11 Well-Known First Aid Methods That 90% Of People Perform Incorrectly
Master crucial lifesaving techniques with confidence by avoiding common emergency mistakes.
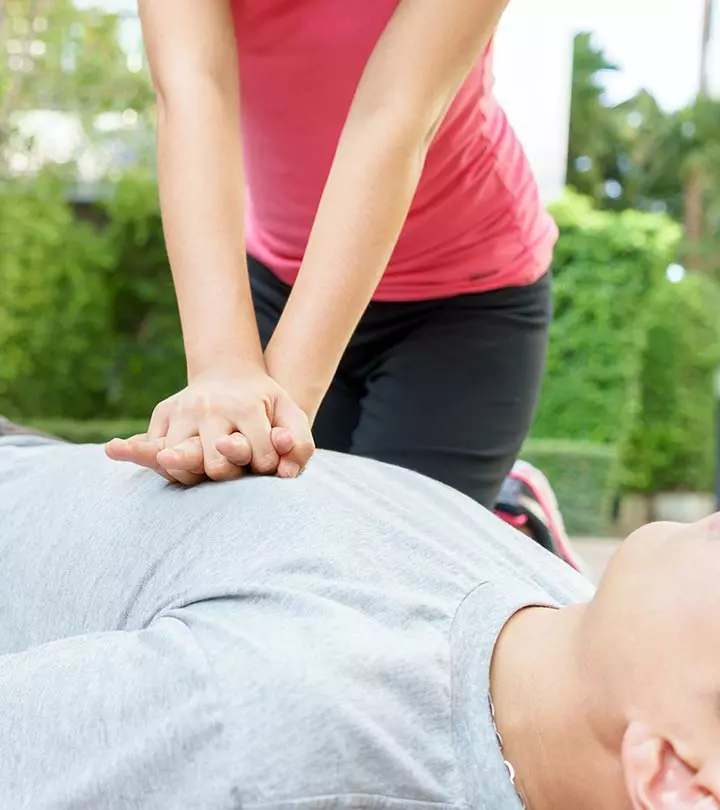

Image: ShutterStock
The knowledge of elementary first aid techniques is very essential. In an emergency, it can prove to be vital in helping save a person’s life till medical assistance arrives on the spot. However, great care should be taken while administering first aid because even a small step performed wrongly could prove fatal for the patient.
Below are 11 common errors in first aid care that should be avoided to prevent further complications.
1. Using Hydrogen Peroxide, Alcohol Or Iodine To Treat Wounds
Possible Dangers: It can be dangerous to use peroxide to clean injuries and lesions. The chemical is strong enough to damage the cells of the connective tissues. So, it actually obstructs the healing process. The other chemicals in iodine tincture and alcohol also cause harm to the normal skin cells. There can be painful skin reactions, burning sensation, soreness, and singing.
Corrective Measures: In such cases, band-aids should be avoided as much as possible. The injury should get air and ventilation to dry and heal. One can use fresh drinking water to clean the wounds and apply some antiseptic or antibiotic ointment for therapeutic use.
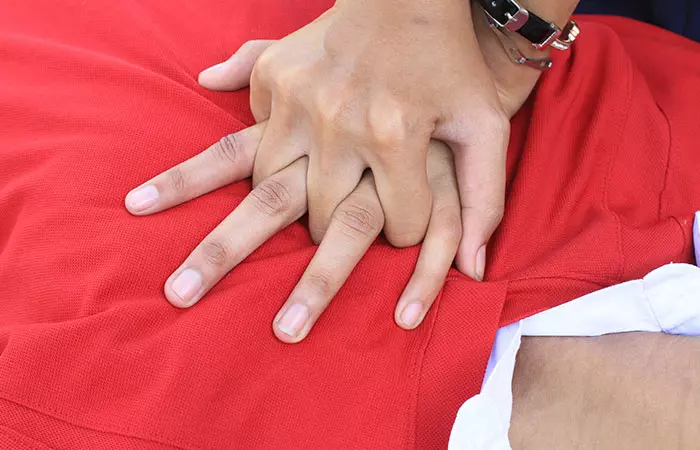
2. Using Force For Cardiac Compressions
Possible Dangers: If undue force is applied for cardiac compressions, it can cause the ribs to break and rupture. It can be quite harmful for the lungs and impedes the normal functioning of the heart.
