Thyroid In Pregnancy: Complete Guide To Care And Management
Discover how hormonal changes impact expecting moms and support fetal growth effectively.
Image: Shutterstock
The thyroid hormone is one of the most important hormones that support your metabolic needs and your growing baby during pregnancy. But when you are pregnant, the body may produce more or less of this hormone, and this could show in the form of a few symptoms. The good news is that you can track the thyroid levels in your body through some tests and learn to manage it better by making a few lifestyle changes.
In this MomJunction post, we tell you about thyroid and its role during pregnancy, what causes a thyroid condition, how it affects pregnancy, and how to manage or treat it.
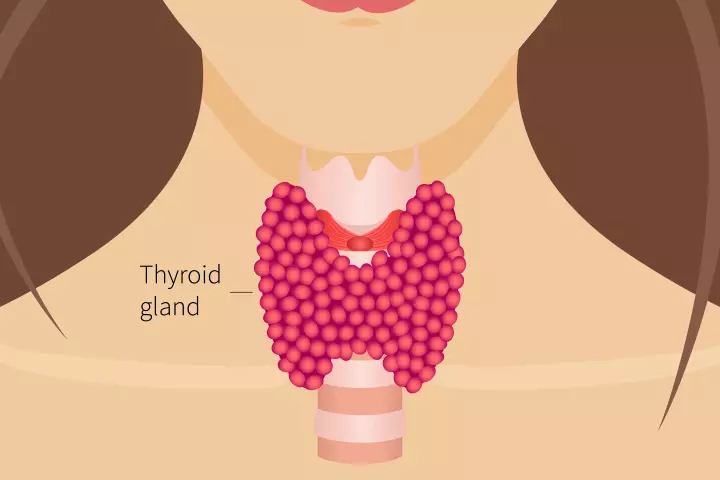
The Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a small gland located in the lower part of the neck, below your Adam’s apple. It is about two inches and resembles a butterfly. It produces the thyroid hormone that controls several physiological activities such as managing energy, heartbeat, and metabolism (1). Too much (hyperthyroidism) or too little (hypothyroidism) of this hormone can cause thyroid problems during pregnancy.
How Does The Thyroid Gland Help In Pregnancy?
Thyroid hormones play a significant role in the health and development of your baby’s nervous system. In the first trimester, the baby relies on the mother for the supply of the thyroid hormone via the placenta. In the 12th week of pregnancy, the baby’s thyroid gland begins to work, but it cannot make adequate thyroid hormone until about the 18th or 20th week (2).
What Is The Role Of Thyroid Hormones In Pregnancy?
The thyroid gland produces the hormones called triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) and releases them into the bloodstream. These hormones travel to different body parts such as the heart, bones, brain, skin, liver, and kidneys to regulate their functioning.
These two hormones are released by the thyroid when the hypothalamus, the part of the brain that regulates hormone production, senses that the hormone levels have gone down. The hypothalamus produces the thyroid stimulating hormone or TSH, which then signals the pituitary gland to release T3 and T4. When there is an imbalance in these three hormones, it may cause two thyroid conditions, which we talk about in the following section (3).
[ Read: Postpartum Thyroiditis ]
What Are The Risks Of Developing A Thyroid Condition During Pregnancy?
Either of the two thyroid conditions could be risky in the following ways.
- Thyroid dysfunction could increase the risk of diabetes during the first trimester and half of the second trimester (4).
- Hypothyroidism early in pregnancy could affect the brain development of the baby (5).
- Women with high thyroid function and low hCG are at risk of preeclampsia (6).
- Women with any autoimmune disorders, who have had a thyroid condition before, or whose family members have a history of thyroid dysfunction may have a risk of thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy (7).
Continue reading to know in detail about hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism during pregnancy.
What Are The Main Types Of Thyroid Conditions?
1. Hyperthyroidism
In this condition, the thyroid gland produces more thyroid hormone than required. This happens when the gland is hyperactive. In the US, around 1% of people have hyperthyroidism. The condition could speed up certain functions such as the heart rate and also the metabolism of the individual. Hyperthyroidism is more likely to occur in women than in men (8).
2. Hypothyroidism
When the thyroid gland is unable to make adequate amounts of T4, it results in hypothyroidism. This occurs when the gland is underactive or when the hypothalamus or pituitary gland is not working. About 5% of the population has hypothyroidism, which is more common in women than in men (8).
A thyroid condition during pregnancy could result in certain complications.
Hyperthyroidism In Pregnancy
It rarely occurs during pregnancy, but knowing the causes, symptoms, and effects on pregnancy could help you deal with it if necessary.
Causes Of Hyperthyroidism
Any of the following factors could result in excess production of the thyroid hormone.
