Is It Possible To Get Pregnant With Endometriosis?
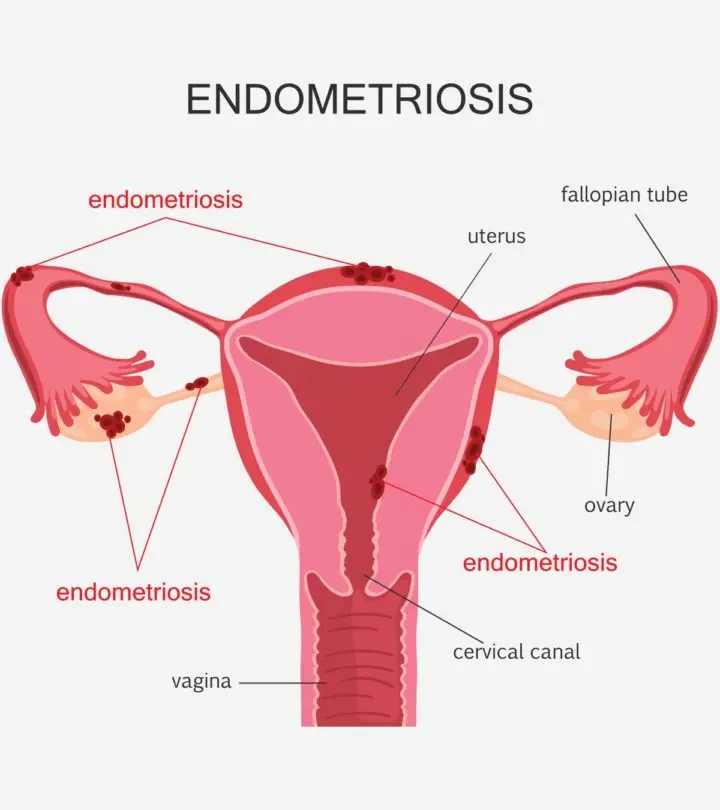
Image: Shutterstock
Endometriosis occurs in almost 6 to 10% of women. (1). It is a painful condition where the uterine lining (endometrial tissue) grows in and around the reproductive areas.
The worrying aspect is that it can affect your ability to get pregnant. But, endometriosis does not necessarily cause infertility and leaves some scope for natural conception.
MomJunction gives an overview of endometriosis, how it can affect your ability to conceive and how to improve your chances of getting pregnant.
In This Article
What Is Endometriosis?
Endometriosis is derived from the word endometrium, which is the uterine lining your body produces every month for egg implantation. When conception does not happen, the body sheds the endometrium, causing the menstrual period.
But if the endometrium travels outside the fallopian tube and to the other areas of the body, it results in endometriosis. The hormones produced during the menstrual cycle will stimulate this extra tissue to grow, break down and bleed in the uterus.
The shredded tissue and blood have nowhere to exit the body and can develop into cysts, adhesions and scar tissues over time. This could further lead to pain, inflammation, and irritation in those areas (2).
Next, let’s see why that extra growth happens.
What Causes Endometriosis?
The cause of endometriosis is unknown, but there are certain possibilities that researchers are still studying (3).
- Problems with menstruation: One possibility could be retrograde menstrual flow, where some of the menstrual tissue flows back into the abdomen and gets implanted there.
- Immune problems: Some women with low immunity will not be able to get rid of the endometrial tissue growing outside the uterus.
- Hereditary: Women with a family history of endometriosis are likely to inherit the condition.
- Surgery: During surgeries such as a C section or hysterectomy, the endometrial tissue is sometimes misplaced.
You would not know if the endometrium is spreading outside the fallopian tube. Even the symptoms are similar to those of normal menstrual pains.
What Are The Symptoms Of Endometriosis?
Common symptoms of endometriosis include (3):
- Pelvic pain
- Irregular heavy menstruation
- Difficulty in conceiving
- Painful intercourse (dyspareunia) in cases of deep infiltrating endometriosis
Some women will also have immune disorders such as asthma, fibromyalgia, and eczema along with endometriosis.
The severity of symptoms is not associated with the amount of diseased tissue. You can have several cysts and spots but a few symptoms, or a few spots and severe symptoms. Some women may not even realize they have endometriosis until they are tested for infertility.
Infertility is a symptom as well as a side-effect of endometriosis.
How Does Endometriosis Affect Fertility?
Most women with endometriosis can get pregnant naturally, while one-third of women find it difficult to conceive (4). In the cases of severe endometriosis, the abnormal cells or scar tissues block the ovaries and fallopian tube.
An egg usually travels from the ovary, along the fallopian tube, and into the uterus for fertilization before implantation. If you have endometriosis in the fallopian tube, the tissue will block the egg from passing into the uterus.