Corrective Measures: Cardiac compressions can be given only when it is ascertained that the pulse is missing. One can initiate the process if no doctor has arrived at the scene. Maintaining a proper rhythm cycle is very important. It is about 100 beats per minute. If the heart is beating, mouth to mouth respiration can also be given. A cycle of 30 cardiac compressions combined with two resuscitations is also another alternative. While in adults, the beats are done by the fists, in babies, it is done by the fingers.
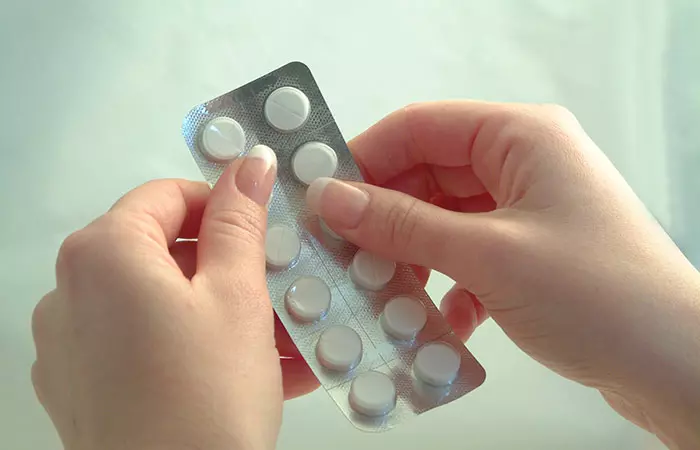
3. Excess Dosage Of Paracetamol
Possible Dangers: The most trusted pain alleviating drug, paracetamol, alternatively known as acetaminophen, is wrongly considered safe even in higher doses. Studies have shown that indiscreet use of this painkiller can be dangerous, even causing kidney failure (1).
Corrective Measures: It is a common component of many fevers, cold, and flu medications. Adults can take a dose of 1 g up to four times a day. Combining it with other medicines without consulting a doctor is a strict no.
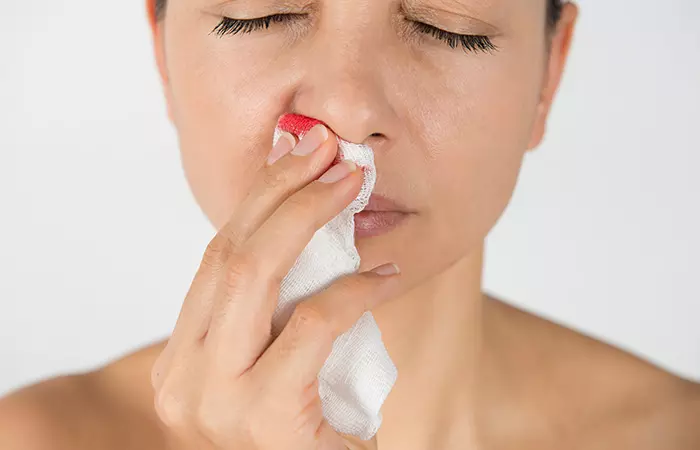
4. Throwing Back Head/Lying On The Back During Nose Bleeds
Possible Dangers: The possibility of blood pressure rising in the head during a nose bleed increases exponentially if the head is tilted back towards the neck or if the person is lying on his/her back. It can result in the blood to run into the food pipe and the throat and cause bouts of vomiting.
Corrective Measures: To control the blood pressure, the patient must sit upright. Cold packs can be used for this purpose. Breathing should be attempted through the mouth while the fingertips are pressed against each nostril for about 15 minutes to stop the bleeding. Emergency services can be called if the symptoms do not resolve or get worse.