- Graves’ disease: Around 80 to 85% of hyperthyroidism cases in pregnancy are caused due to Graves’ disease. However, its likelihood is around 1 or 2 in 1000 cases. The condition makes the immune system overactive, which enlarges the gland and produces more of the thyroid hormone (9).
- Hyperemesis gravidarum: Excessive nausea and vomiting during pregnancy could also be responsible for hyperthyroidism in pregnant women (10).
- Others: Some other rare causes of hyperthyroidism in pregnancy include the formation of the nodules in the gland, high levels of hCG, and gestational hyperthyroidism (11).
Symptoms Of Hyperthyroidism
While the symptoms differ from one pregnant woman to another, there are a few common ones such as (8):
- Irritation and nervousness
- Confusion and increased perspiration
- Brittle hair and thinning of the skin, shivering hands, weak arms and thigh muscles
- Weight loss and trouble in sleeping
- High blood pressure and rapid heartbeat
Effects Of Hyperthyroidism In Pregnancy
Although this is a rare condition in pregnant women, it could result in certain complications when left unattended (12).
Effects on the mother include:
- Placenta abruption
- Toxemia
- Thyroid crisis
- Premature delivery
Effects on the baby include:
- Low birth weight
- Small size for gestational age
- Intrauterine growth retardation
Next, we see the causes, symptoms, and effects of hypothyroidism in pregnancy.
Hypothyroidism In Pregnancy
Identifying hypothyroidism during pregnancy is not easy, as most of the symptoms are similar to those of pregnancy.
Causes Of Hypothyroidism
Some common causes of hypothyroidism include:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: This autoimmune disorder is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in pregnancy. In this case, the immune system sends antibodies, which destroy cells present in the gland. It further causes enlargement of the gland, also called goiter (13).
- Deficiency of iron: When your diet does not have an adequate amount of iodine as required by your body, it could result in decreased thyroid levels in pregnancy (14).
[ Read: Gestational Diabetes ]
Symptoms Of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is the result of decreased thyroid hormone levels, which also slows down metabolism. The symptoms mostly go unnoticed either because they are mild or because they are similar to the pregnancy symptoms.
- Weight gain and swelling of face
- Tiredness
- Constipation, tingling or pain in hand, and muscle cramps
- Hoarse voice and changes in hair and skin
- Slow heart rate and trouble focusing
Effects Of Hypothyroidism In Pregnancy
When hypothyroidism is not treated, it could lead to several complications (15).
Effects on the mother include:
- Spontaneous miscarriage
- Preeclampsia
- Perinatal mortality
- Abruptio placentae
Effects on the fetus include:
- Premature birth
- Less than normal weight
- Low mental capacity
Proper diagnosis is essential to avoid the effects of thyroid conditions in pregnancy.
Diagnosis Of Hyperthyroidism And Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy
After checking your symptoms, the doctors may recommend certain tests to diagnose thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy. The major tests include:
- Test for T3
- Test for T4
- Thyroid antibody tests
- Thyroid stimulating tests
The tests primarily measure the T4 and TSH levels for diagnosis of the thyroid condition in pregnant women. For instance, high TSH and low T4 indicate hypothyroidism, while excess T4 could be a sign of hyperthyroidism (16).
Based on the test results, doctors recommend the treatment for the thyroid condition.
Treatment For Hyperthyroidism And Hypothyroidism
In both cases, doctors prescribe medicines to treat the thyroid condition. Hyperthyroidism in pregnancy should be treated in time to prevent any complications. Usually, antithyroids (ATDs) such as prodrug carbimazole, methimazole, and propylthiouracil are prescribed to block the production of thyroid hormone (17).
Usually, levothyroxine is prescribed to treat hypothyroidism. Thyroxine may also be prescribed, although its recommended dosage depends on the thyroid condition (18). Specific diets can also be followed to manage the thyroid condition better.
Nutrition Tips For Thyroid Dysfunction During Pregnancy
For hyperthyroidism:
These dietary tips can help normalize the excess thyroid levels in pregnancy.
- Try to limit iodine-rich foods such as dulse, kelp, or seaweed. You should also avoid iodine supplements.
- You may add iron-rich (white beans, lentils, kidney beans, and poultry) and selenium-rich foods (Brazil nuts, bread, brown rice, and puffed rice) in your diet to avoid thyroid problems (19).
- Try to have foods that are rich in zinc (Oysters, beef, yogurt, pumpkin seeds), vitamin D (orange juice, tuna fish, swordfish), and healthy fats as hyperthyroidism can also result in zinc deficiency (20).
- You can avoid nitrate (processed foods and fertilized vegetables) and gluten (wheat, rye, barley) based foods (21) (22).
For hypothyroidism
Here is what you can do to increase the production of the thyroid hormone.
- Add iodine-rich foods such as eggs, dairy, fish, and seafood to your diet (23).
