When Do Lasting Childhood Memories Start?
Discover the origins of early recollections and how our youngest years shape identity.
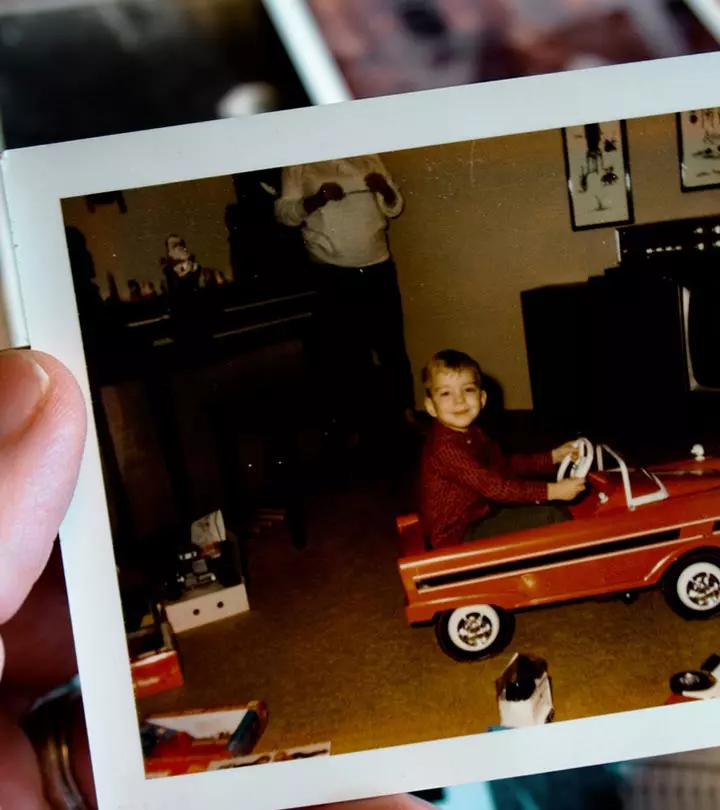

Image: iStock
Have you ever questioned why your kid won’t recall taking their first steps or celebrating a second birthday? If you think about it, you probably have very vague memories of your life experience as a preschooler. This phenomenon is due to a condition known as childhood amnesia, often called infantile amnesia, which is the natural and progressive loss of recollections from the first few years after birth. Here in this article, we’ll discuss the reason for forgetting our memories and how to recall them if possible. Read along.
What is Childhood Amnesia?
Childhood amnesia, also known as infantile amnesia, is the inability of adults to recall episodic memories from birth to age two to four, as well as from birth to age ten. As a result, some adults keep fewer memories than one might anticipate, given time. Others believe early memories are encoded and stored differently. According to some studies, children can recall events from the time they are one year old, but as they become older, their memories may become less vivid. Psychologists have different ideas on when childhood amnesia begins. Some people describe it as the age at which a person can recall their first memory.
Let’s find out more about the types of memories present in children.
Types Of Memory In Kids
Memory comes in a variety of forms. One sort of memory may be well-stored in a kid, but not the other. Understanding the different types of memory can help parents better understand their children’s learning styles.
We are aware that we are saving information when we remember a memory. What kind of memory depends on what that knowledge is and how long we cannot forget it. Based on how long the information is stored, there are two main categories of memory: short-term and long-term memory.
Long-Term Memory
Explicit and implicit memory are the two main categories of long-term memory. For example, when you recall who attended your birthday bash last month or can name every tropical fruit, you use explicit memory, which necessitates conscious attention. Because it involves remembering a specific event, experience, or episode, remembering who attended your special event last month falls under the category of episodic memory.
The main memory assessed in schools is semantic, sometimes known as “knowledge” memory, which includes memorizing the titles of all tropical fruits. Contrarily, implicit memory doesn’t involve conscious thought. Instead, it automatically enables you to perform actions, like tying your shoes or riding a bike.