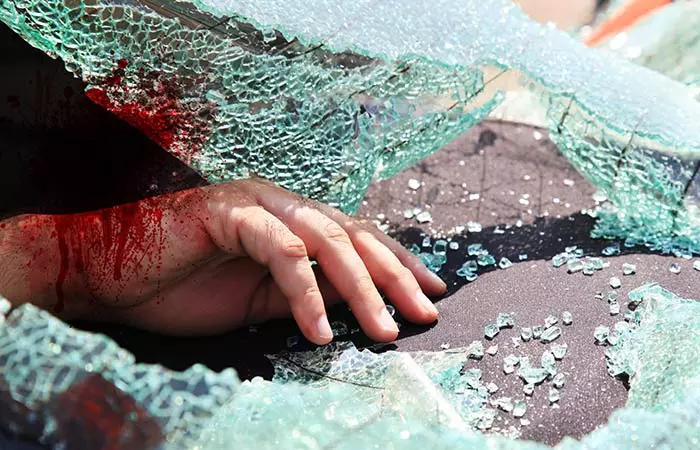
5. Helping Accident Victims To Relocate/Shift Positions
Possible Dangers: The accident victims undergo severe trauma due to sudden impact and their bodies are very vulnerable, especially the head, neck, and the spinal area. Any attempt to move the injured bodies without proper supervision can be risky and cause paralysis and even death.
Corrective Measures: If the injured person is unresponsive regarding the extent of the trauma, monitor his/her breathing closely. You can also keep talking to them, asking them questions to keep them conscious for as long as possible. Call emergency and paramedical services immediately.
6. Induce Vomiting To Counter Poisoning
Possible Dangers: Vomit inducing pills or emetic medicines are often used as a counter step against poisoning so that all the toxins come out. But it can be dangerous because they may cause sore throat, acidity, and problems in the digestive tract. Not only this, the strong impact of vomiting can cause the toxic vomit to enter the lungs.
Corrective Measures: In case of poisoning, immediately call the emergency services. If the reason or poison source is known, gather necessary information from concerned and qualified persons so that remedial action can be taken. Do not try quack methods and wait for professional help.
7. Using A Tourniquet To Control Bleeding
Possible Dangers: A tourniquet is commonly used to control bleeding, but it is a complex tool to use. The permissible duration, inflation pressure, and release to be applied in each case differs, and it is rather unclear and controversial. Studies have shown that in case of wrong judgement, nerve-related complications can arise (2).
Corrective Measures: The use of a tourniquet should be strictly according to the manual instructions, and all its accessories properly maintained. It must be applied with great care with proper padding to rule out further damage to injured limbs.
In fact, dressing the wound with a pre-washed clean cloth bandage or sterile gauze roll is equally effective before medical assistance arrives.
8. Putting A Spoon Or Pulling Tongue During Seizures
Possible Dangers: During a seizure, placing any object inside the mouth of the patient can cause additional discomfort and gagging.
Corrective Measures: It must be remembered that the scope of inflicting self-harm in case of seizures is limited, and unless it becomes life-threatening, one shouldn’t use foreign objects in the body. Rather, the doctor should be called, and the patient must be protected from injuries caused by banging or hitting against objects. They can be made to lie on their side for relaxation and optimum breathing.
9. Sucking Out Venom In Case Of Poisonous Bites
Possible Dangers: If the venom goes into your system through saliva, it will affect the mucous membrane. It can cause poisoning and accumulation of fluid in the lungs, causing respiratory failures and, in extreme cases, death.
Corrective Measures: The portion of the limb, where the patient has been bitten, should be positioned downwards to avoid the poison reaching the heart for as long as possible. Fluids should be given to dilute the flow inside the body, and medical assistance should be sought right away.
10. Rushing The Wounded Person To The Nearest Hospital
Possible Dangers: It is said that the first 30 minutes after a mishap are most crucial. If the patient is taken to a hospital with inadequate facilities, there will be a delay in treatment, and this could be fatal.
Corrective Measures: The victim should be taken to a hospital that is equipped to handle the injuries sustained. The emergency medical assistance team should be called immediately for the information regarding necessary treatment.
11. Administering An Injection
Possible Dangers: Using an injection on a wrong part of the muscle, or using it on a muscle that is taut, going too deep or too little into the skin are common wrong injection techniques. These can lead to complications like muscle fibrosis, nerve injuries, abscesses, and, in extreme cases, even gangrene.
Corrective Measures: An injection should be handled only after cleaning and disinfecting your hands and the area to be administered. Almost two-third of the needle should penetrate into the upper right-hand side of the buttock, after which a medicated cotton swab should be pressed over the site of the injection.
By following the above suggestions, the results of rescue efforts can be more effective and sustained. These are important for people to know so that they start following it and save lives of people faced with a critical emergency situation.
Read full bio of Chandrama Deshmukh