- Zinc and selenium are necessary nutrients for normal functioning of the thyroid hormones in your body. Some sources of these minerals include eggs, chicken, Brazil nuts, and fish (19).
- Gluten and goitrogens can be harmful if you have hypothyroidism. So it is best to avoid foods such as peanuts, tofu, cabbage, spinach, barley, rye, and wheat (24) (25).
In addition to the diet, a few lifestyle changes may also be necessary to manage the condition better to avoid any complications.
How To Avoid Thyroid Complications During Pregnancy?
Making certain changes to your lifestyle and keeping certain tips in mind can help you avoid any complications.
- Smoking could lead to thyroid dysfunction; so if you are trying to get pregnant or are pregnant, then you should quit smoking (26).
- Excess consumption of soy food could also lead to thyroid problems in pregnancy. So limit your soy intake (27).
- Keep checking your thyroid levels regularly.
- Take the prescribed medicines on time to normalize the thyroid levels in pregnancy.
[ Read: Preeclampsia: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment ]
Thyroid could be a concern only when the levels are not managed. Proper management with medication prescribed by the doctor and monitoring of the thyroid levels can keep the hormone levels in check. A change in the lifestyle and diet can also keep the conditions away, thus minimizing the chances of any thyroid-related complications when you are pregnant. The aim should be to maintain the ideal amounts of the thyroid hormone in the body. Not more or less.
Do you have any experiences to share? Tell us about them in the comments section.
References
2. Thyroid Hormones; Vivo Pathophysiology; Colorado State University
3. The lowdown on thyroid slowdown; Harvard Health Publishing; Harvard Medical School
4. Thyroid dysfunction may lead to diabetes during pregnancy; Endocrine Society (2018)
5. Clinical Thyroidology For The Public; American Thyroid Association (2017)
6. R. I. M. Korevaar et al.; The Risk of Preeclampsia According to High Thyroid Function in Pregnancy Differs by hCG Concentration; The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2016)
7. B. Vaidya et al.; Detection of Thyroid Dysfunction in Early Pregnancy: Universal Screening or Targeted High-Risk Case Finding?; the Journal of Endocrinology & Metabolism (2007)
8. Thyroid Disease; Radiologyinfo.org
9. M. Inoue, N. Arata, and G. Koren; Hyperthyroidism during Pregnancy; Official Publication of The College of Family Physicians of Canada (2009)
10. F. Azizi and Atieh Amouzegar; Management of hyperthyroidism during pregnancy and lactation; Research Institute for Endocrine Society (2011)
11. F. Azizi; Treatment of hyperthyroidism in pregnancy; Endocrine Abstracts (2012)
12. Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy; American Thyroid Association
13. Iodine deficiency; Healthdirect Australia Limited
14. J.H. Mestman; Hyperthyroidism in pregnancy; Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology (1997)
15. R. C. Smallridge and P. W. Ladenson; Hypothyroidismin Pregnancy: Consequences to Neonatal Health; The Journal of ClinicalEndocrinology & Metabolism(2001)
16. O. P. Soldin; Thyroid Function Testing in Pregnancy and Thyroid Disease: Trimester-specific Reference Intervals; Ther Drug Monit (2006)
17. S. L. Andersen and P. Laurberg; Managing hyperthyroidism in pregnancy: current perspectives; International Journal of Women’s Health (2016)
18. R. K Sahay and V. S. Nagesh; Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy; Indian Journal of Endocrinology & Metabolism (2012)
19. M. B. Zimmermann and J. Kohrle; The impact of iron and selenium deficiencies on iodine and thyroid metabolism: biochemistry and relevance to public health; Thyroid: Official Journal of the American Thyroid Association (2002)
20. D. Kim; The Role of Vitamin D in Thyroid Diseases; International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2017)
21. M. H. Ward et al.; Nitrate intake and the risk of thyroid cancer and thyroid disease; Epidemiology (2010)
22. Tejaswini Ashok et al.; Celiac Disease and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease; The Two Peas in a Pod; Cureus. (2025)
23. H. R. Chung; Iodine and thyroid function; Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism (2014)
24. R. Krysiak, W. Szkrobka, and B. Okopien; The Effect of Gluten-Free Diet on Thyroid Autoimmunity in Drug-Naïve Women with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: A Pilot Study; Experimental and clinical endocrinology & diabetes (2018)
25. J. K. Bajaj, P. Salwan, and S. Salwan; Various Possible Toxicants Involved in Thyroid Dysfunction: A Review; Journal of Clinical & Diagnostic Research (2016)
26. N. Sawicka-Gutaj et al.; Influence of cigarette smoking on thyroid gland—an update; Endokrynologia Polska (2014)
27. D. Collesano; Thyroid: Is it affecting your reproductive health?; Stony Brook Medicine (2019)