Moreover, the tissue may also damage the egg or sperm. This is probably due to severe inflammation in the body, which interferes with the hormonal balance and keeps you from conceiving.
How To Improve Your Chances Of Getting Pregnant With Endometriosis?
Healthcare providers usually prescribe medications such as progestins that are likely to increase the level of pregnancy hormones in the body. Apart from this, following a proper diet, exercise, supplementation, and detoxification can help your chances of conceiving even with endometriosis.
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Following a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains
- Moderate exercise such as walking and aerobics every day
Also, note that younger women are associated with higher fertility rates, and women above 35 are at a greater risk of infertility and miscarriage when they have endometriosis (5).
But what if this condition develops when you are pregnant?
How Does Endometriosis Affect Pregnancy?
In most cases, pregnancy triggers decidualization (changes to the cells of the endometrium) of the endometrial tissues, thus mitigating the symptoms of endometriosis (6).
However, in other instances, it leads to some complications such as (7) –
- High blood pressure (preeclampsia)
- Bleeding after 24 weeks of pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Placenta previa (where the placenta covers the cervix partially or totally, affecting the delivery)
- Cesarean delivery
- The baby is born earlier or smaller
To avoid these, contact your doctor as soon as you have the symptoms discussed above.
How Is Endometriosis Diagnosed?
The symptoms of endometriosis are similar to most other conditions such as pelvic inflammatory diseases, sexually transmitted infections, and urinary tract problems. Therefore, it is hard to diagnose the condition. Your doctor will ask you about the symptoms and performs the below tests to confirm endometriosis (8):
- Pelvic examination: Your doctor will manually feel the areas in your pelvis to check for cysts and scars behind the uterus. However, the doctor may not be able to detect endometrial patches that could eventually develop into cysts.
- Imaging test: An ultrasound test that uses high-frequency sound waves is used to take pictures of your internal organs and check for ovarian cysts and scars. Another common imaging test is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) which creates an image of the internal anatomy.
- Medication: If the above tests do not help in finding the cysts of endometriosis, you may be suggested to take these medicines:
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists obstruct the menstrual cycle, thus lowering the amount of estrogen in the body. It helps treat pelvic pain.
- Hormonal birth control medications also relieve the pelvic pain.
If the pain subsides with the medicines, it possibly indicates endometriosis. The medicines only work as long as you take them and the pain reverts after you stop using them.
- Laparoscopy: This is a procedure that your doctor uses to view your pelvic region for the endometriosis tissue. Under general anesthesia, a small incision is made near the navel, and a laparoscope is inserted to look for the tissues outside the uterus. It helps to understand the location, extent, and size of the endometrial tissues to decide the best treatment.
The high levels of progesterone induce a bit of remission to the endothelial tissue. For this reason, your doctor would not suggest a laparoscopy when you are trying to get pregnant. Surgical procedure (laparoscopy) is only performed when the endometriosis is severe enough to affect your ability to conceive (9).
What Is The Treatment For Endometriosis?
There is no cure for endometriosis. However, there are treatments for the symptoms and problems the condition causes (10).
1. Medications
If you are not trying to conceive, hormonal birth control is recommended. It includes:
- Continuous cycle (you will have no periods) or extended cycle (you will have a few periods in a year) birth control. These are available in shot or pill forms, which will either stop bleeding or eliminate pain. This option works as long as you take the pills, and works best for those with less pain or symptoms.
- Intrauterine device (IUD) helps relieve the pain and bleeding but only for some time.
If you are trying to conceive, Your doctor will suggest a GnRH agonist, which prevents the body from stimulating hormones required for ovulation, period cycle, and endometriosis tissue growth. It leads to temporary menopause and will help to control endometriosis.
2. Surgery
This is the option for severe symptoms, or if you have fertility problems or the medications are not providing any relief. Surgery involves locating the endometriosis prone area and removing the patches. Post surgery, hormone treatment is resumed to help you get pregnant.
Other treatments
Here are other treatments that may work alone or in combination with the treatment options mentioned above (8).
- Over-the-counter medicines help you deal with mild symptoms such as pain. Ibuprofen (Advil and Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) should ideally work.
- Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) therapies/ natural remedies such as acupuncture, chiropractic treatment, and supplements like thiamine, omega-3 fatty acids or magnesium, and herbs such as licorice root, turmeric, ginger or cinnamon twig.
How Can You Prevent Endometriosis?
There is no way to prevent endometriosis. Staying healthy can only help relieve the symptoms. Regular exercise, relaxation techniques, and adequate sleep will help manage the pain and discomfort. Endometriosis can only get better with menopause.
On a positive note, several women with endometriosis conceive and deliver a healthy baby. So if you are trying to get pregnant, talk to your doctor about it and find ways to conceive safely and healthily.
Have something to share about endometriosis and pregnancy? Write to us in the comment section.

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.