interfere with the mother’s ability to breastfeed successfully.
The above problems may occur, but there is insufficient evidence to suggest that breast implants can entirely impede a woman’s ability to breastfeed (5). Taking a few precautions can make breastfeeding a safe activity even with breast implants. You should have a discussion with the doctor performing your surgery about the importance of breastfeeding and your milk production and make sure they do everything they can to maintain that for you
What To Remember When Breastfeeding With Implants?
Here are a few things you should be observant about when breastfeeding with implants.
- If your implants are several years old, they may deflate abruptly due to the pressure from milk lobes. Therefore, keep an eye on the size and speak to a doctor if you notice drastic changes in the size of breasts.
- Consult a doctor soon in the case of painful engorgement. Any infection in the breast can cause excessive inflammation if there are implants within the breast.
- If your baby has trouble latching due to your low nipple sensitivity or because the nipple has an altered shape due to surgery, then consult a lactation expert to ease the problem.
These precautions can make breastfeeding easy. A preferred option would be to postpone breast implantation to a time after lactation.
Can You Breastfeed With Breast Lift And Reduction?
Yes. Breast lift and reduction are other breast augmentation methods that may not necessarily affect your ability to breastfeed. A lift raises the breast and makes them firmer by removing excess skin and tightening existing tissue. It is increasingly becoming an alternative to breast implants (6). Breast reduction is the removal of excess breast tissue and fat to make the breasts proportionate to the body (7).
In both cases, there is no insertion of a foreign body in the body. However, these surgeries are similar to breast implantation, since the type of incision and recovery time plays a crucial role in allowing the woman to breastfeed (8) (9). The challenges and problems remain the same. To reiterate, do have a discussion with your doctor about the importance of breastfeeding and your milk supply. Make sure they are taking all the precautions to avoid severing milk ducts and nerves.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does the type of implant affect breastfeeding?
No. It does not matter if you have silicone or saline implants (2). Silicone is a compound made of silicon and oxygen (5). Saline is made of sodium chloride and water. No evidence suggests either one of them being better for women who intend to breastfeed. The risks also remain the same.
2. Can materials from the implant pass into the breast milk?
It is highly unlikely. Both silicone and saline breast implants are airtight units and seldom leak unless subjected to pressure. A study found that there is no difference in the levels of silicone in the milk of women with silicone implants and those who do not have implants (10).
Moreover, if silicone or saline leaks into the breasts, it has to cross through several layers of cell membranes to eventually find its way into milk (11). Therefore, it is highly unlikely that the contents of the implants will leak into breast milk.
Although the process of breast augmentation does not affect the production of breast milk or its supply, there is limited knowledge available on the subject. However, there are many factors that can influence breast milk depending upon the efficiency of the procedure. Therefore, it is advised to consult a doctor or a lactation specialist in case you experience symptoms like pain in the breast or a decreased production of milk. Even though breast augmentations are a common procedure these days, they may mildly affect your ability to breastfeed. Thus, have a detailed discussion with your doctor before going ahead with it.
References
2. Breastfeeding After Implants; Washington University in St. Louis
3. M Schiff et al.; The impact of cosmetic breast implants on breastfeeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis; Int Breastfeed J. (2017)
4. Breast Implant Complications; USFDA
5. The Transfer of Drugs and Other Chemicals Into Human Milk; AAP (2001)
6. Breast Lift; ASPS
7. Breast Reduction; University of California
8. Breastfeeding after Breast Reduction Surgery; Michigan Medicine
9. What is a breast lift?; Northwell Health
10. G Koren; Do silicone breast implants affect breastfeeding?; Canadian Family Physician (1998)
11. Bondurant S, Ernster V, Herdman R; Safety of Silicone Breast Implants; National Academies Press (US) (1999)