Short-Term Memory
Working and short-term memory are two types of memory that temporarily store information. Short-term memory is the extremely brief period during which anything is retained in your mind before being forgotten or transferred to long-term memory, such as recalling a phone number. Working memory, also known as the brain’s “mental workspace,” is exhibited when you have to remember a phone number.
When Do We Begin To Recall Our Memories?
Few adults recall anything before three, which is when most adults’ earliest episodic memories begin. However, researchers assert that childhood memories quickly fade at about age 7.
Patricia and Marina requested 3-year-olds to speak to their parents about six earlier experiences in their lives as part of their research into a childhood memory. (1)
When kids were older, they were asked to recall these incidents. The kids identified more than 60% of the happenings between the ages of five and seven. But by the ages of eight and nine, this had decreased to fewer than 40%, according to the researchers. However, these memories aren’t usually permanently lost. Before the age of 3, when similar incidents or visual triggers are present, sensory-emotional experiences may be retained, leading to conscious memory development.
Is It Possible to Recall Childhood Memories?
Lack of childhood memories may annoy you, particularly if you have the impression that they are just out of reach or hidden beneath the surface.
Experts differ on whether memories that have been forgotten can be remembered, although other studies think that memories haven’t entirely vanished from your brain.
Later in life, specific triggers might help you remember things and release the remnants that are still there. This study concentrated on rats, which similarly appear to suffer from a type of infantile amnesia. (2)
However, if you want to try retrieving any childhood memories, the following suggestions might be helpful too.
1. Revisit Familiar Places
Returning to where you spent your formative years could bring back some lost memories. You might start to remember similar incidents from your early years when you stroll through familiar streets and take in nostalgic fragrances – scent can be a particularly potent trigger.
However, even if you can’t recall exactly how things used to appear, you might notice these distinctions if many of the items in your childhood area have changed.
2. Continue Learning
Your brain can be strengthened by lifelong learning, enhancing memory and other learning abilities. So while brain training won’t guarantee that you’ll remember your childhood, it won’t hurt and may even increase the likelihood that you’ll remember what you do remember. Regular physical activity and mental exercise can improve memory and general cognitive performance.
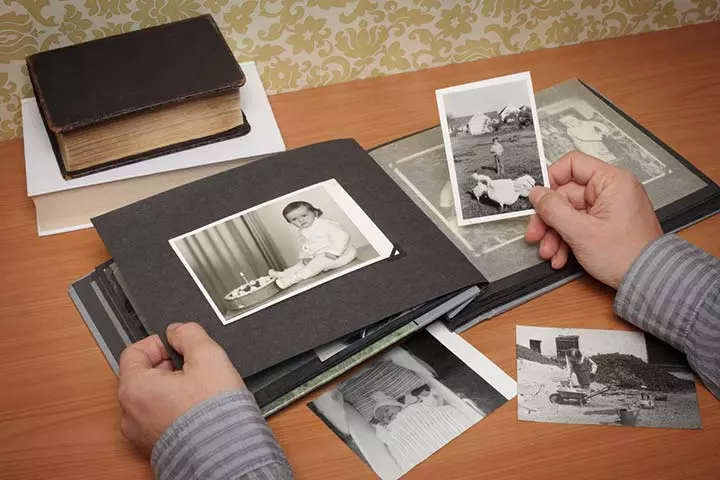
3. See Old Photos
Photos from your childhood may also help in relieving earlier experiences. For example, maybe for your second birthday, you got a little toy train that you carried around with you for over a year. Then, realizing that you wouldn’t let the train leave your sight, your parents might feel shocked that you remembered.
Childhood amnesia may appear well explained by the early hypothesis that memories are forgotten or suppressed. Still, more recent research shows that something else in our brains is contributing to this phenomenon. Further research is necessary to determine if this is caused by the continuous synthesis of new neurons, the lack of development in particular brain regions, or a combination of the two. It is impossible to attribute childhood amnesia to simple forgetfulness.
Overcome Childhood Amnesia: Recall Your Earliest Memories
Watch now to explore why we forget our early years, discover when memory first forms, and uncover practical strategies to trigger childhood memory recall. Reconnect with your past today!